使用 Flask 创建 Web 应用程序
本教程介绍如何使用 Flask Web 框架开发基于 Web 的应用程序。 我们的 MeteoMaster 应用处理存储在数据库中的气象数据,并以以下图表的形式展示:
散点图 — 年均气温和湿度的汇总报告,涵盖布拉格、圣 彼得堡、旧金山、巴黎和新加坡。
折线图 — 各城市的月均气温和湿度。
'凌驾于天气之上' 应用概述
您将使用多种 Web 技术实现以下应用功能:
功能 | 技术 |
|---|---|
气象数据操作 | SQLite 数据库用于存储数据, SQLAlchemy 包用于在 Python 代码中对数据库执行操作。 |
图形表示 | matplotlib 包用于绘制图表。 |
查看和编辑内容 | |
管理内容 | Flask 用于编排应用内容。 |
MeteoMaster 是一个 Web 应用,由以下组件构成:
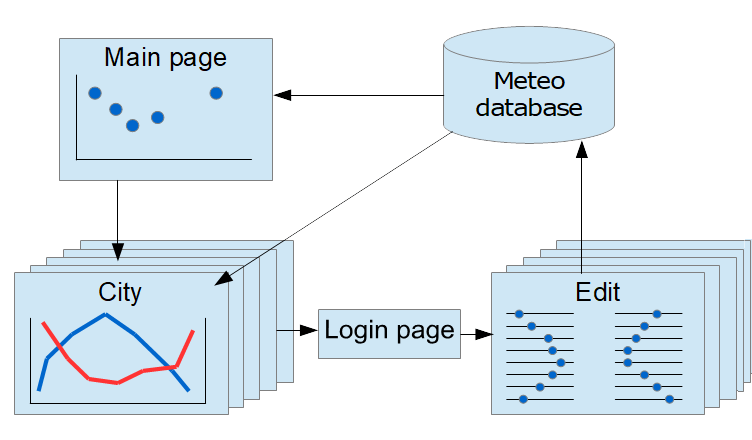
- 主页
应用入口点,用于渲染散点图,并提供指向特定城市气候详细摘要的链接。
- 城市
一系列页面,包含各城市的详细气候信息。
- 登录
身份验证页面。 要编辑气象数据,需输入有效的凭据。
- 编辑
用于编辑城市特定数据的一系列页面。
每个 HTML 页面都有一个对应的 Flask 视图,由 Python 代码实现。
在 PyCharm 中创建 Flask 应用
按照 创建 Flask 项目 中的说明创建基本的 Flask 项目,以开始为应用制作原型。
在 新建项目 对话框中选择 Flask。
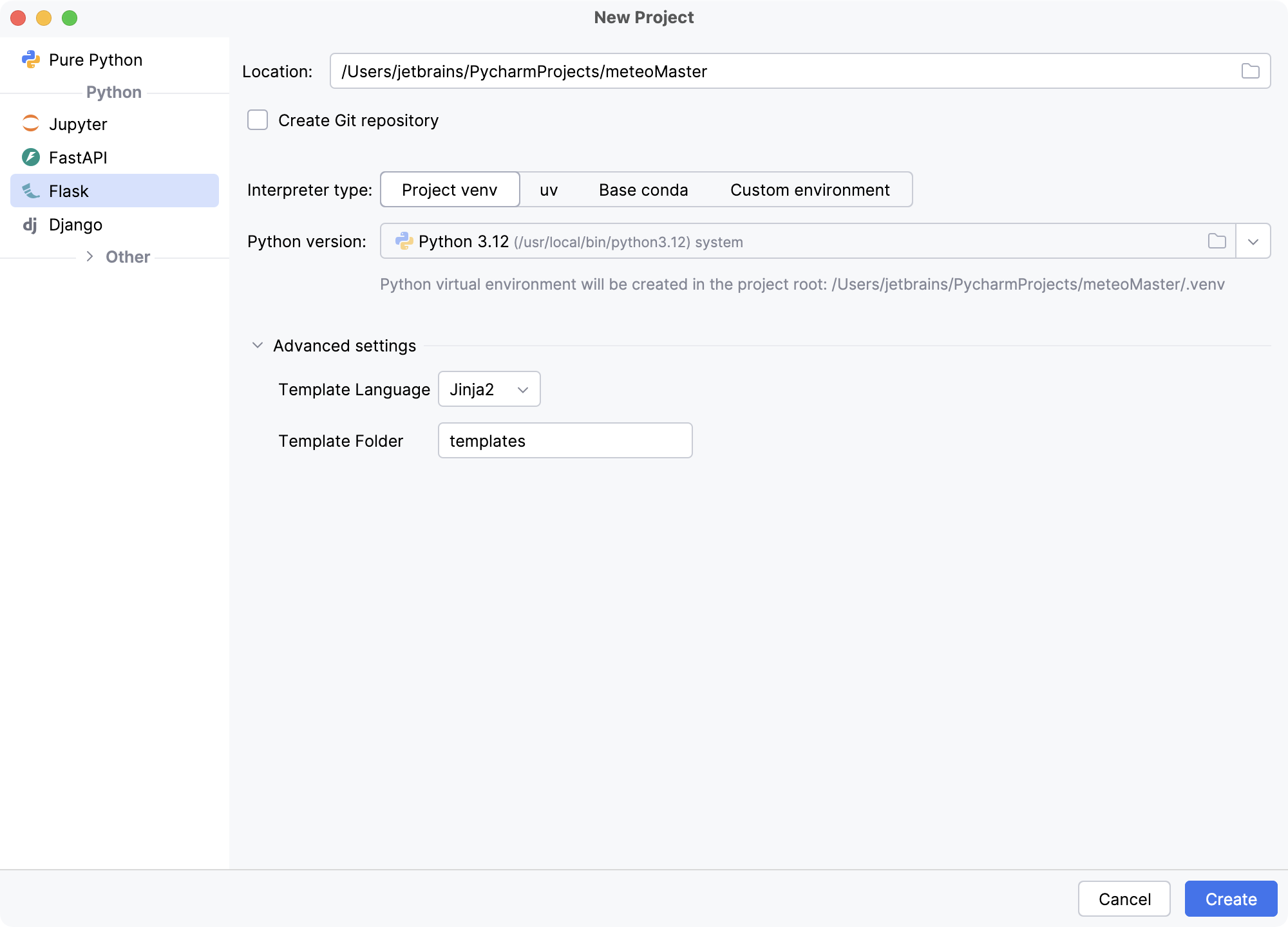
在 位置 字段中,提供项目位置的路径,并输入 meteoMaster 作为项目名称。 保留其余设置为默认值,然后点击 创建。
PyCharm 将为您创建新的虚拟环境,并选择使用 Jinja2 作为模板语言。 因此,您将获得预定义的项目结构和基本的 "Hello World!" 代码。
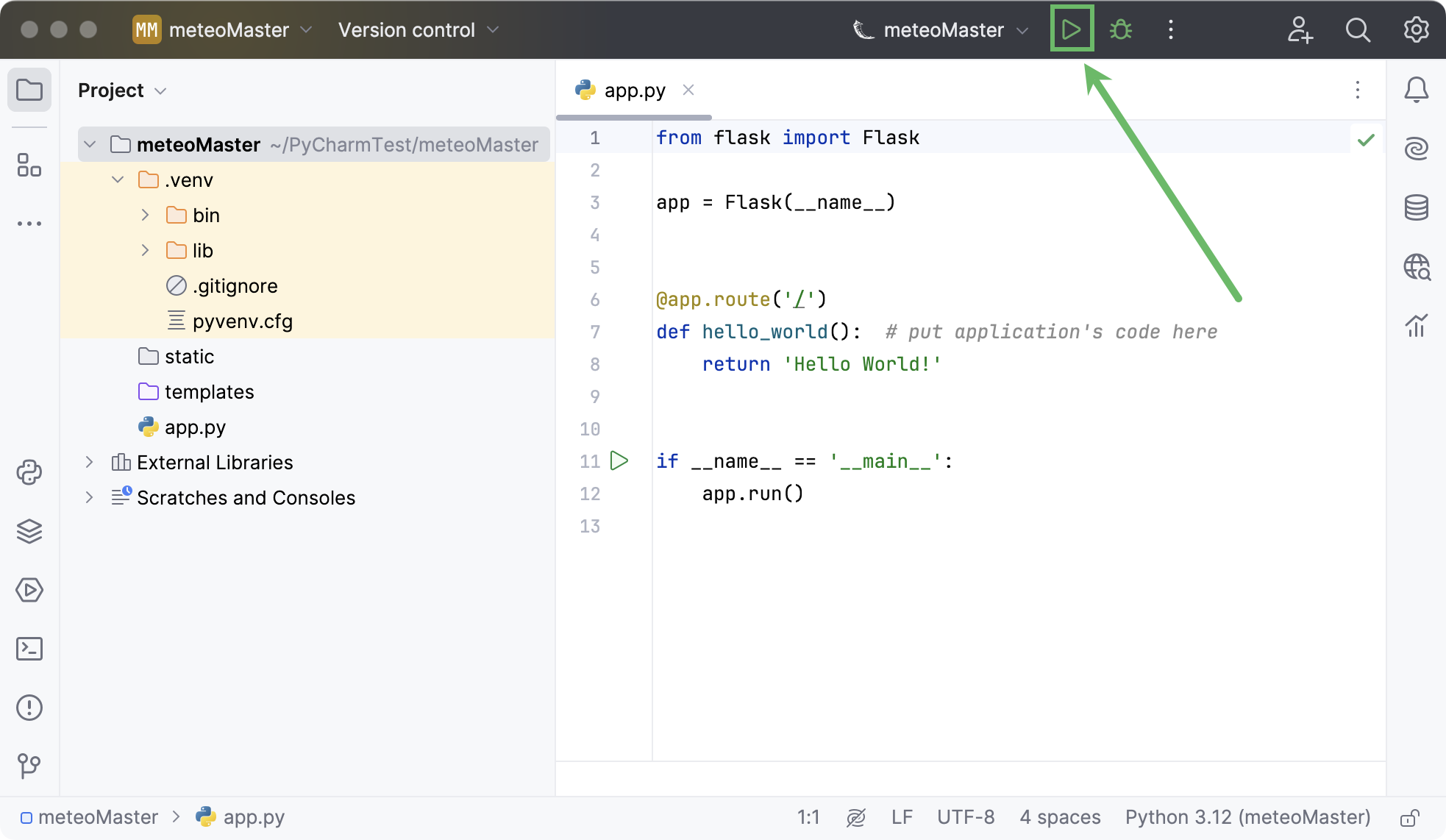
在顶部的 运行 小部件中点击
运行 'meteoMaster' ,以启动自动创建的运行配置。
在 运行 工具窗口中,点击超链接并预览基本的 'Hello, world' 应用页面。
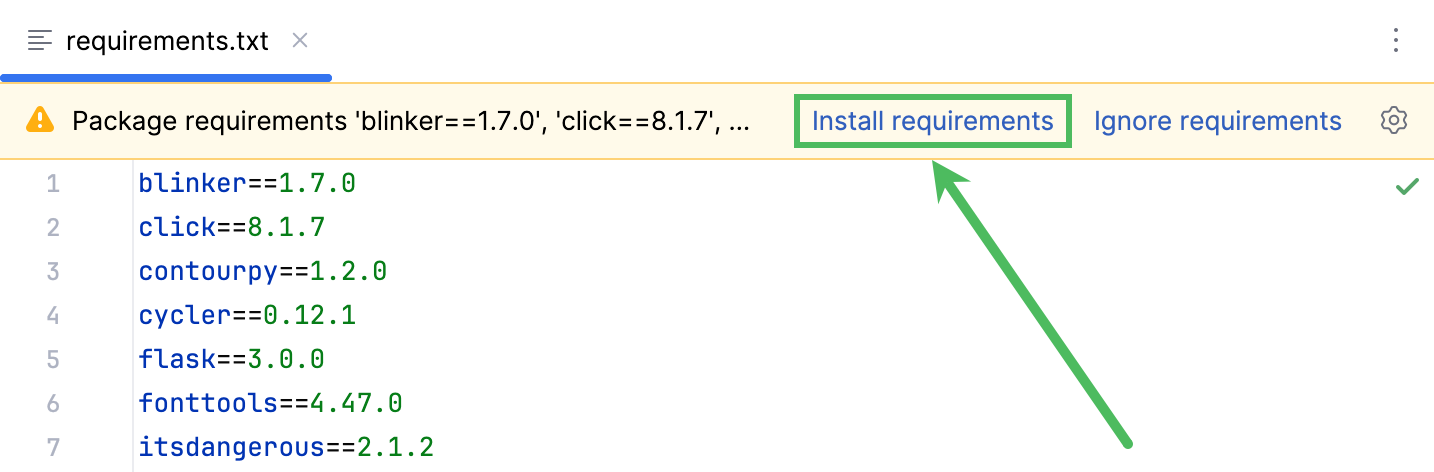
现在安装 MeteoMaster 应用所需的所有软件包。 最简单的方法是使用项目依赖项(请参阅 使用 requirements.txt)。 右键点击项目根目录并选择 ,然后将文件名指定为 requirements.txt ,并向其中添加以下依赖项列表。
blinker==1.7.0 click==8.1.7 contourpy==1.2.0 cycler==0.12.1 flask==3.0.0 fonttools==4.47.0 itsdangerous==2.1.2 jinja2==3.1.2 kiwisolver==1.4.5 markupsafe==2.1.3 matplotlib==3.8.2 numpy==1.26.2 packaging==23.2 pillow==10.2.0 pyparsing==3.1.1 python-dateutil==2.8.2 six==1.16.0 sqlalchemy==2.0.24 typing-extensions==4.9.0 werkzeug==3.0.1点击 安装依赖项 链接以继续安装这些软件包。
设置数据库
现在为您的应用设置数据源。 使用 PyCharm,这非常简单。
从以下位置下载包含五个城市气象数据的预定义数据库:
https://github.com/allaredko/flask-tutorial-demo/blob/master/user_database
将 user_database 文件保存在项目根目录中。
双击添加的文件。 在打开的 数据源与驱动程序 对话框中,点击 测试连接 以确保数据源已正确配置。 如果您看到 配置不完整 警告,请点击 下载驱动程序文件。
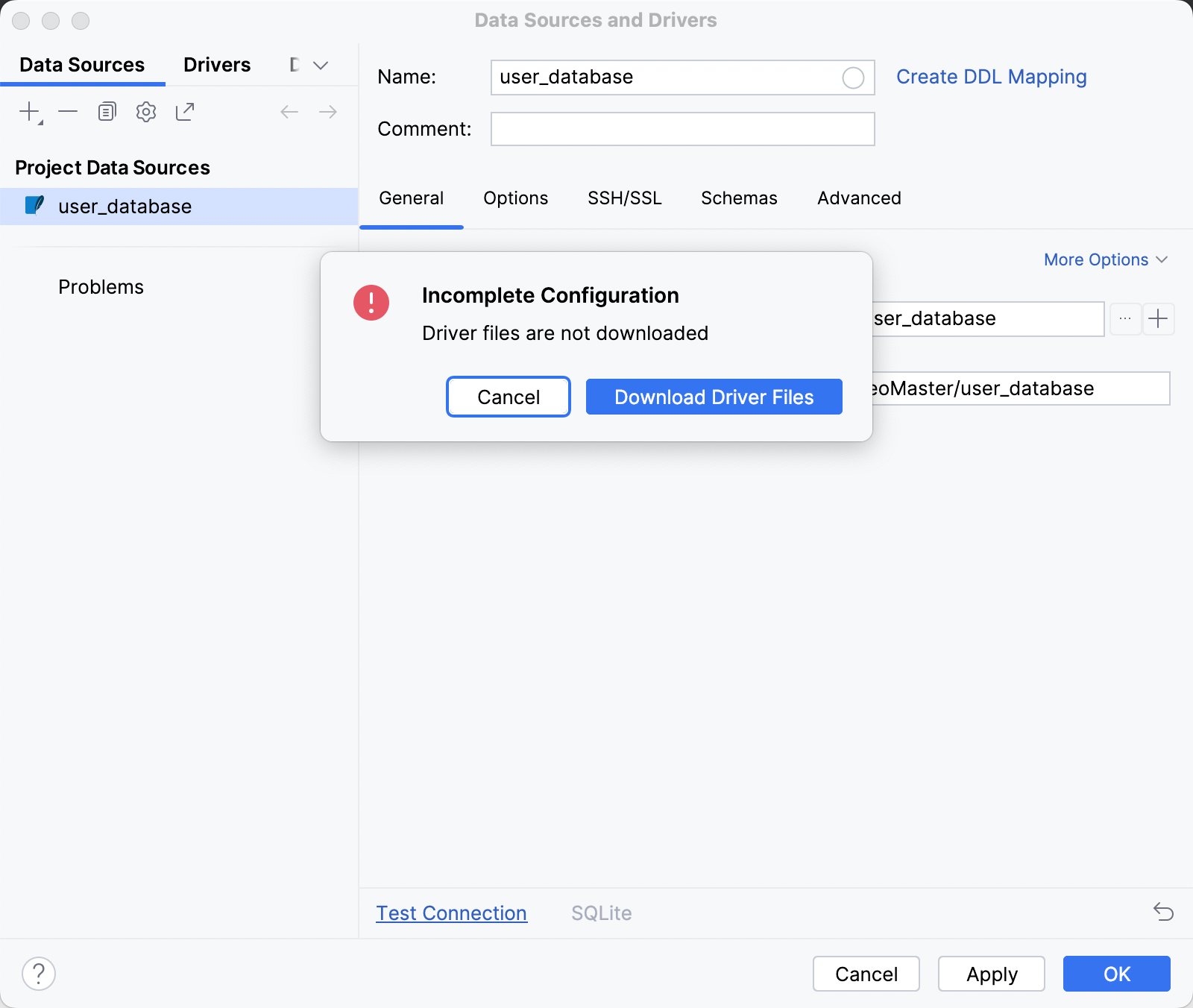
点击 确定 完成数据源创建, 数据库工具窗口 将打开。
您应当看到以下表:
city和meteo。 双击每个表以预览数据。city表包含三列:city_id、city_name和city_climate(城市气候的简要文字描述)。meteo表包含四列:city_id、month、average_humidity和average_temperature。 在table的city_id列上定义了一个 外键 ,用于在两个表之间建立关系。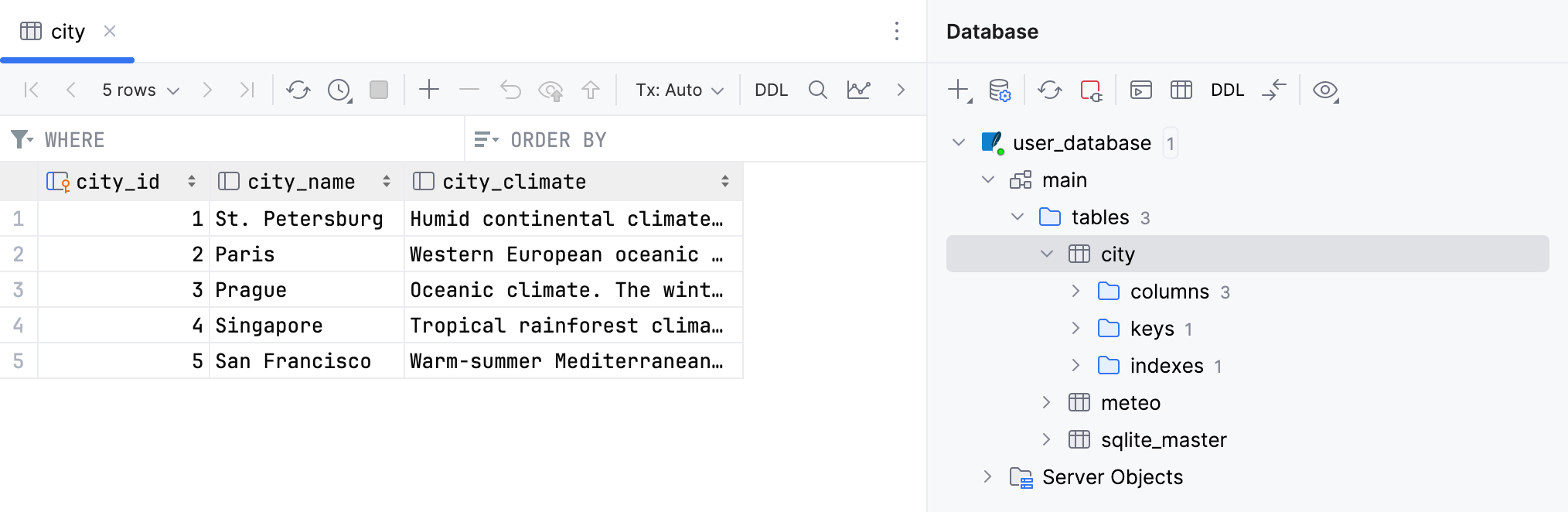
创建一个 Python 文件, user_database.py ,以使用新创建的数据库。 使用 SQLAlchemy 声明式基类 语法来描述数据库。
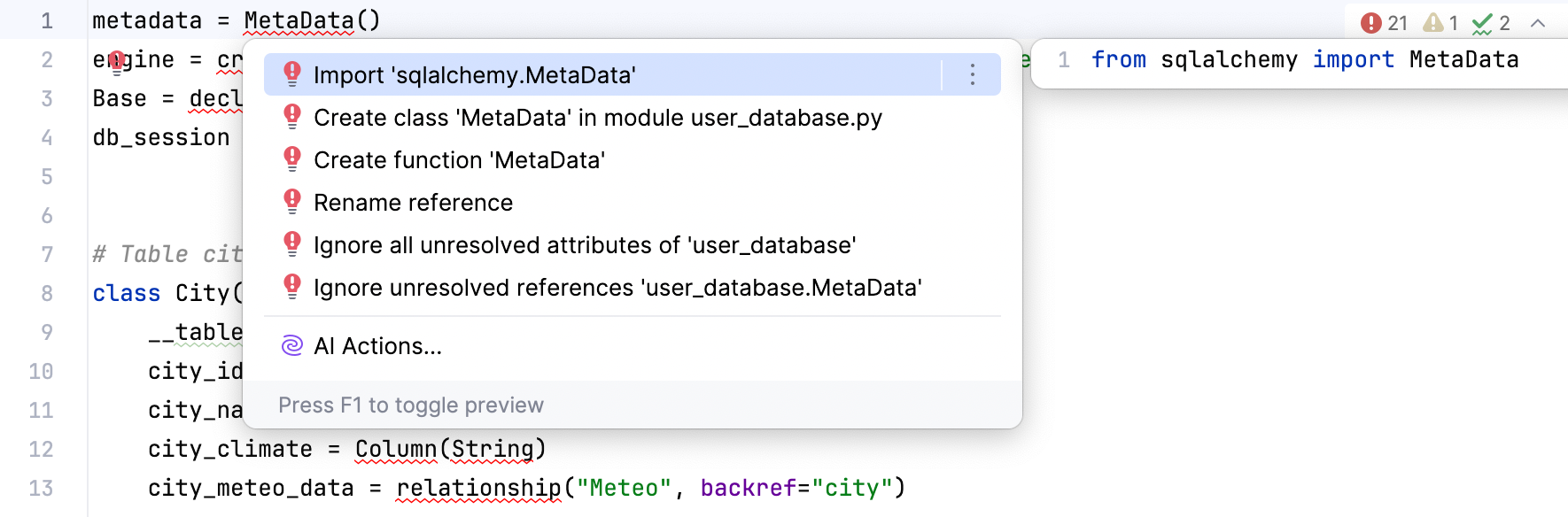
