Query consoles
Overview
Query consoles are SQL files that are attached to a data source. You can write and execute SQL statements in query consoles the same way as you do it in terminal. The consoles are not included in the project context.
For more information about working with query results in query consoles, refer to Query results.
When you create a data source, a query console is created automatically and attached to this data source by default. If necessary, you can create additional query consoles for this data source.
Each query console creates a new connection session. If you do not want to create new connections, enable Single session mode.
The following video gives a short overview of query consoles in DataGrip.
Database connection session
For each query console, a database connection session is created automatically. You can create new connection sessions and attach your query console to existing ones in the console toolbar.
Location
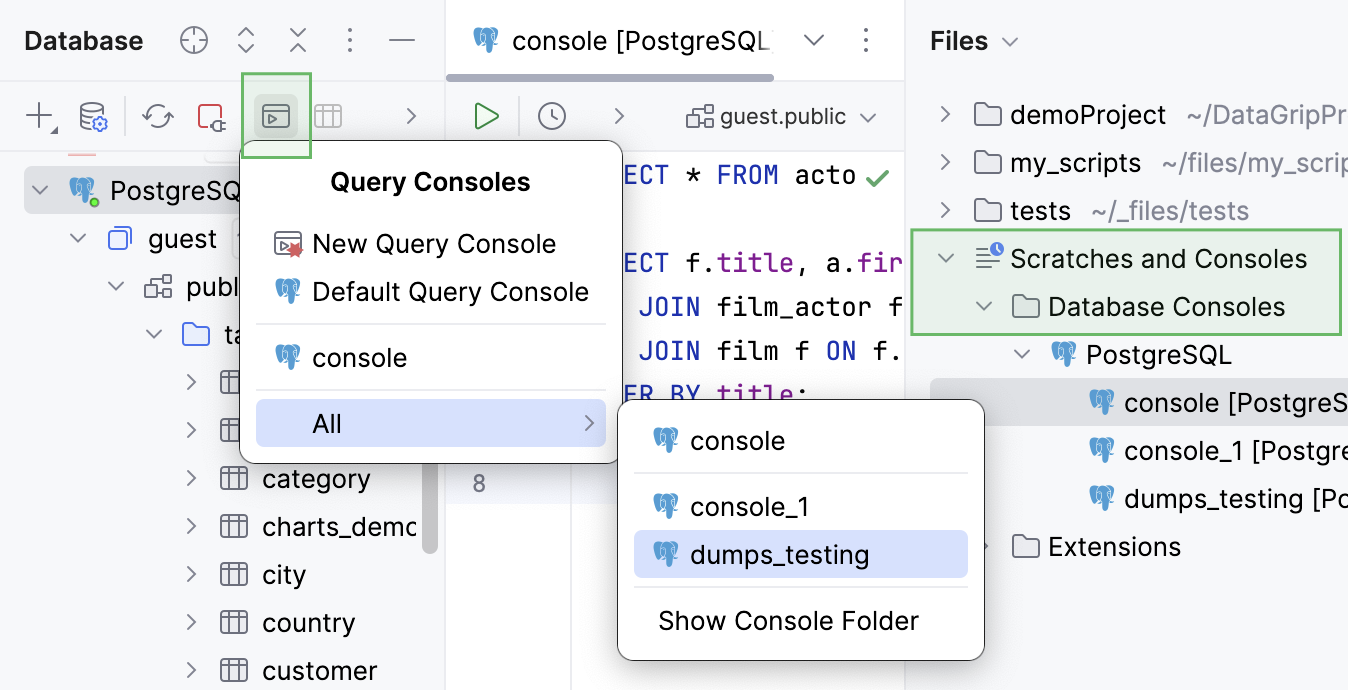
All the created query consoles are located in the internal Database Consoles directory. To open this directory, open the Files tool window Alt+2 and navigate to .
On your machine, the query console files are stored in the consoles subdirectory of the IDE configuration directory.
Code editor
The code editor is where you compose your SQL statements using the resolve modes and coding assistance features, and execute them against the associated data source.
Find the code editor toolbar controls in Code editor controls. Read more about the editor in Editor basics.
SQL statement execution
When you execute a statement, the Services tool window opens. The Services tool window displays available connection sessions, Output and Result tabs. For more information about the tool window, refer to the Services tool window topic.
If the executed statement retrieves data (for example,
SELECT), results are displayed in the Result tab that has a title of a qualified table name. For more information about creating custom titles for result tabs, refer to Use custom titles for tabs with results.If the executed statement does not retrieve data, results are displayed in the Output tab.
