Get started with .NET desktop apps
JetBrains Rider provides comprehensive support for creating and developing various types of .NET desktop applications on Windows, including WPF, Windows Forms, and UWP. This guide outlines the essential steps to create and run your first desktop application.
Prerequisites
Besides having JetBrains Rider on your machine, you only need to install .NET SDK — the latest stable version is recommended. You can verify the SDK installation by opening the Terminal window and running:
What to Choose: WPF vs. Windows Forms
WPF: Modern UI framework with XAML-based design, vector-based rendering, and comprehensive binding system. Ideal for visually rich applications.
Windows Forms: Traditional, rapid development approach with the drag-and-drop designer. Good for internal business applications where development speed is prioritized over visual customization.
JetBrains Rider supports creating UWP desktop apps, but be aware the UWP framework is in maintenance and no longer under active development by Microsoft.
For new desktop applications, WPF is generally recommended unless you have specific requirements that favor Windows Forms or UWP.
Create a .NET desktop application project
Launch Rider and click New Solution on the Welcome screen. If Rider is already open, select from the menu.
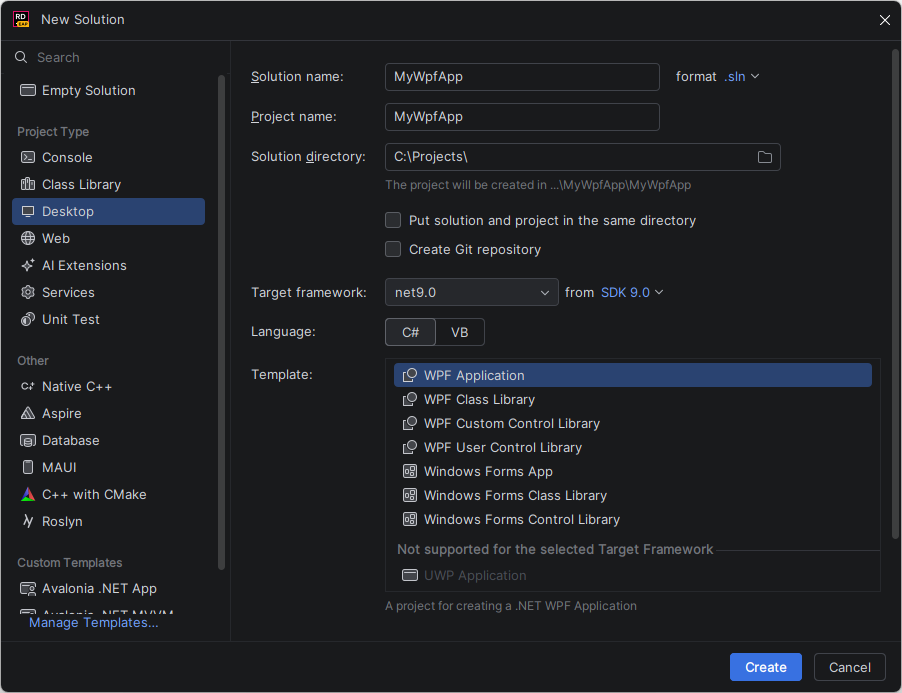
In the New Solution dialog that opens, select Desktop under the Project Type on the left.
Fill in basic settings:
Solution name — if you are new to .NET, a solution is the typical unit for an independent piece of development, similar to a workspace in most other frameworks.
Project name — automatically generated to be the same as the solution name, but you can change it if you plan to have multiple projects in the solution.
Solution directory — where to save the solution.
Put solution and project in the same directory — you can select this checkbox if you do not plan to add more projects to your solution.
Create Git repository — select this checkbox if you want to version your code with Git and use integrated Git features. You can create a Git repository at any time later.
Target framework — the latest stable version available on your machine is preselected automatically.
Language — we will use C# in this tutorial.
Select a project template — will will use WPF Application or Windows FOrms App.
Click Create.
Rider generates the necessary files and folders and opens the solution.
Understand project structure
A WPF application project typically contains:
App.xaml — Application definition file that contains application-level resources
MainWindow.xaml — The main window UI definition in XAML
MainWindow.xaml.cs — The code-behind file for the main window
A Windows Forms project includes:
Program.cs — application entry point
Form1.cs — The main form file that contains the logic
Form1.Designer.cs — Auto-generated code for the form design
Rider provides navigation, inspections, and refactorings across all these components.
First run
Desktop templates include a minimal configuration and basic startup logic, so you can run your project right away by clicking Run on the toolbar.
Rider builds the solution and opens the application window, which is empty in the beginning.
Next steps
After creating your first .NET desktop application, consider exploring the following:
Add controls to your UI by using visual designer (for Windows Forms apps) or XAML editor (for WPF apps).
Implement user interactions with event handlers. To learn more, follow the official Microsoft documentation for WPF apps and Windows Forms apps.
Set a breakpoint in your code, for example, in Program.cs, and click Debug
on the toolbar. When the program stops, explore values of the variables and step through the program to understand how the program is executed.