System architecture
Qodana Self-Hosted contains a set of containerised processes executed on a Linux server that is optimized for containerisation.
Each Qodana service has exactly one task.
Component level
This section provides a detailed breakdown of individual services and components that make up Qodana Self-Hosted and focuses on their interaction, responsibilities and structure. The diagram below the internal structure of the system, planning deployments, and troubleshooting specific components.
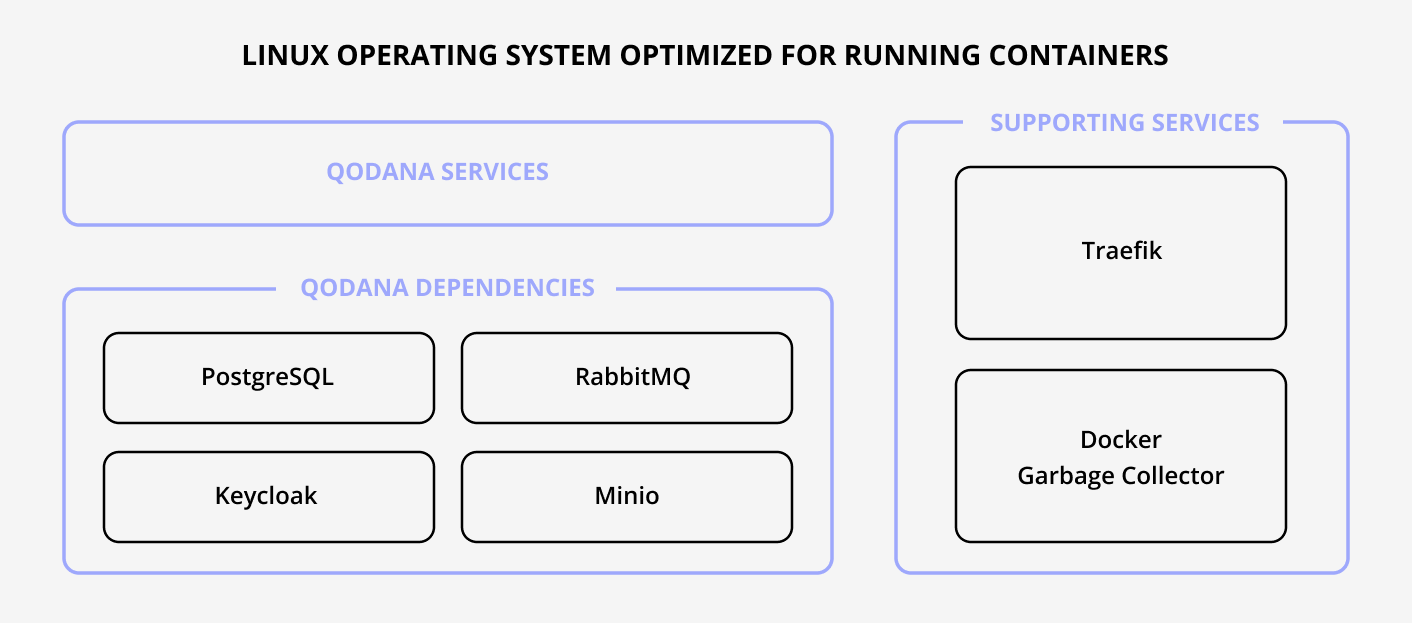
If deployed on a single Linux server, Qodana Self-Hosted contains several containerized services. Each service saves its state in a remote component that can be a PostgreSQL database. Qodana services communicate between each over through RabbitMQ queues.
Qodana Self-Hosted does not have a user management module. It relies on an external identity provider like Keycloak. All major OIDC providers are supported out of the box.
As an ingress controller, Traefik enables the management of services through labels to expose them outside the Linux server environment. The ingress controller operates on top of the Server Name Indication (SNI) extension of the HTTPS protocol and serves multiple hostnames on its IP address.
System level
This section provides a high-level overview of how Qodana Self-Hosted operates as a cohesive system and focuses on relationships between various components, their roles, and interaction to ensure the system functions effectively.
Understanding the system level is crucial for planning deployments, troubleshooting issues, and optimizing performance.
The diagram below shows the system architecture with all services deployed on a single server. It highlights the stateless nature of the services, the use of external storage for state management, and the communication pathways between components.