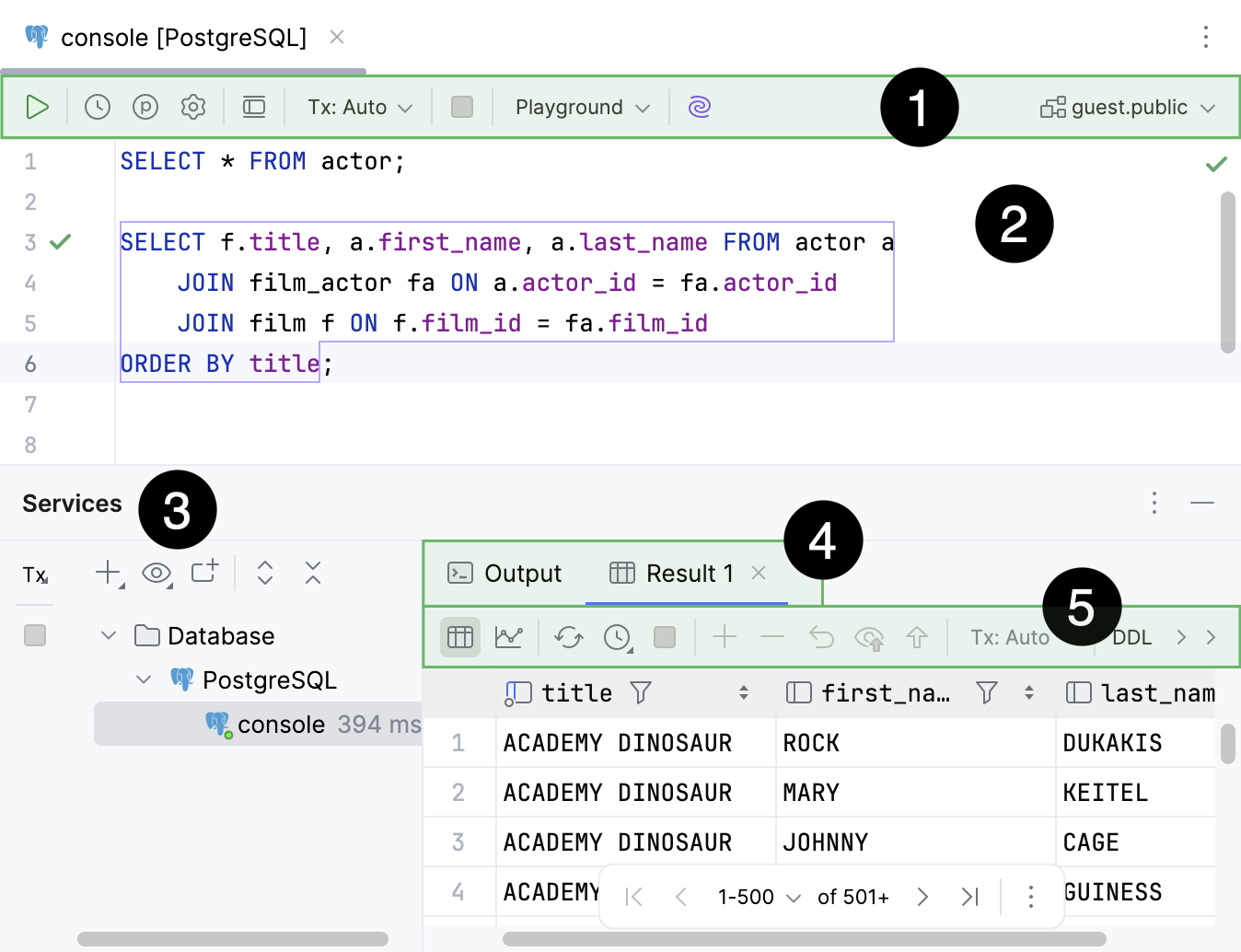
Services tool window.
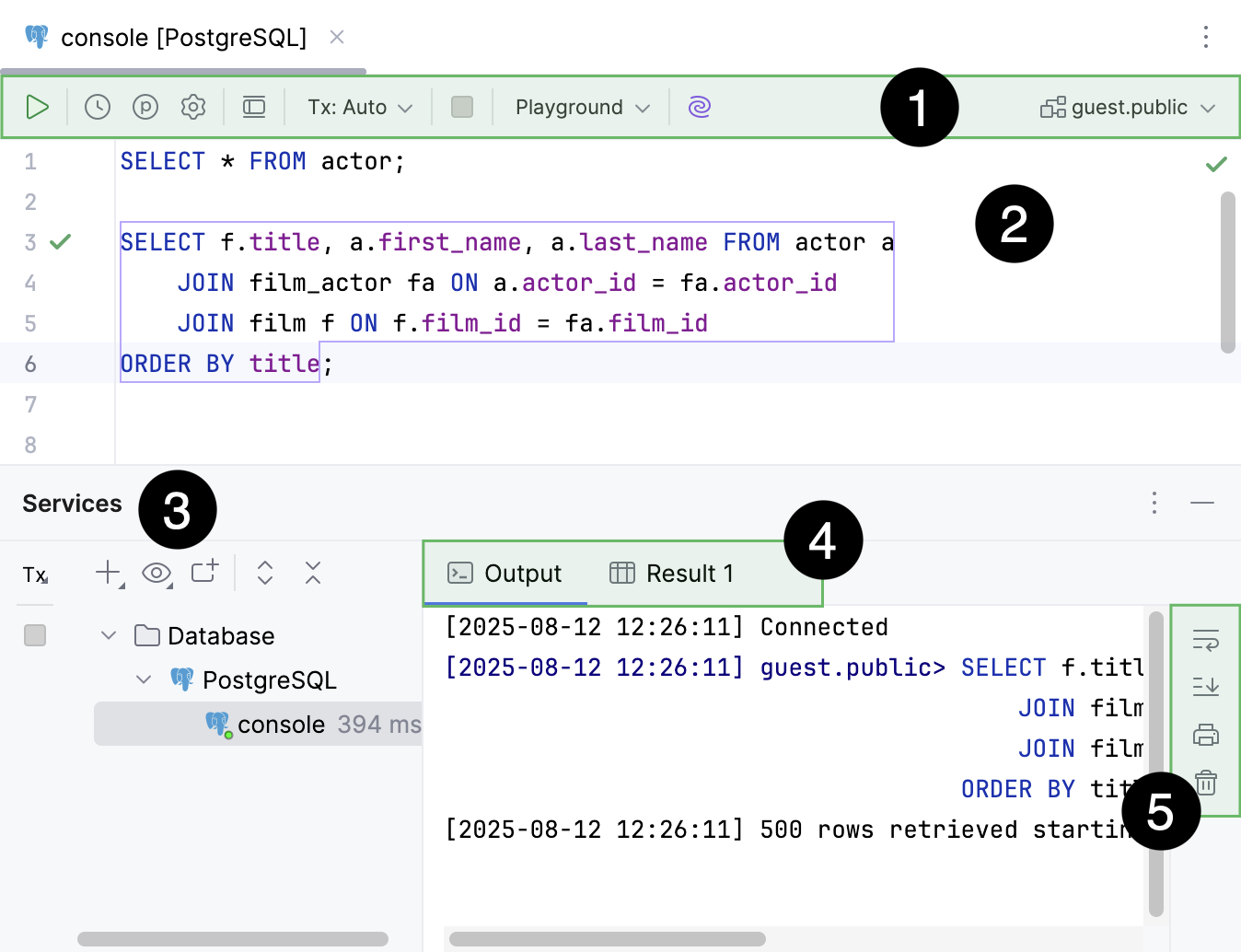
Services tool window.
Work with query console
Create a query console
To create a query console, use one of the following actions in the Database Explorer (⌘ 1) .
Click a data source and select .
Right-click a data source and select .