metadata = MetaData() engine = create_engine('sqlite:///user_database', connect_args={'check_same_thread': False}, echo=False) # echo=False Base = declarative_base() db_session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)() # Table city class City(Base): __tablename__ = 'city' city_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) city_name = Column(String) city_climate = Column(String) city_meteo_data = relationship("Meteo", backref="city") # Table meteo class Meteo(Base): __tablename__ = 'meteo' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) city_id = Column(ForeignKey('city.city_id')) month = Column(String) average_humidity = Column(Integer) average_temperature = Column(Float)无需手动为该代码片段添加 import 语句,应用建议的 快速修复 :只需点击灯泡图标(或按 Alt+Enter)。
现已定义表及其关系,请添加以下函数以从数据库检索数据:
# Retrieving data from the database def get_cities(): return db_session.query(City) # Generating the set of average temperature values for a particular city def get_city_temperature(city): return [month.average_temperature for month in city.city_meteo_data] # Generating the set of average humidity values for a particular city def get_city_humidity(city): return [month.average_humidity for month in city.city_meteo_data] data = get_cities() MONTHS = [record.month for record in data[0].city_meteo_data] CITIES = [city.city_name for city in data]user_database.py 文件的完整代码如下:
- user_database.py
- from sqlalchemy import MetaData, create_engine, Column, Integer, String, ForeignKey, Float from sqlalchemy.orm import declarative_base, sessionmaker, relationship metadata = MetaData() engine = create_engine('sqlite:///user_database', connect_args={'check_same_thread': False}, echo=False) # echo=False Base = declarative_base() db_session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)() # Table city class City(Base): __tablename__ = 'city' city_id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) city_name = Column(String) city_climate = Column(String) city_meteo_data = relationship("Meteo", backref="city") # Table meteo class Meteo(Base): __tablename__ = 'meteo' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True) city_id = Column(ForeignKey('city.city_id')) month = Column(String) average_humidity = Column(Integer) average_temperature = Column(Float) # Retrieving data from the database def get_cities(): return db_session.query(City) # Generating the set of average temperature values for a particular city def get_city_temperature(city): return [month.average_temperature for month in city.city_meteo_data] # Generating the set of average humidity values for a particular city def get_city_humidity(city): return [month.average_humidity for month in city.city_meteo_data] data = get_cities() MONTHS = [record.month for record in data[0].city_meteo_data] CITIES = [city.city_name for city in data]
绘制散点图
您已准备好检索数据并构建第一个图表——各城市年均气温和湿度的散点图。 使用 matplotlib 库来设置图表并赋值。