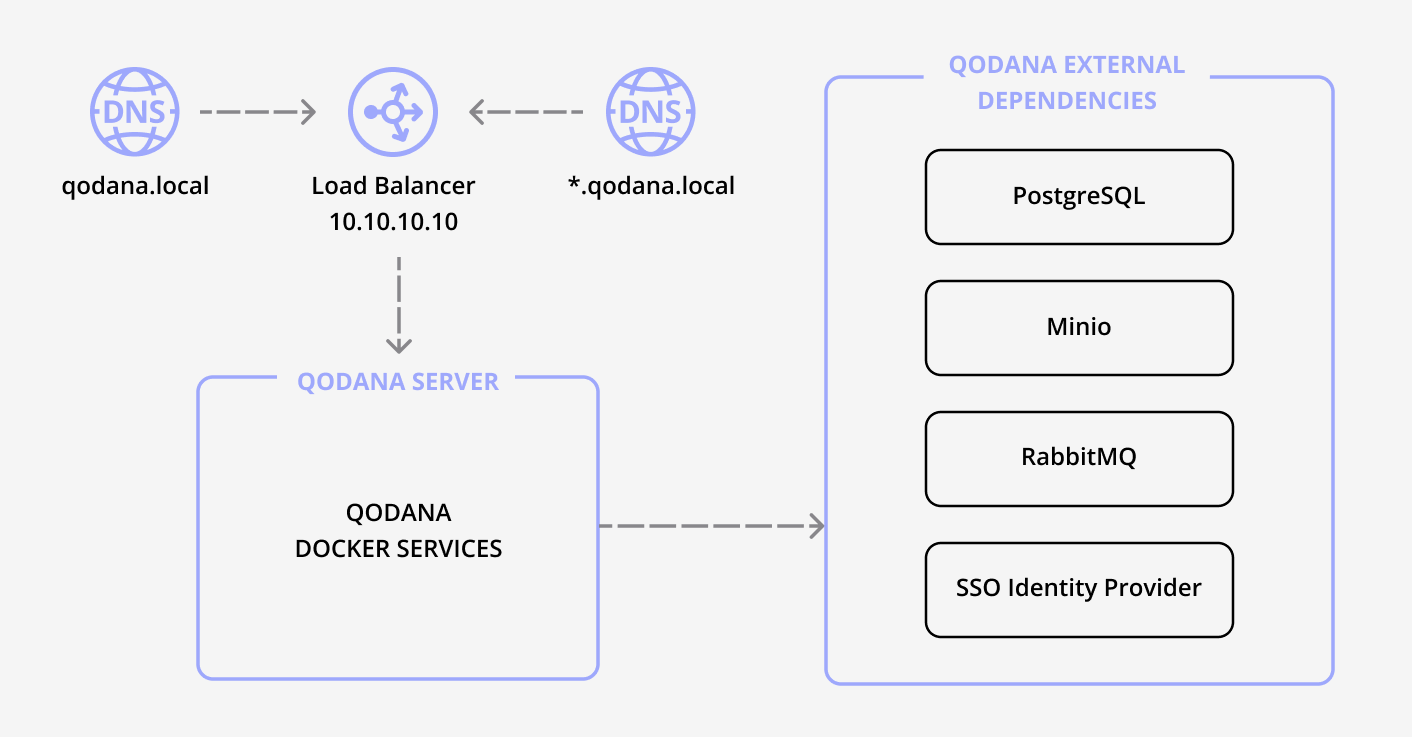
Qodana Self-Hosted services do not store any information about previous interactions or sessions. Instead, all necessary data is stored externally, such as in a database or object storage. This design ensures that the services can restart or scale without losing any important information. The state is always stored in a PostgreSQL database or storage with pre-signed URLs. Qodana clients require direct access to the object storage. Pre-signed URLs allow clients to access the object storage directly without exposing credentials.
You can use the IP address of the Linux server in the DNS or opt for a load balancer in front of the server that will redirect to the IP address of the server. The second option is a possibility for enabling HTTPS at the load balancer level and keeping protected the IP address of the server.