Click a data source, press Alt+Insert, and select Query Console.
Click a data source, press Ctrl+Shift+F10, and select New Query Console.
Click a data source and press Ctrl+Shift+Q.
Open a query console
In a query console, you can write SQL queries, run them, and get the result.
In the Files tool window, navigate to the Scratches and Consoles | Database Consoles internal directory . Expand the data source group that includes your query console, then double-click the query console.
In the Database Explorer, click
Jump to Query Console, navigate to the All submenu, and select a query console that you want to open or create a new one.
To open the default query console of a data source, click the data source and press F4.
Rename a query console
To rename a query console, do one of the following:
Right-click a query console tab and select Rename File.
Open the Files tool window Alt+2 and navigate to the Scratches and Consoles | Database Consoles internal directory .
Expand a data source group that includes your query console.
Right-click the query console and then select Rename (Shift+F6).
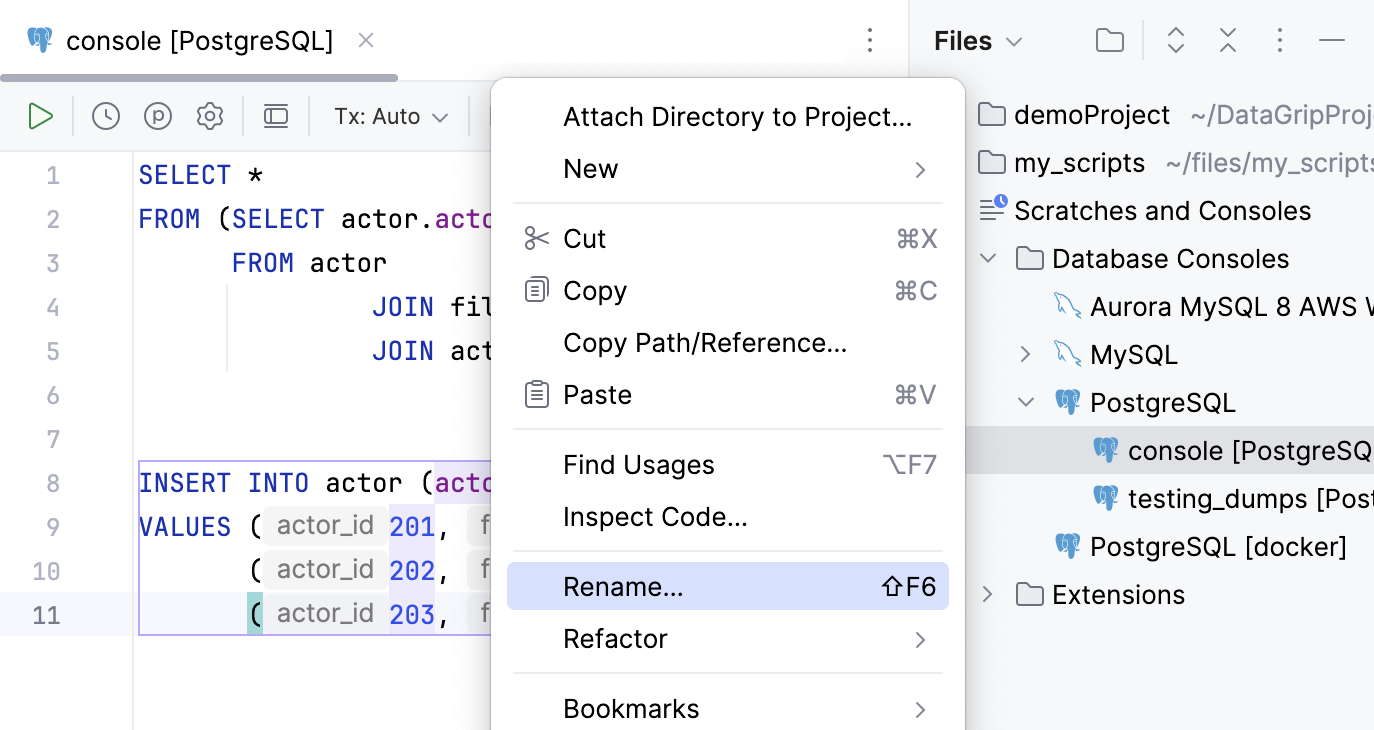
Group consoles under the data source directory