再创建一个 Python 文件, charts.py ,并填入以下代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from user_database import data, get_city_temperature, get_city_humidity, CITIES yearly_temp = [] yearly_hum = [] for city in data: yearly_temp.append(sum(get_city_temperature(city))/12) yearly_hum.append(sum(get_city_humidity(city))/12) plt.clf() plt.scatter(yearly_hum, yearly_temp, alpha=0.5) plt.title('Yearly Average Temperature/Humidity') plt.xlim(70, 95) plt.ylabel('Yearly Average Temperature') plt.xlabel('Yearly Average Relative Humidity') for i, txt in enumerate(CITIES): plt.annotate(txt, (yearly_hum[i], yearly_temp[i])) plt.show()预览图表的最快方法是在编辑器中的任意位置点击鼠标右键,然后在上下文菜单中选择 运行 'charts'。 PyCharm 会在 图表 工具窗口中呈现散点图。
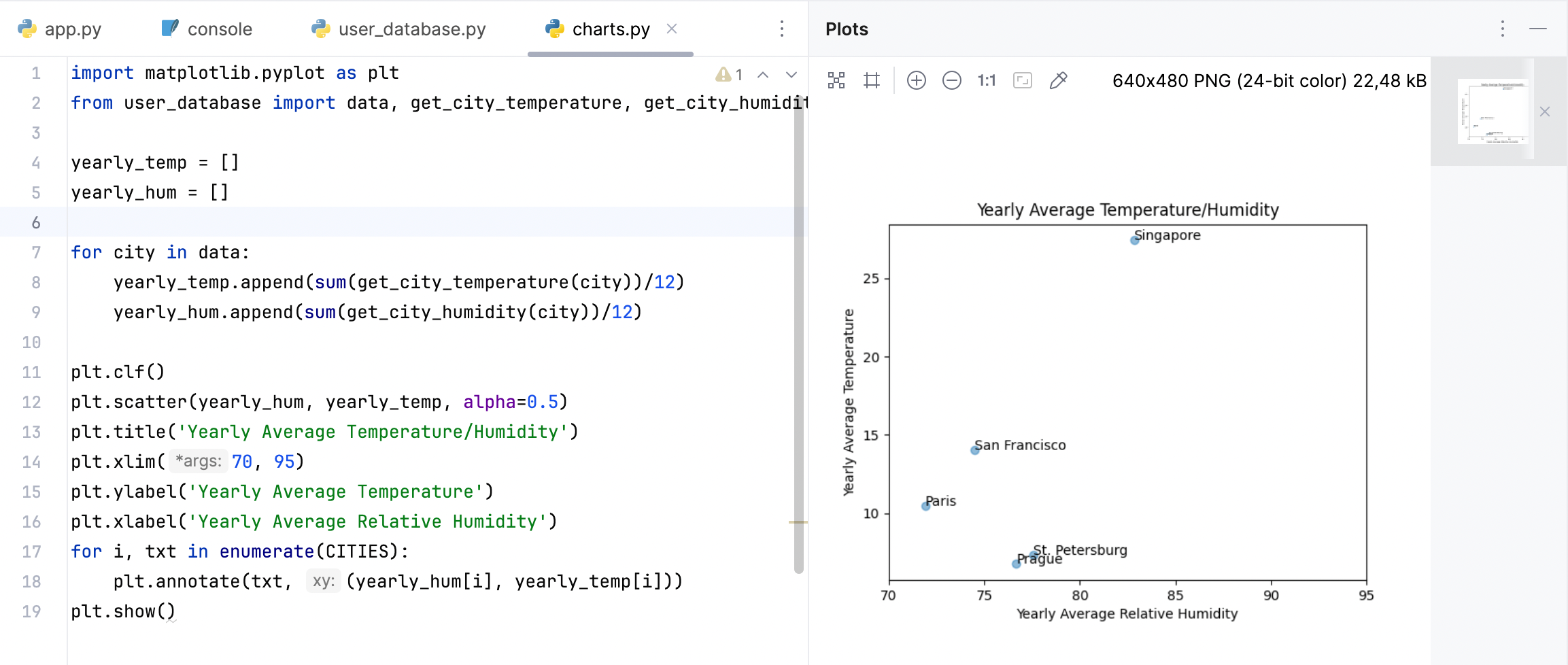
现在将图表保存为图像,以便将其添加到应用的主页中。 将
plt.show()替换为使用savefig(img)方法的片段,并将代码封装到get_main_image()函数中。 您应得到如下结果:from io import BytesIO import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from user_database import data, MONTHS, get_city_temperature, get_city_humidity, CITIES def get_main_image(): """Rendering the scatter chart""" yearly_temp = [] yearly_hum = [] for city in data: yearly_temp.append(sum(get_city_temperature(city))/12) yearly_hum.append(sum(get_city_humidity(city))/12) plt.clf() plt.scatter(yearly_hum, yearly_temp, alpha=0.5) plt.title('Yearly Average Temperature/Humidity') plt.xlim(70, 95) plt.ylabel('Yearly Average Temperature') plt.xlabel('Yearly Average Relative Humidity') for i, txt in enumerate(CITIES): plt.annotate(txt, (yearly_hum[i], yearly_temp[i])) img = BytesIO() plt.savefig(img) img.seek(0) return img
创建主页
设置应用的主页,并为散点图创建一个视图。
在 app.py 文件中,将
hello_world函数的定义替换为使用app.route()装饰器的以下代码:def get_headers(response): response.headers['Cache-Control'] = 'no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate' response.headers['Pragma'] = 'no-cache' response.headers['Expires'] = '0' @app.route('/') def main(): """Entry point; the view for the main page""" cities = [(record.city_id, record.city_name) for record in data] return render_template('main.html', cities=cities) @app.route('/main.png') def main_plot(): """The view for rendering the scatter chart""" img = get_main_image() response = send_file(img, mimetype='image/png') get_headers(response) return response应用建议的快速修复以添加缺失的导入语句。
请注意,PyCharm 会高亮显示 main.html ,因为您尚未创建该文件。
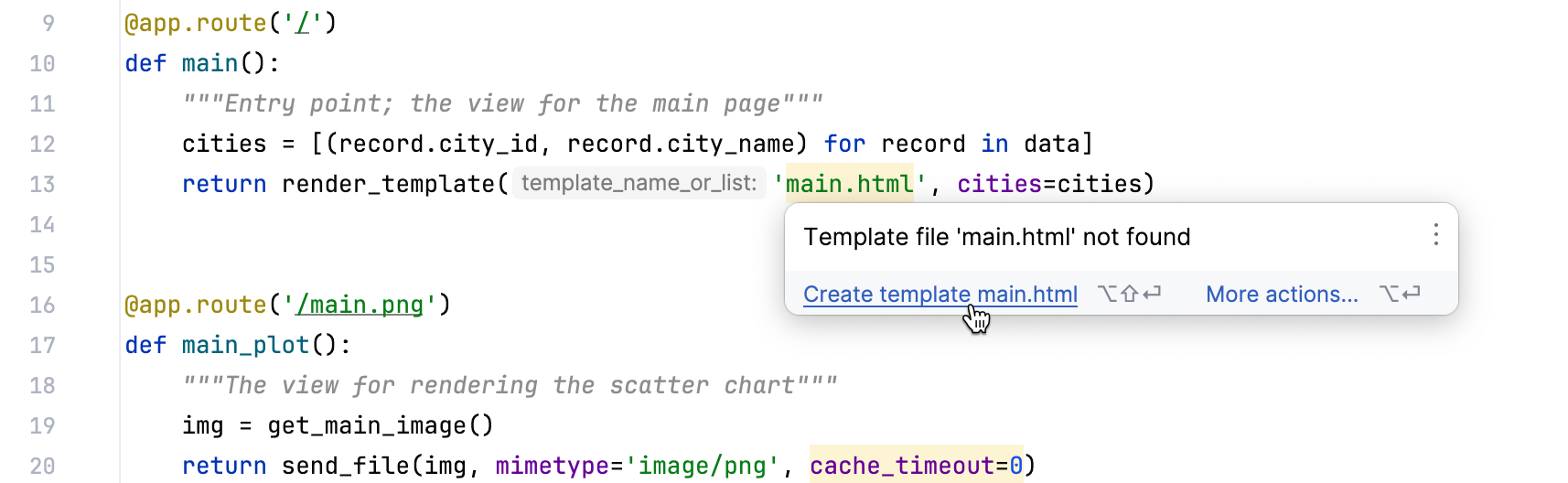