Tenancy model
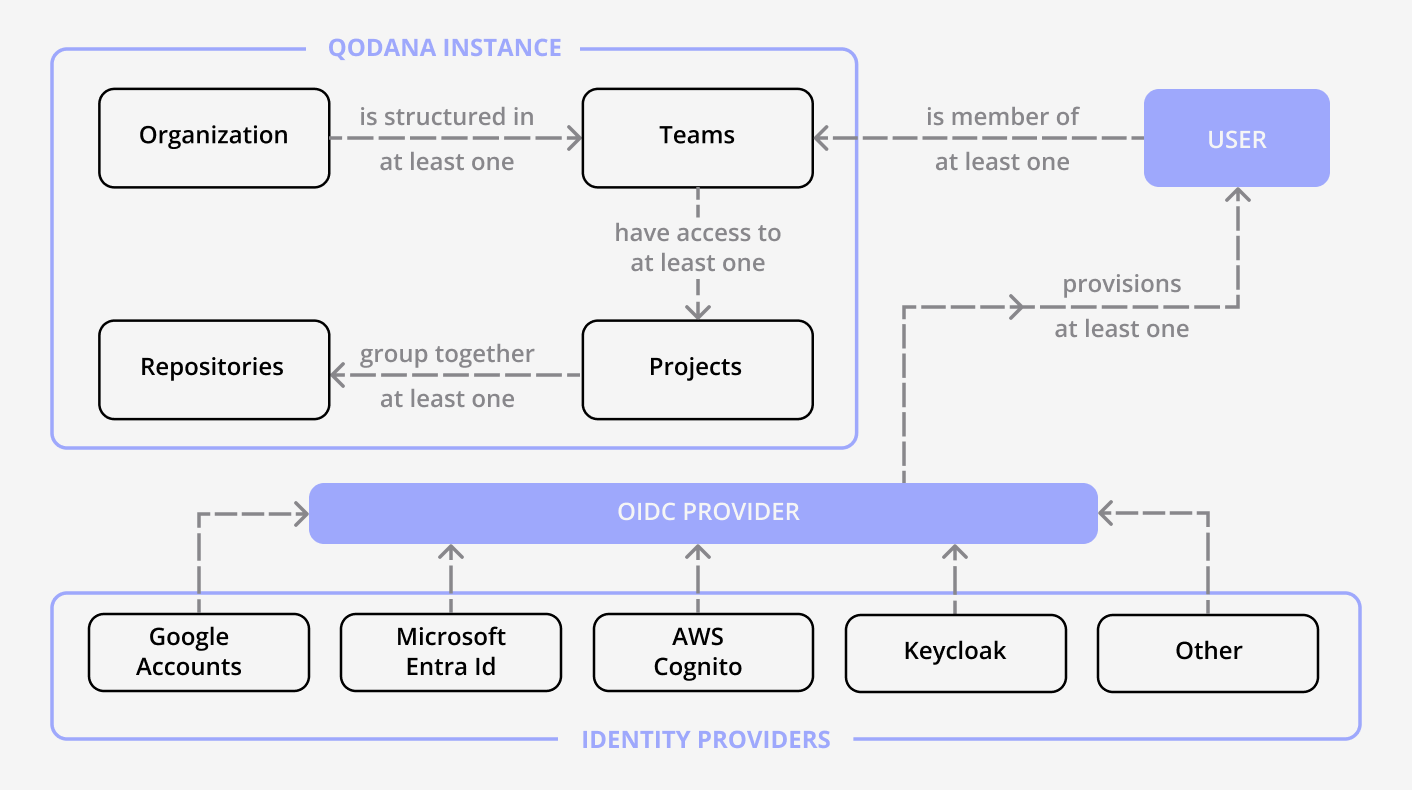
Qodana Self-Hosted is used by a single organization to monitor and manage the quality of their software artifacts. An organization can contain one or multiple teams. Each team is made up of at least one user. A user is synced from a single Open Id Connect (OIDC) Provider. An OIDC provider is global at the organization level. A team can own one or more projects. A project is linked to one repository. A repository linked to a project can be changed after project initialization.
Qodana Self-Hosted supports many OIDC Providers out of the box. It is necessary to configure the provider during installation.
Qodana Self-Hosted supports GitHub out of the box. For any other VCS it is possible to integrate backwards: use the project token to link it and the related continuous integration (CI) system with Qodana.