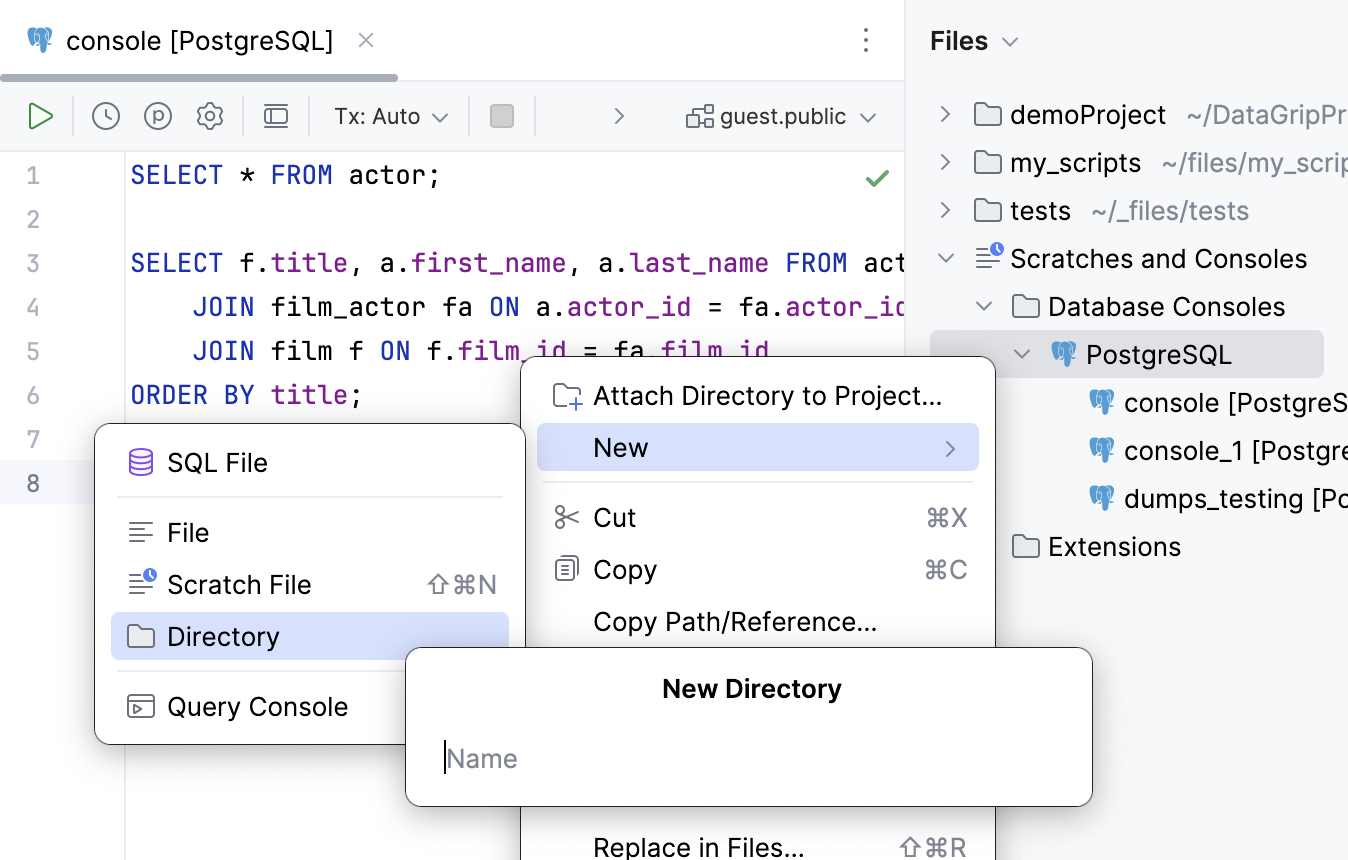
Open the Files tool window Alt+2 and navigate to the Scratches and Consoles | Database Consoles internal directory .
Right-click a data source group where you want to create a new directory, then select .
Specify a name of the directory.
Select and drag query consoles to the directory.
In the Move dialog, click Refactor.
Delete a query console
In the Files tool window, navigate to the Scratches and Consoles | Database Consoles internal directory .
Expand a data source group that includes your query console.
Right-click a query console and select Delete. Alternatively, press Delete.
Copy a query console to a new location
In the Files tool window, navigate to the Scratches and Consoles | Database Consoles internal directory .
Expand a data source group that includes your query console.
Right-click a query console and select .
In the To directory field, specify a new location for the file.
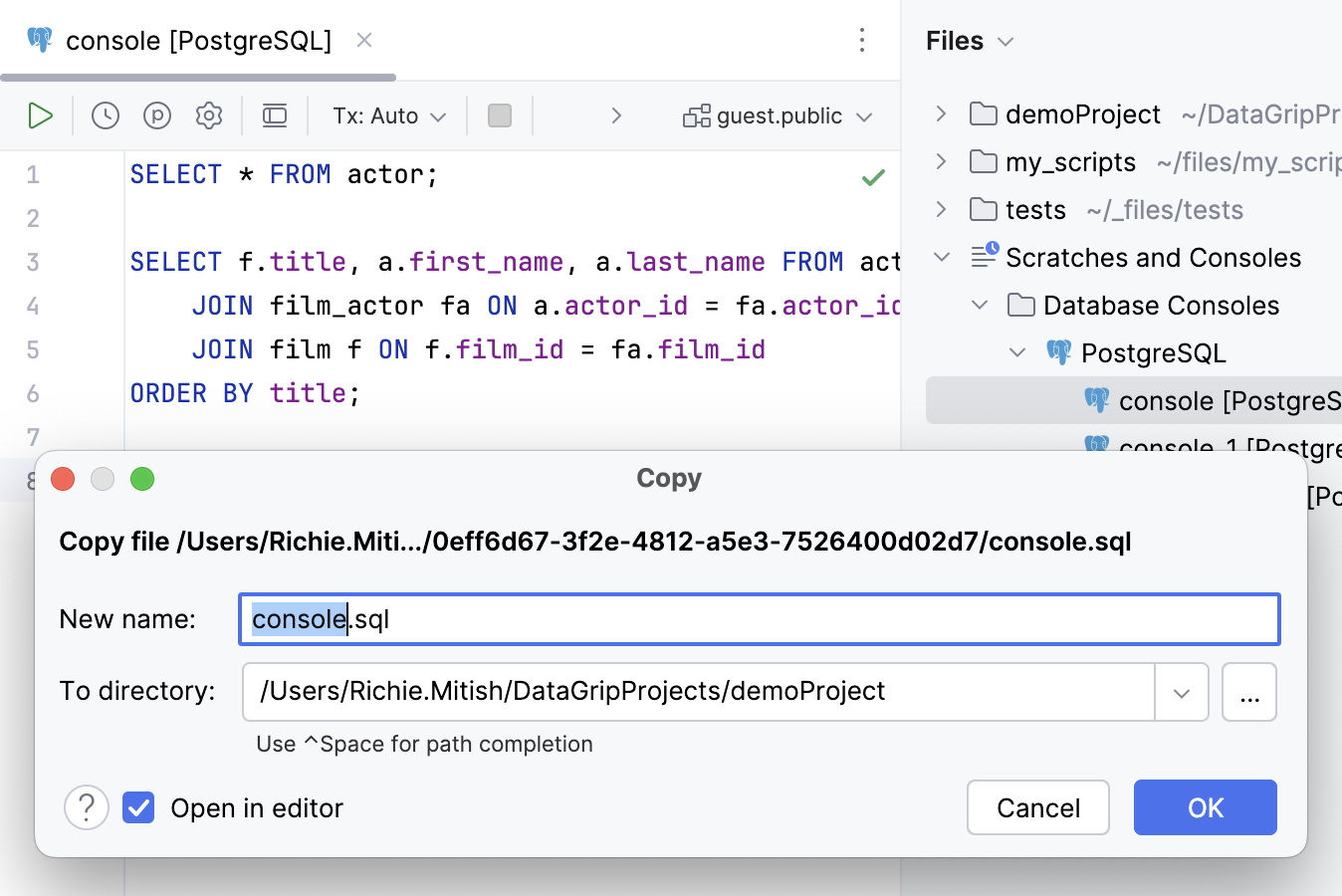
Open a query console in the file browser
To open a query console in your file browser, do one of the following:
Right-click a query console tab and navigate to .