使用 PyCharm 的意图操作,您可以快速创建缺失的模板文件。 按 Alt+Enter ,然后在上下文菜单中选择 创建模板 main.html。 确认模板文件的名称和位置,然后点击 确定。 因此, main.html 将添加到 templates 目录中。 打开新添加的文件,并将以下代码粘贴到其中:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link href="../static/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"> <title>Typical Climate</title> </head> <body> <div id="element1"> <img src="{{ url_for('main_plot') }}" alt="Image"> </div> <div id="element2"> <p>What city has the best climate?</p> <p>When planning your trip or vacation you often check weather data for humidity and temperature.</p> <p>Below is the collection of the yearly average values for the following cities: </p> <ul> {% for city_id, city_name in cities %} <li><a href="">{{ city_name }}</a></li> {% endfor %} </ul> </div> </body> </html>请注意,在该片段中,
{{ city_name }}是一个 Jinja2 模板变量,用于将city_namePython 变量传递给 HTML 模板。此外,请创建样式表,用于为您的应用中的所有 HTML 页面设置字体和布局。 右键点击 static 目录并选择 ,然后将 css 文件名指定为 style.css ,并粘贴以下样式定义:
body { font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; } #element1 { display: inline-block; } #element2 { display: inline-block; vertical-align: top; margin-top: 90px; alignment: left; width: 25%; }您可以使用自动创建的
meteoMaster配置来运行修改后的应用,随时评估结果。点击
运行 或
重新运行 ,然后在 运行 工具窗口中点击 http://127.0.0.1:5000/ 链接。
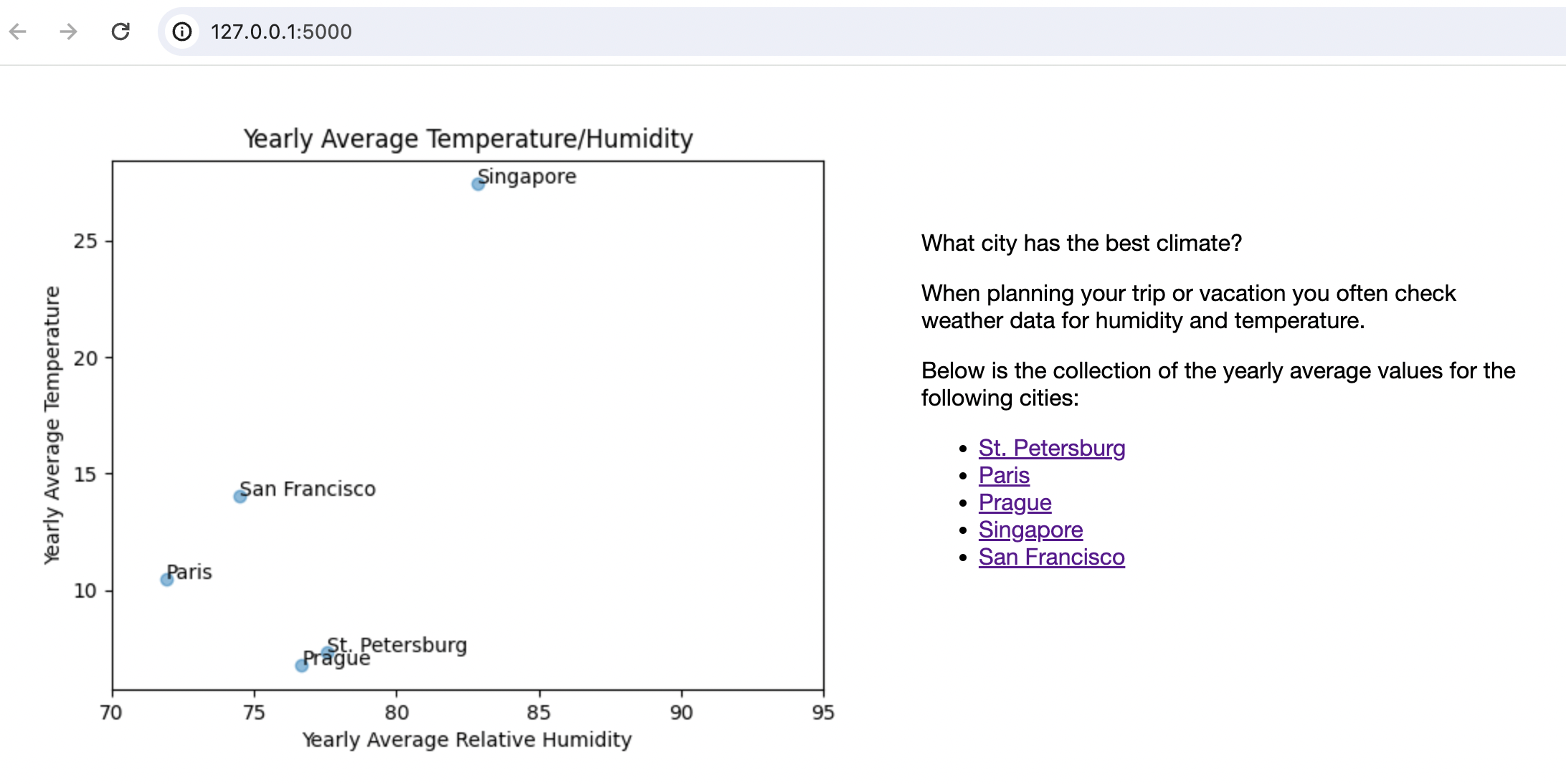
您应看到以下页面:
绘制折线图
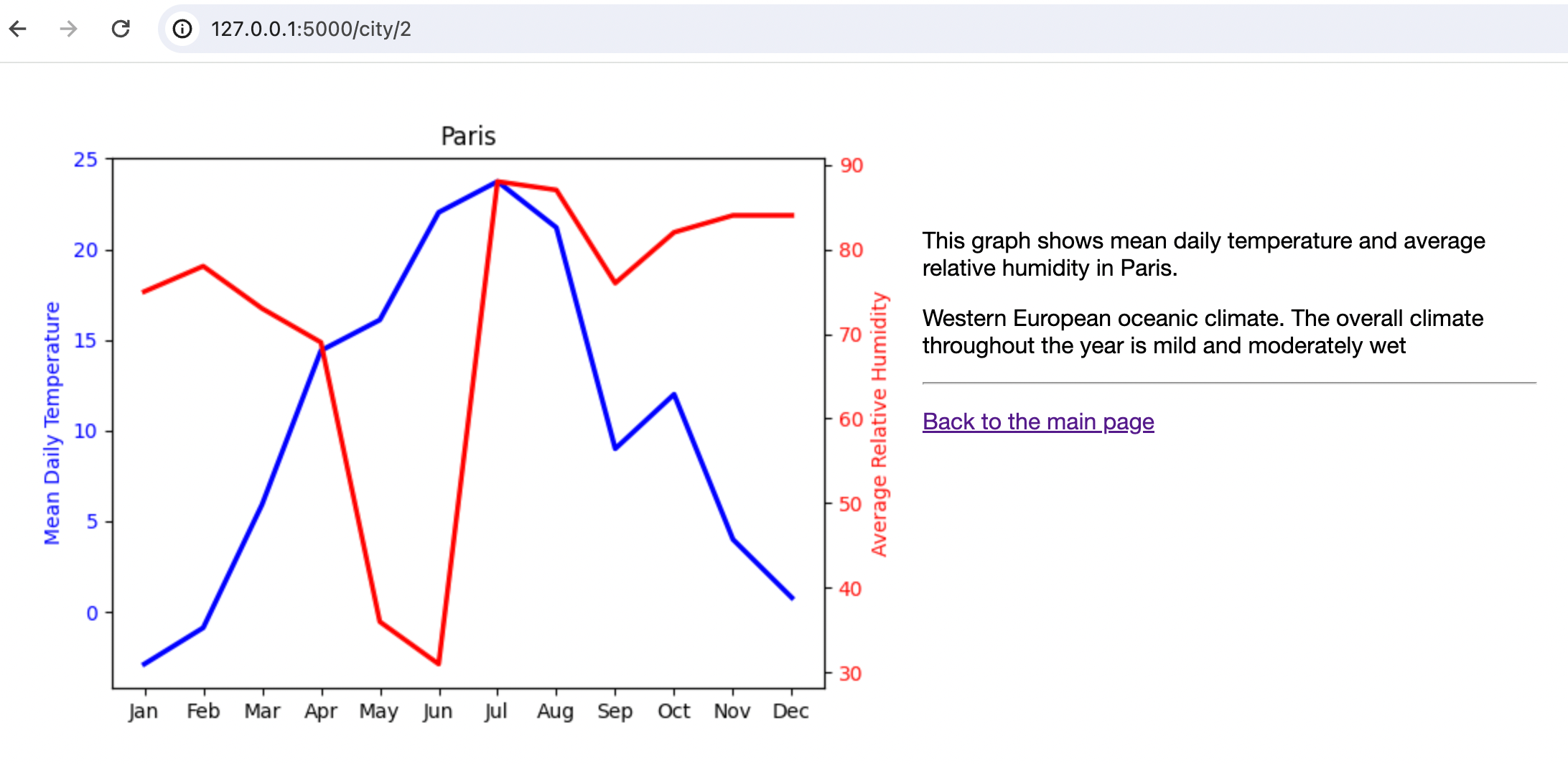
为向应用用户提供某个特定城市的详细气候信息,渲染带有相关信息的折线图。
将
get_city_image函数添加到 charts.py 文件中:def get_city_image(city_id): """Rendering line charts with city specific data""" city = data.get(city_id) city_temp = get_city_temperature(city) city_hum = get_city_humidity(city) plt.clf() plt.plot(MONTHS, city_temp, color='blue', linewidth=2.5, linestyle='-') plt.ylabel('Mean Daily Temperature', color='blue') plt.yticks(color='blue') plt.twinx() plt.plot(MONTHS, city_hum, color='red', linewidth=2.5, linestyle='-') plt.ylabel('Average Relative Humidity', color='red') plt.yticks(color='red') plt.title(city.city_name) img = BytesIO() plt.savefig(img) img.seek(0) return img此函数绘制两张折线图:每个城市的月度 日平均气温和 平均相对湿度。 与
get_main_image函数类似,它会将图表保存为图像。再创建一个 .html 文件以显示折线图。
在项目根目录中右键点击 templates 目录并选择 ,然后输入 city.html 作为文件名,并将以下代码粘贴到新创建的文件中:
- <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link href="../static/style.css" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"> <title>{{ city_name }}</title> </head> <body> <div id="element1"> <img src="{{ url_for('city_plot', city_id=city_id) }}" alt="Image"> </div> <div id="element2"> <p>This graph shows mean daily temperature and average relative humidity in {{ city_name }}.</p> <p> {{ city_climate }}</p> <hr/> <p><a href="/">Back to the main page</a></p> </div> </body> </html>
最后一步是使用
