.NET
TeamCity .NET build step allows you to build, test and deploy any applications that target .NET (Core) and .NET Framework, as well as download and push NuGet packages.
.NET Step in Configurations and Pipelines
In classic build configurations, .NET is a single build step whose settings change depending on the selected command.
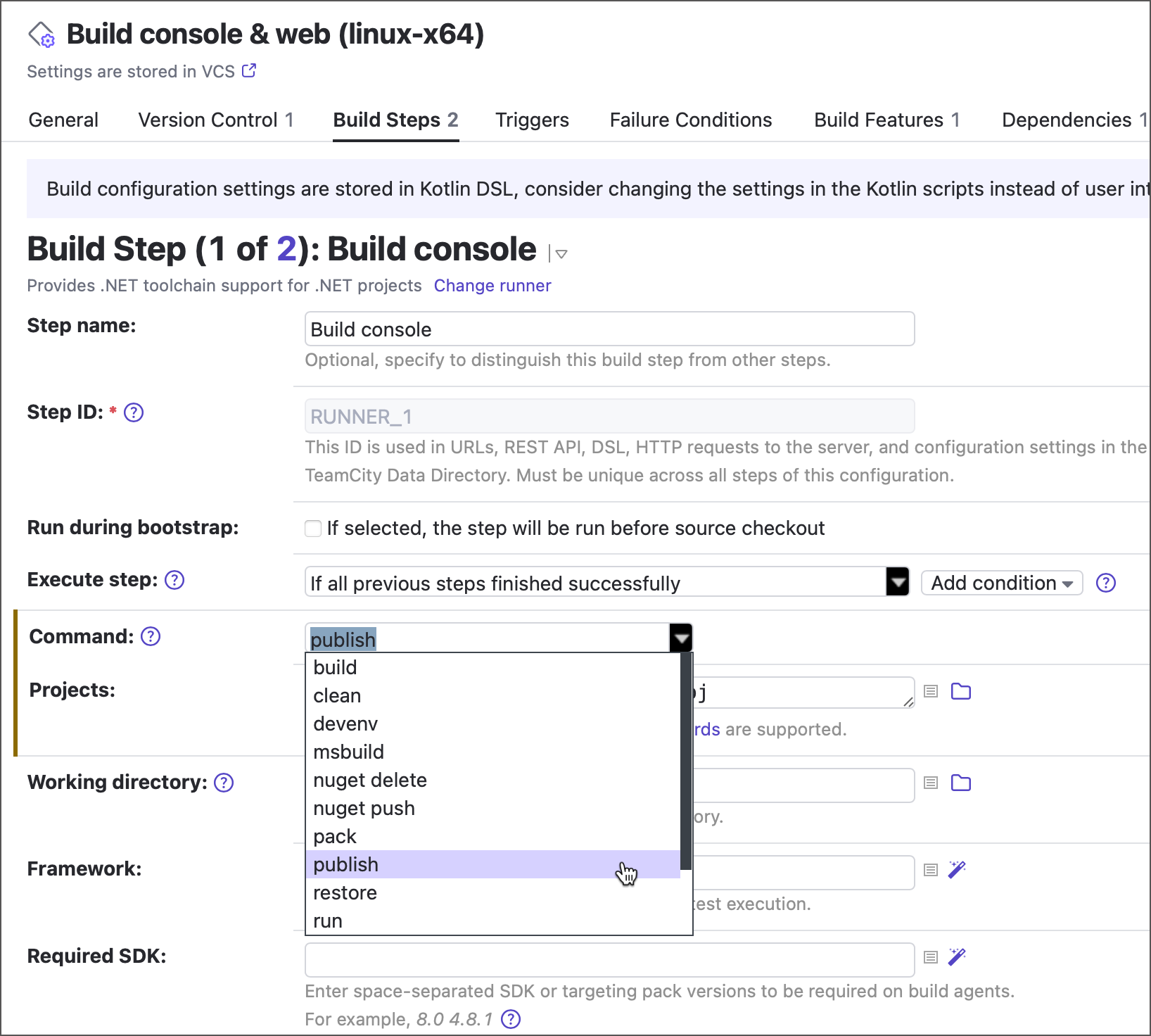
In pipelines, each of these commands is available as a separate build step.
Agent Requirements
The .NET step requires the following software to be installed on a build agent machine:
Command | Required software |
|---|---|
.NET CLI commands |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
.NET Version Detection Algorithm
TeamCity searches for the .NET executable files in the following order:
In the directory defined in the environment variable
DOTNET_HOMEfor a TeamCity agent. For example,DOTNET_HOME=D:\SDK\dotnet\.In the default directory for the .NET executable file:
Windows:
C:\Program Files\dotnetorC:\Program Files (x86)\dotnet, or other default program files directory (depending on the environment variableProgramW6432)Unix:
/usr/share/dotnetMac:
/usr/local/share/dotnet
In paths specified in the
PATHenvironment variable.