Open the Files tool window Alt+2 and navigate to the Scratches and Consoles | Database Consoles internal directory . Expand a data source group that includes your query console. Right-click the query console, and select .
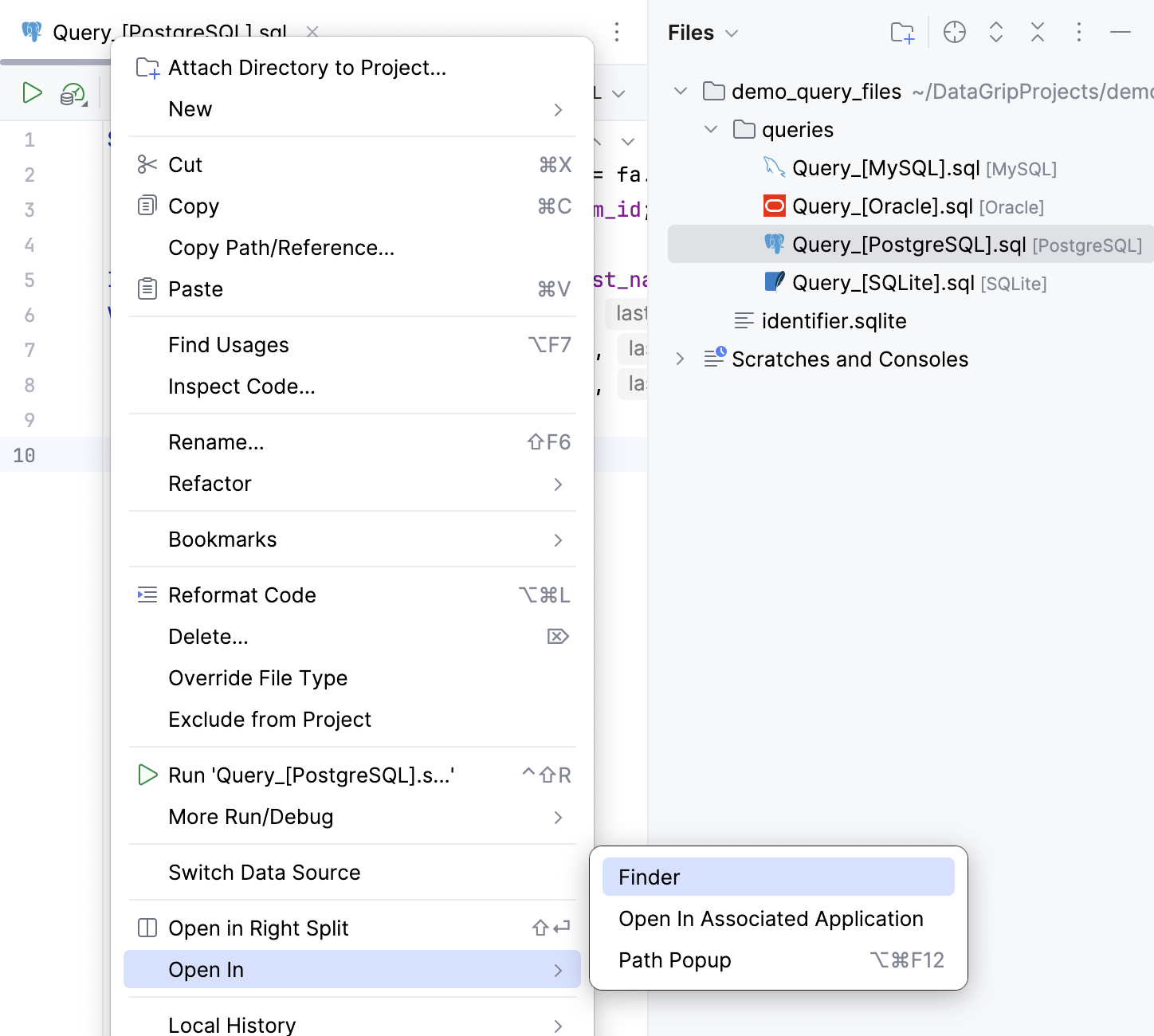
Configure query console settings
Set the default schema
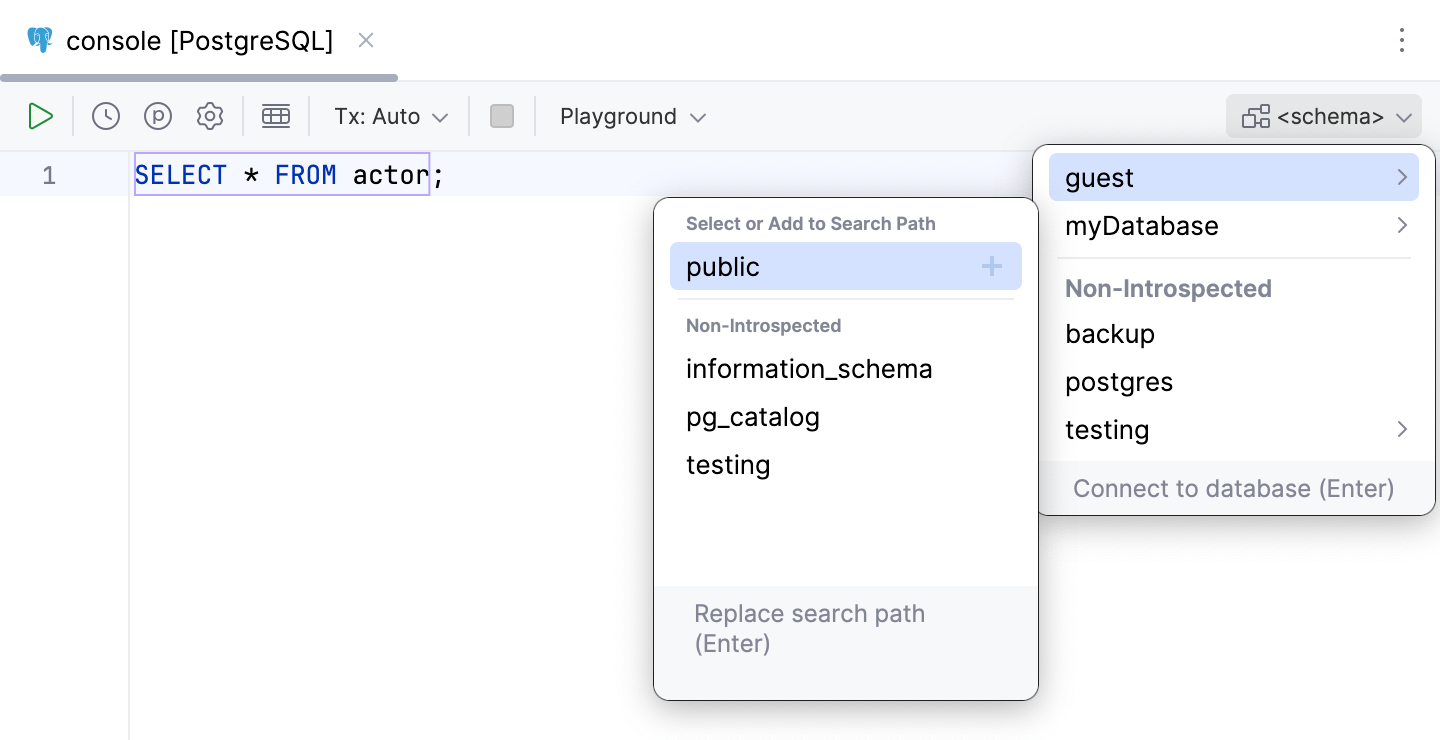
When you select the default schema for a query console, you can omit the name of that schema or database in your statements.