Flask.route函数创建另外两个视图。 将 app.py 文件中添加以下代码片段:@app.route('/city/<int:city_id>') def city(city_id): """Views for the city details""" city_record = data.get(city_id) return render_template('city.html', city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id, city_climate=city_record.city_climate) @app.route('/city<int:city_id>.png') def city_plot(city_id): """Views for rendering city specific charts""" img = get_city_image(city_id) response = send_file(img, mimetype='image/png') get_headers(response) return response不要忘记使用快速修复 Alt+Enter 来添加缺失的导入语句。
现在修改 main.html 文件,以填充城市列表,并添加指向相应 city/* 页面的链接。 将
<li><a href="">{{ city_name }}</a></li>替换为<li><a href="{{ url_for('city', city_id=city_id) }}">{{ city_name }}</a></li>。
重新运行 运行/调试配置 以重新启动应用,并点击指向巴黎的链接。 您应当进入 city/2 页面。
创建登录表单
到目前为止,您已经创建了一个功能完备的应用程序,该应用程序从数据库检索气象数据,并将其以图表的形式展示。 然而,在现实情况下,您通常希望编辑数据。 合理地,编辑应仅允许授权用户进行,因此,让我们创建一个登录表单。
在项目根目录中右键点击 templates 目录并选择 ,然后输入 login.html 作为文件名,并将以下代码粘贴到新创建的文件中:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="../static/style.css"> <title>Login form </title> </head> <body> <p>Login to edit the meteo database: </p> <div class="container"> <form action="" class="form-inline" method="post"> <input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" name="username" value="{{ request.form.username }}"> <input type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password" name="password" value="{{ request.form.password }}"> <input class="btn btn-default" type="submit" value="Login"> </form> <p>{{ error }}</p> </div> </body> </html>此代码实现了一个典型的登录表单,带有 用户名 和 密码 字段。
将以下代码添加到 app.py 文件,以创建登录表单的 Flask 视图并控制登录会话。
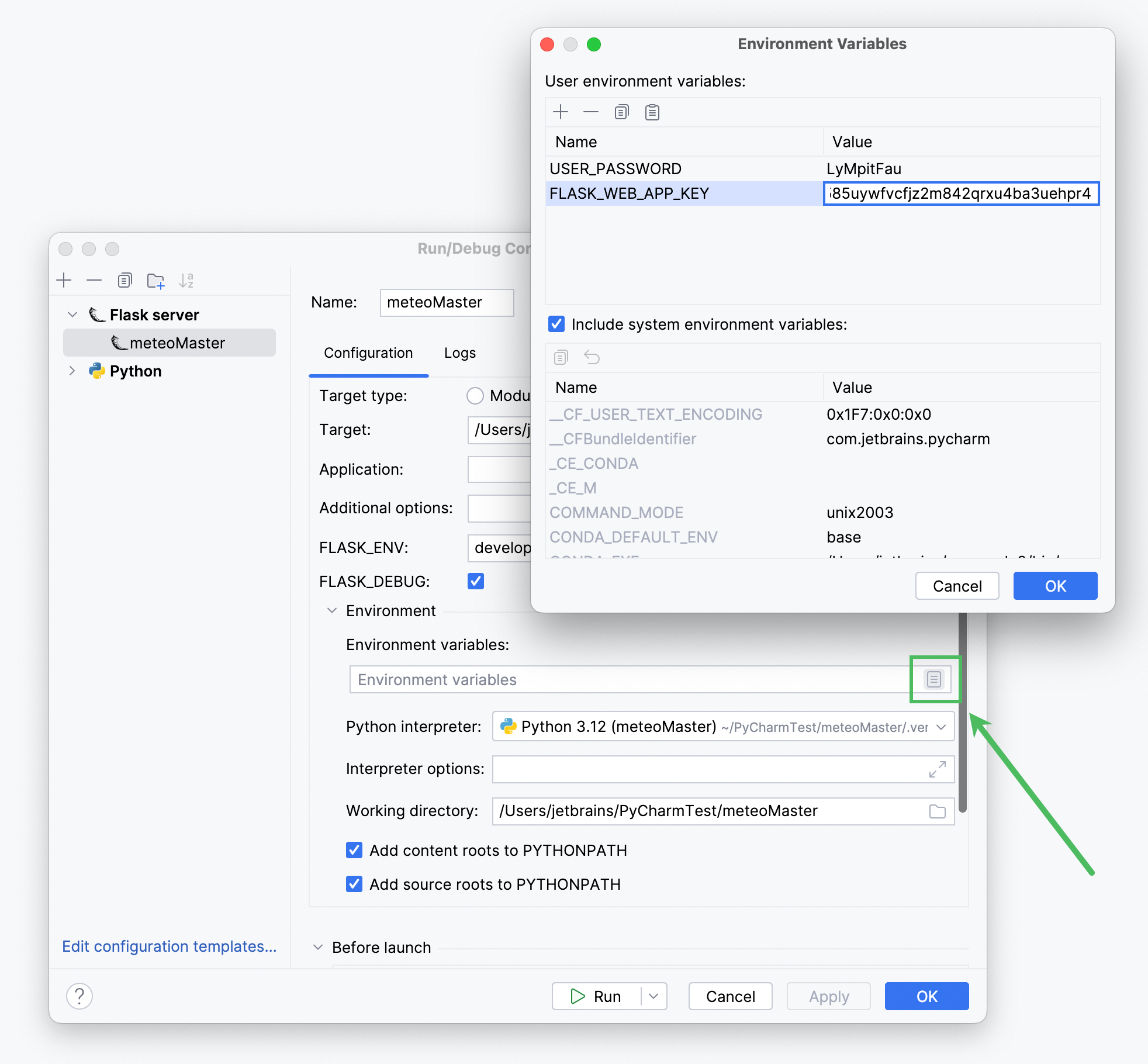
@app.route('/login/<int:city_id>', methods=["GET", "POST"]) def login(city_id): """The view for the login page""" city_record = data.get(city_id) try: error = '' if request.method == "POST": attempted_username = request.form['username'] attempted_password = request.form['password'] if attempted_username == 'admin' and attempted_password == os.environ['USER_PASSWORD']: session['logged_in'] = True session['username'] = request.form['username'] return redirect(url_for('edit_database', city_id=city_id)) else: print('invalid credentials') error = 'Invalid credentials. Please, try again.' return render_template('login.html', error=error, city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id) except Exception as e: return render_template('login.html', error=str(e), city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id) def login_required(f): @wraps(f) def wrap(*args, **kwargs): """login session""" if 'logged_in' in session: return f(*args, **kwargs) else: pass return redirect(url_for('login')) return wrap app.secret_key = os.environ['FLASK_WEB_APP_KEY']使用 Alt+Enter 快捷键来添加缺失的导入语句。 请注意,此代码片段引入了两个环境变量:
USER_PASSWORD和FLASK_WEB_APP_KEY。您可以在 meteoMaster 运行/调试配置 中记录新创建的环境变量的值,因为与将其硬编码到 app.py 文件中相比,这是一种更安全的存储安全敏感信息的方法。
在 运行 小部件中点击
,并选择 编辑配置。 在 运行/调试配置 对话框中,确保已选择 meteoMaster 配置,并在 环境变量 字段中点击
图标,然后添加这两个变量。
在 city.html 文件中修改
<div id="element2">元素,以支持登录功能:<p>This graph shows mean daily temperature and average relative humidity in {{ city_name }}.</p> <p> {{ city_climate }}</p> {% if session['logged_in'] %} <p>Want to add more data?</p> <p>Go and <a href="{{ url_for('edit_database', city_id=city_id) }}">edit</a> the meteo database.</p> {% else %} <p>Want to edit meteo data?</p> <p>Please <a href="{{ url_for('login', city_id=city_id) }}">login</a> first.</p> {% endif %} <hr/> <p><a href="/">Back to the main page</a></p>重新启动应用,并点击任意城市链接,然后点击 "请先登录" 句子中的 login 链接。 您应当看到登录表单。
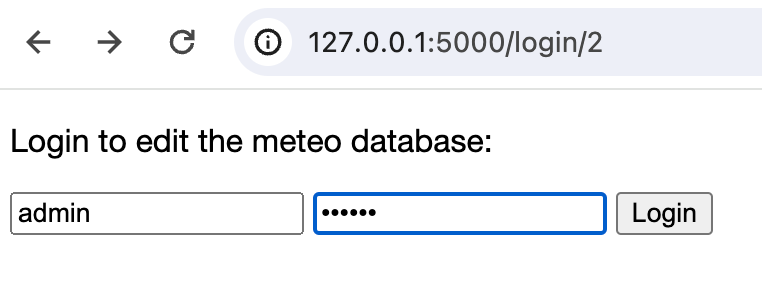
暂时,此表单尚不支持编辑,因为您尚未实现相应的页面。 与此同时,您可以尝试输入任意错误的密码,以检查是否会显示消息: "凭据无效。 请重试。"
编辑数据
最后一步是启用对气象数据的编辑。
在项目根目录中右键点击 templates 目录并选择 ,然后输入 edit.html 作为文件名,并将以下代码粘贴到新创建的文件中:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="../static/style.css"> <title>Edit meteo data for {{ city_name }}</title> </head> <body> <p>Edit the data for {{ city_name }} as appropriate:</p> <div class="container"> <form name="meteoInput" action="" class="form-inline" method="post"> <table> <tr> <td>Month</td> <td colspan="2" align="center">Average Temperature</td> <td colspan="2" align="center">Average Humidity</td> </tr> {% for month in months %} <tr> <td>{{ month }}</td> <td> <input placeholder="20" class="form-control" name="temperature{{ loop.index0 }}" value="{{ meteo[0][loop.index0]}}" type="range" min="-50.0" max="50.0" step="0.01" oninput="temp_output{{ loop.index0 }}.value=this.value" > </td> <td> <output name="temp_output{{ loop.index0 }}">{{ '%0.2f' % meteo[0][loop.index0]|float }}</output> <label> C</label> </td> <td> <input placeholder="20" class="form-control" name="humidity{{ loop.index0 }}" value="{{ meteo[1][loop.index0]}}" type="range" min="0" max="100" oninput="hum_output{{ loop.index0 }}.value=this.value"> </td> <td> <output name="hum_output{{ loop.index0 }}">{{ meteo[1][loop.index0]}}</output> <label> %</label> </td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table> <input class="btn btn-default" type="submit" value="Save"> </form> <p>{{ error }}</p> </div> </body> </html>此片段也使用了 Jinjia2 模板来处理输入数据,并将其传递给执行提交到数据库的 Python 代码。