To set the default schema or database, click the <schema> dropdown located in the upper-right part of the toolbar. Then, select the schema that you need.
For more information about schemas, refer to the Schemas topic.
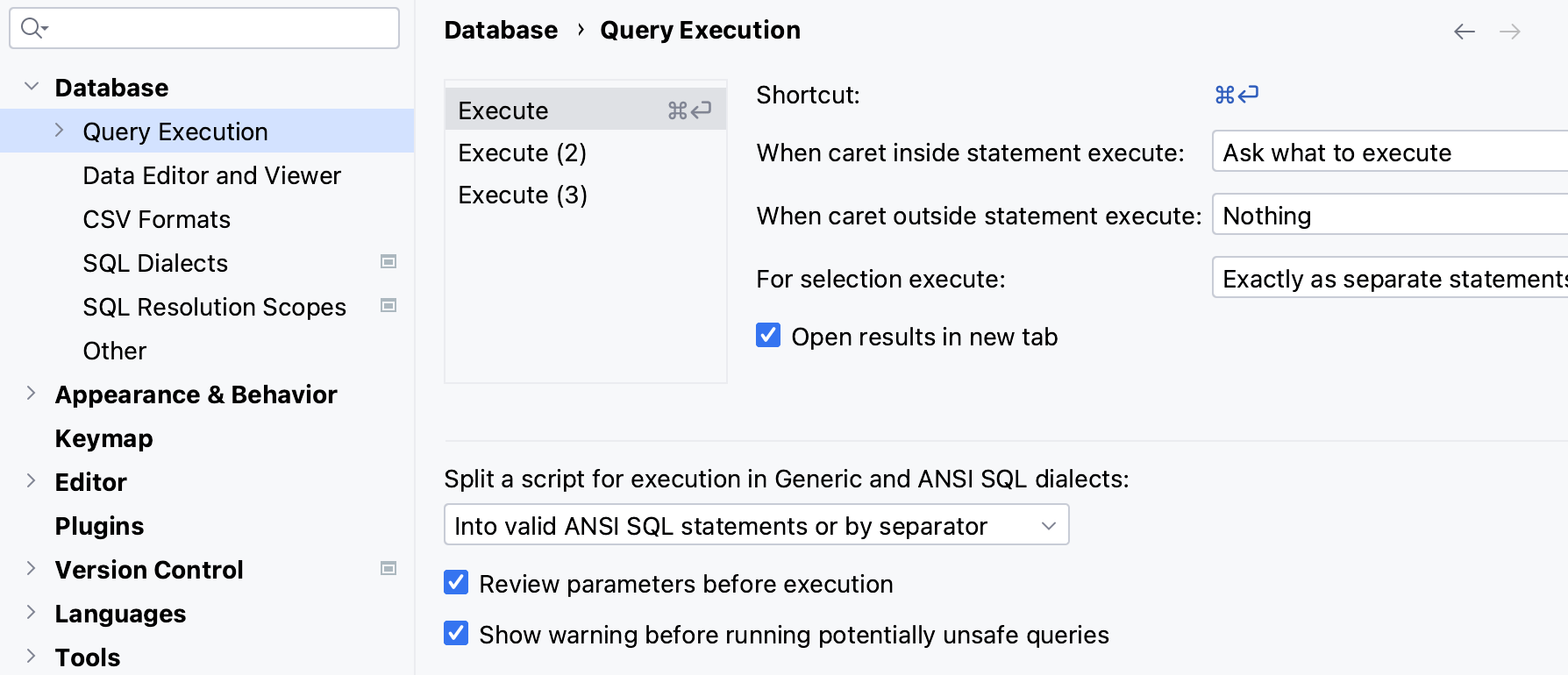
View query execution settings
Open a query console and click
Open Query Execution Settings on its toolbar.
Open settings by pressing Ctrl+Alt+S, navigate to . For more information about the settings, refer to Query execution.
Configure query console dialects
Change the SQL dialect in the code editor
Right-click the editing area and select Change Dialect (<current_dialect>) to. In the Change SQL Dialect window, select a dialect.
Productivity tips
View history of a query console
In a query console, right-click any area and select .
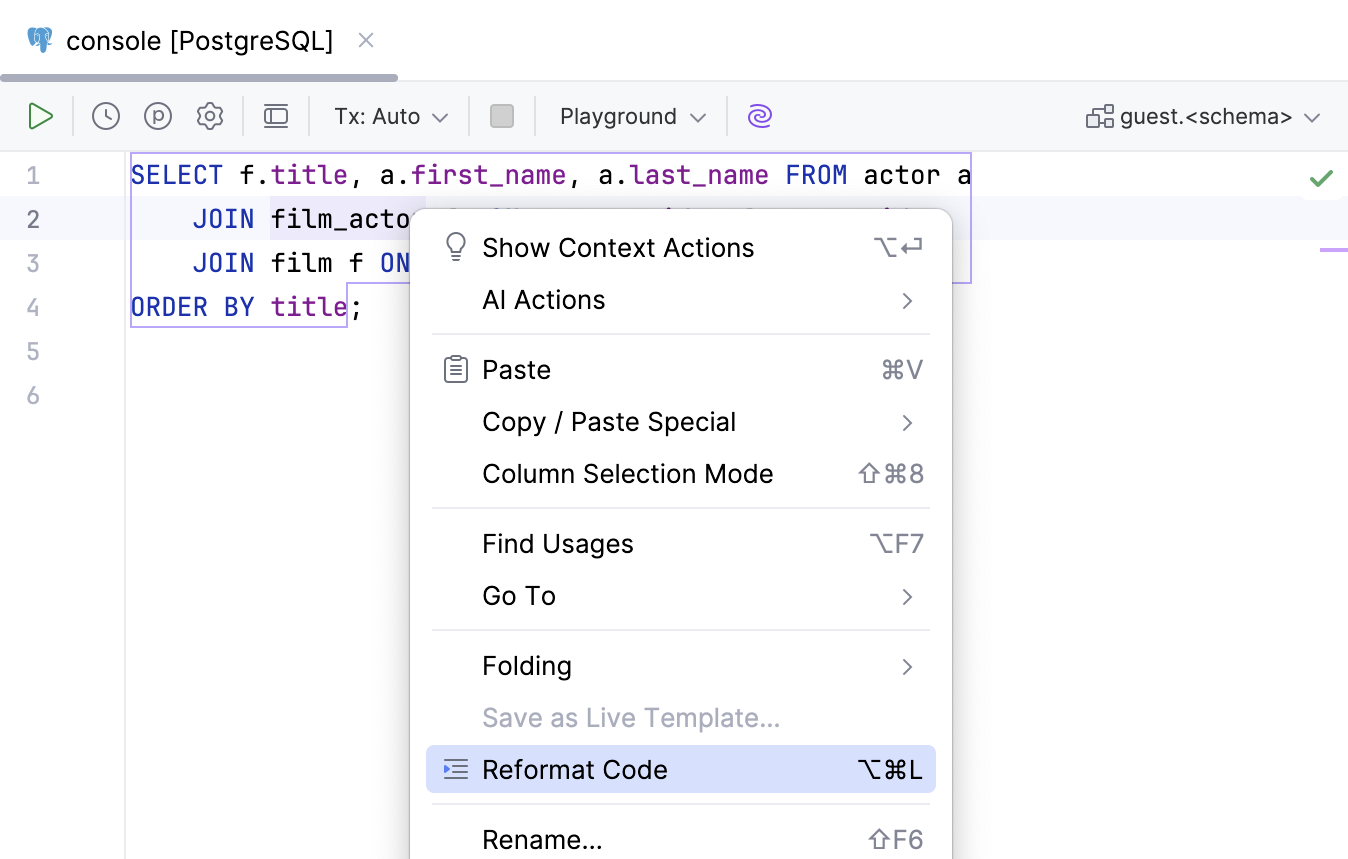
Apply a code style in the editor
Right-click any area or a selection of code in the editor and select Reformat Code. Alternatively, press Ctrl+Alt+L.
Select the scope.
Click Run.
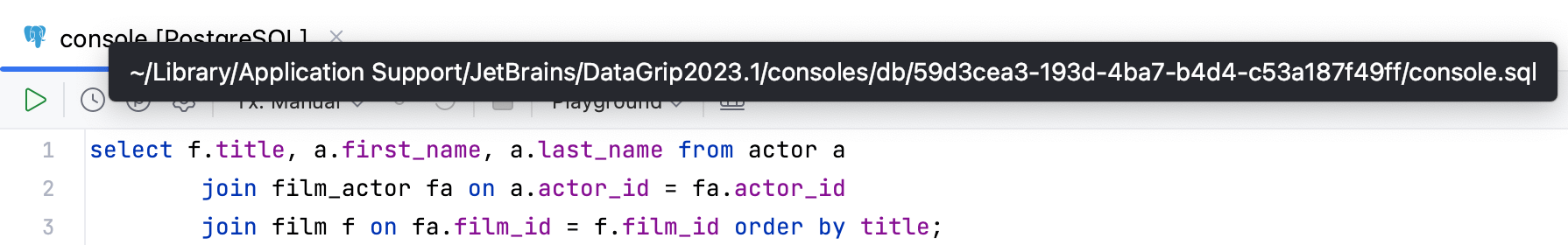
View the file path of a query console
To see the details of a file, hover over the query console tab.
Navigate to a query console from the Select In window
Press Alt+F1, select Files View and press Enter.
Edit data in INSERT statements as a table
Select
INSERTstatements that you want to edit.Right-click the selection and click Edit as Table.