再向 app.py 文件添加一个代码片段,用于创建编辑页面的 Flask 视图、处理输入数据并更新数据库:
@app.route('/edit/<int:city_id>', methods=["GET", "POST"]) @login_required def edit_database(city_id): """Views for editing city specific data""" month_temperature = [] month_humidity = [] city_record = data.get(city_id) meteo = [get_city_temperature(city_record), get_city_humidity(city_record)] try: if request.method == "POST": # Get data from the form for i in range(12): # In a production application we ought to validate the input data month_temperature.append(float(request.form[f'temperature{i}'])) month_humidity.append(int(request.form[f'humidity{i}'])) # Database update for i, month in enumerate(city_record.city_meteo_data): month.average_temperature = month_temperature[i] month.average_humidity = month_humidity[i] db_session.commit() return redirect(url_for('main', city_id=city_id)) else: return render_template('edit.html', city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id, months=MONTHS, meteo=meteo) except Exception as error: return render_template('edit.html', city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id, months=MONTHS, meteo=meteo, error=error)app.py 文件的完整代码如下:
- app.py
- import os from functools import wraps from flask import Flask, send_file, render_template, request, session, redirect, url_for from charts import get_main_image, get_city_image from user_database import data, db_session, get_city_temperature, get_city_humidity, MONTHS app = Flask(__name__) def get_headers(response): response.headers['Cache-Control'] = 'no-cache, no-store, must-revalidate' response.headers['Pragma'] = 'no-cache' response.headers['Expires'] = '0' @app.route('/') def main(): """Entry point; the view for the main page""" cities = [(record.city_id, record.city_name) for record in data] return render_template('main.html', cities=cities) @app.route('/main.png') def main_plot(): """The view for rendering the scatter chart""" img = get_main_image() response = send_file(img, mimetype='image/png') get_headers(response) return response @app.route('/city/<int:city_id>') def city(city_id): """Views for the city details""" city_record = data.get(city_id) return render_template('city.html', city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id, city_climate=city_record.city_climate) @app.route('/city<int:city_id>.png') def city_plot(city_id): """Views for rendering city specific charts""" img = get_city_image(city_id) response = send_file(img, mimetype='image/png') get_headers(response) return response @app.route('/login/<int:city_id>', methods=["GET", "POST"]) def login(city_id): """The view for the login page""" city_record = data.get(city_id) try: error = '' if request.method == "POST": attempted_username = request.form['username'] attempted_password = request.form['password'] if attempted_username == 'admin' and attempted_password == os.environ['USER_PASSWORD']: session['logged_in'] = True session['username'] = request.form['username'] return redirect(url_for('edit_database', city_id=city_id)) else: print('invalid credentials') error = 'Invalid credentials. Please, try again.' return render_template('login.html', error=error, city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id) except Exception as e: return render_template('login.html', error=str(e), city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id) def login_required(f): @wraps(f) def wrap(*args, **kwargs): """login session""" if 'logged_in' in session: return f(*args, **kwargs) else: pass return redirect(url_for('login')) return wrap app.secret_key = os.environ['FLASK_WEB_APP_KEY'] @app.route('/edit/<int:city_id>', methods=["GET", "POST"]) @login_required def edit_database(city_id): """Views for editing city specific data""" month_temperature = [] month_humidity = [] city_record = data.get(city_id) meteo = [get_city_temperature(city_record), get_city_humidity(city_record)] try: if request.method == "POST": # Get data from the form for i in range(12): # In a production application we ought to validate the input data month_temperature.append(float(request.form[f'temperature{i}'])) month_humidity.append(int(request.form[f'humidity{i}'])) # Database update for i, month in enumerate(city_record.city_meteo_data): month.average_temperature = month_temperature[i] month.average_humidity = month_humidity[i] db_session.commit() return redirect(url_for('main', city_id=city_id)) else: return render_template('edit.html', city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id, months=MONTHS, meteo=meteo) except Exception as error: return render_template('edit.html', city_name=city_record.city_name, city_id=city_id, months=MONTHS, meteo=meteo, error=error) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run()
重新运行 运行配置,或保存 app.py 文件(Ctrl+S ),以触发自动重新启动。 现在,您可以在应用的主页上选择例如
Paris,点击 edit ,输入管理员凭据,即可进入可以编辑气象数据的页面。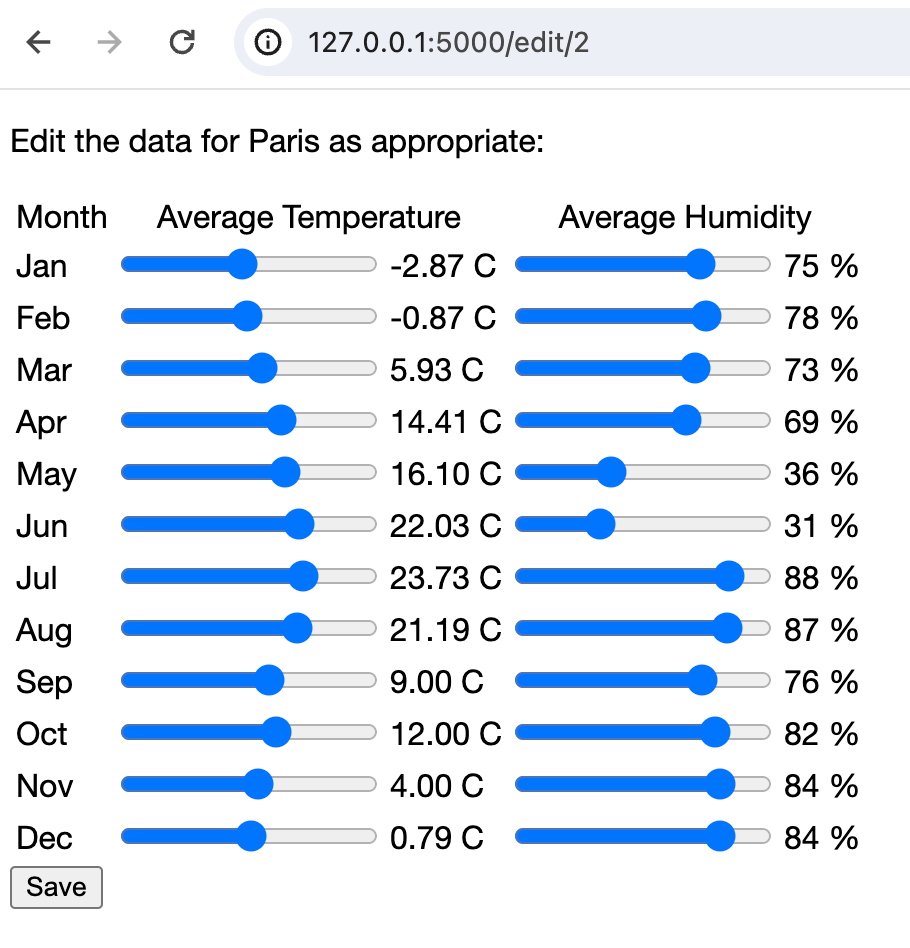
至此,您已完成创建一个基于 Flask 的、与数据库交互的应用程序的任务。 现在,您已经完全掌控了天气。 请修改任一城市的气象数据,以便这些更改在图表上更加显著。 然后预览这些更改。