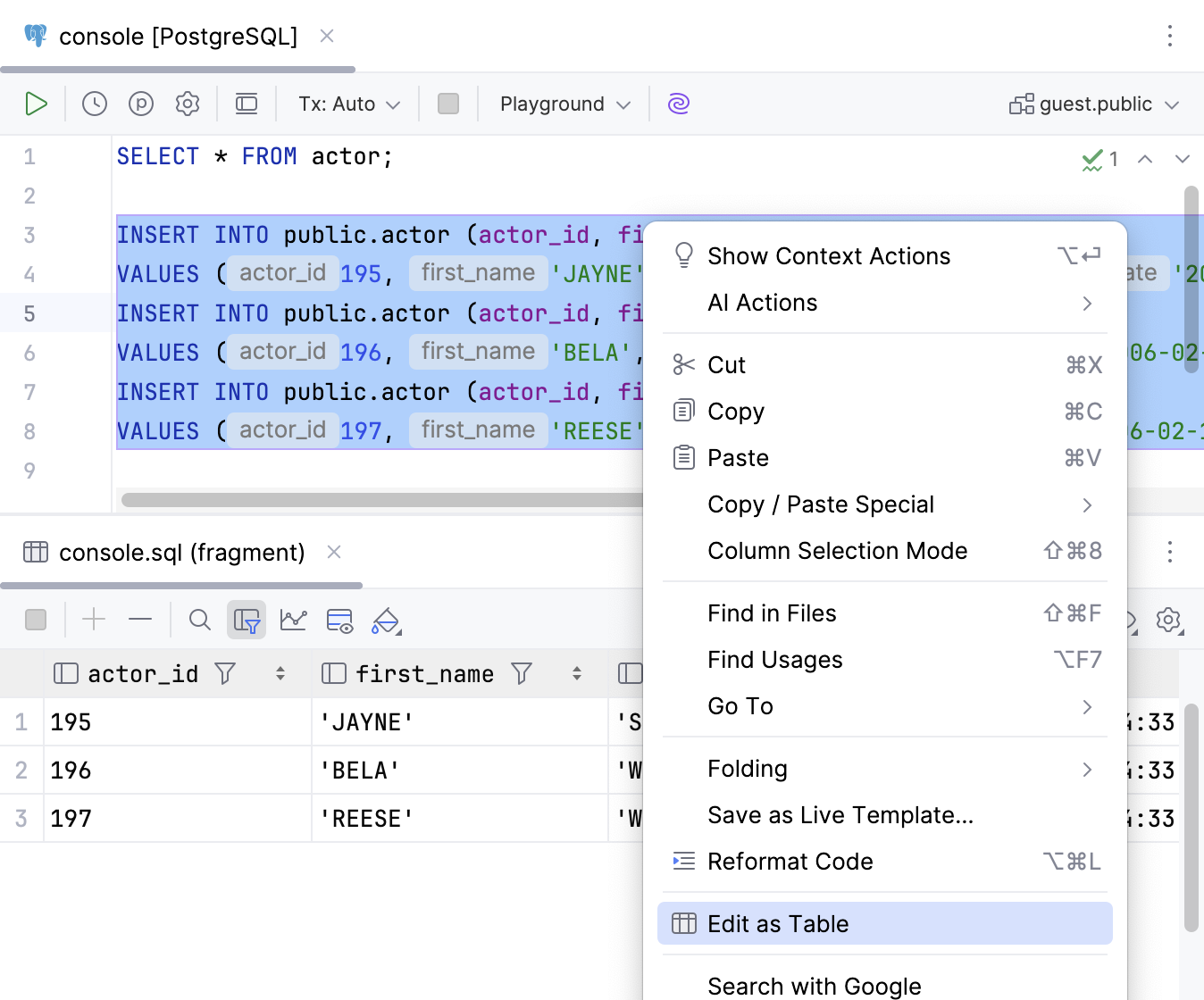
In the table editor that opens, make necessary changes in the table cell. Press Enter to confirm.
Context menu
In the code editor context menu, use the following actions to increase your productivity:
Edit as Table
In
INSERTstatements, opens the editor for working with the data in a table format.- Change Dialect (<CurrentDialect>)
Oracle only. Change the SQL dialect. Select a dialect from the list.
Shows an execution plan (or explain plan) for the current statement. The result is shown in a mixed tree/table format on a dedicated Plan tab.
To build a diagram of the execution plan, click
Show Diagram on the left of the Plan tab, or press Ctrl+Alt+Shift+U.
To build a flame graph, click
Flame Graph.
Shows an execution plan (or explain plan) for the current statement. The result is shown in table format. Technically,
EXPLAIN <CURRENT_STATEMENT>or similar statement is executed.Execute Ctrl+Enter
Execute the current statement or the sequence of selected statements.
Execute to File
Execute the current statement and save results in a text file. Select the output format and specify the file location and name.
- Run 'query console [data_source]' Ctrl+Shift+F10
Execute all the statements in the query console.
- Ctrl+Alt+Shift+U
Opens a diagram in a separate editor tab.
- Ctrl+Alt+U
Opens a diagram in a popup.
Query console reference
Use the code editor to compose and execute your SQL statements as well as to perform other associated tasks.
Read more about the editor in Editor basics.
Toolbar controls
Icon | Action and shortcut | Description |
|---|---|---|
Execute Ctrl+Enter | Execute selected SQL statement or statements. If nothing is selected, the current statement is executed. | |
Explain Plan | Open the Explain Plan actions menu. For more information about functionality, refer to the Query execution plan topic. | |
Browse Query History Ctrl+Alt+E | Open a dialog that shows all the statements that you have run for the corresponding data source. See also, Use the Query History dialog. | |
View Parameters | Open or close the Parameters dialog. For more information about user parameters, refer to the Run queries topic. | |
Open Query Execution Settings | Open the section of the Settings dialog to view or edit the query execution settings. For more information about these settings, refer to Query Execution. | |
In-Editor Results | Toggle the display of query result within the code editor of query console. For more information about the in-editor results, refer to In-Editor Results. | |
| Transaction Mode and Transaction Isolation | Select the isolation level for database transactions and the way the transactions are committed.
For more information about database transaction modes and isolation, refer to Submit changes to a database. |
Commit | (For the Manual transaction mode.) Commit the current transaction. This button is available only for the manual transaction mode. See also, transaction mode and isolation. | |
| Roll back | (For the Manual transaction mode.) Roll back changes. This button is available only for the manual transaction mode. See also, transaction modes and isolation. |
Cancel Running Statements Ctrl+F2 | Terminate execution of the current statement or statements. | |
| File Resolve Mode | Select the resolve mode to manage the context that database objects in your code are resolved to.
For more information about the resolve modes, refer to Resolve modes. |
Enable DBMS_OUTPUT | (Oracle and IBM Db2 LUW only) Toggles | |
Generate Code with AI | Opens the input field for your prompt to AI Assistant. For more information about AI Assistant in-editor code generation, refer to the AI Assistant documentation, | |
| Switch current schema | Select the default schema or database. For PostgreSQL, Amazon Redshift, and Greenplum use the <schema> list to form the schema search path. For more information about about default schemas, refer to Set the default schema. |