TeamCity will use the first .NET version it finds. If you have several .NET versions installed, we recommend that you specify the most recent version in the DOTNET_HOME variable.
Step Settings
The list of .NET step settings and their corresponding UI labels slightly differ depending on whether you configure a build configuration or a pipeline.
Main Settings
- Command
Allows you to choose one of the following commands:
restore
(requires .NET CLI 2.1.400+ for authentication in private feeds)nuget delete
(requires .NET CLI 2.1.500+ for authentication in private feeds)nuget push
(requires .NET CLI 2.1.500+ for authentication in private feeds)devenv(read more in the Visual Studio reference)
- Projects
The newline-separated list of paths to projects and solutions. Supports
*wildcards are supported. Does not support parameter references.- Working directory
The directory where the build step starts. By default, this is the same root directory where the agent checks out remote sources. See this topic for more information: Build Working Directory.
- Framework
Target framework. For example,
netcoreappornetstandard. Supports parameter references.- Required SDK
A space-separated list of SDKs that must be installed on a build agent. For example, For example,
8 4.8.2.Agents without these are labeled as incompatible to run this build.
- Configuration
Target configuration. For example,
ReleaseorDebug. Supports parameter references.- Runtime
Target runtime. Supports parameter references.
If the specified project file mentions any runtime ID, you can quickly select this runtime by clicking the
 button.
button.- Options
Additional options available for certain commands.
Do not build the projects — allows you to publish or test projects without building them first.
Run tests in a single session — allows TeamCity to invoke a separate testing command for each target when multiple test assemblies are listed as targets for a
testorvstestcommand.
- NuGet package sources
NuGet package sources to use during restoring.
- Output directory
The directory where to place outputs. Supports prameter references.
- Version suffix
The value of the
$(VersionSuffix)property in the project. Supports parameter references.- Command line parameters
Additional command line parameters for the
dotnetcommand.- Logging verbosity
Allows you to choose one of the following logging verbosity modes:
<Default>MinimalNormalDetailedDiagnostic
'msbuild' Command Options
The msbuild command is used for building a project and all its dependencies with the Microsoft Build Engine. Depending on the selected MSBuild version, msbuild can either be run as the cross-platform .NET CLI command or as the Windows-only msbuild.exe tool.
The msbuild command shares some of the common options with the basic CLI commands of the .NET runner (see the corresponding section for more details).
Supported MSBuild versions: 4 or later / 12 or later.
- Targets
The list of targets separated by a space or semicolon. A target is an arbitrary script for your project purposes. Click the list icon next to the field to view available targets.
- MSBuild version
The version of the installed MSBuild engine. To ensure that a specific version of native MSBuild is used (for example, in a Docker container), you need to set the path to
MSBuild.exein thePATHenvironment variable. See the Agent Requirements section for more details.If you set the version in this field and choose to run the current step inside a container, make sure to specify the path to
MSBuild.exein thePATHenvironment variable. This way, the .NET runner will be able to find the required executable file even within the Docker container.
'vstest' Command Options
The vstest command is used for testing a project with the VSTest engine and automatically importing the test results. Depending on the selected VSTest version, vstest can either be run as the cross-platform .NET CLI command or as the VSTest console.
Supported VSTest versions: 2013 or later.
- Test assemblies
The newline-separated list of paths (relative to the build checkout directory) to assemblies to run tests on. Supports wildcards.
- Excluded test assemblies
The new-line separated list of paths (relative to the build checkout directory) to assemblies that the
vstestcommand should ignore. Supports wildcards.- VSTest version
The version of VSTest to use. See the Agent Requirements section for more information.
- Platform
The target platform. For example,
x86,x64, orARM. Leave<Auto>to let VSTest select the platform automatically.- Run in isolation
Allows TeamCity to run the tests in an isolated process.
- Test filtration
Allows you to select on of the following test filtration modes:
Test names — Of all tests discovered in the included assemblies, only the tests with the names matching the provided values will be run. For multiple values, separate them with a new line. If the field is empty, all tests will be run. See details in the Microsoft documentation.
Test case filter — Run tests that match the given expression. See details in the Microsoft documentation.
See also: Run selected unit tests
- Test retry count
In the event of a test failure, TeamCity can seamlessly initiate automated re-runs of said test during the same build run. Failed tests are re-launched until they either achieve success or exhaust the maximum number of attempts. This technique allows you to identify flaky tests and distinguish them from genuinely problematic tests that consistently fail regardless of the number of launch attempts.
Tests that initially failed but managed to finish successfully during subsequent re-runs are automatically muted. You can check the Tests tab of a build results page to see how many re-runs were required for each test.
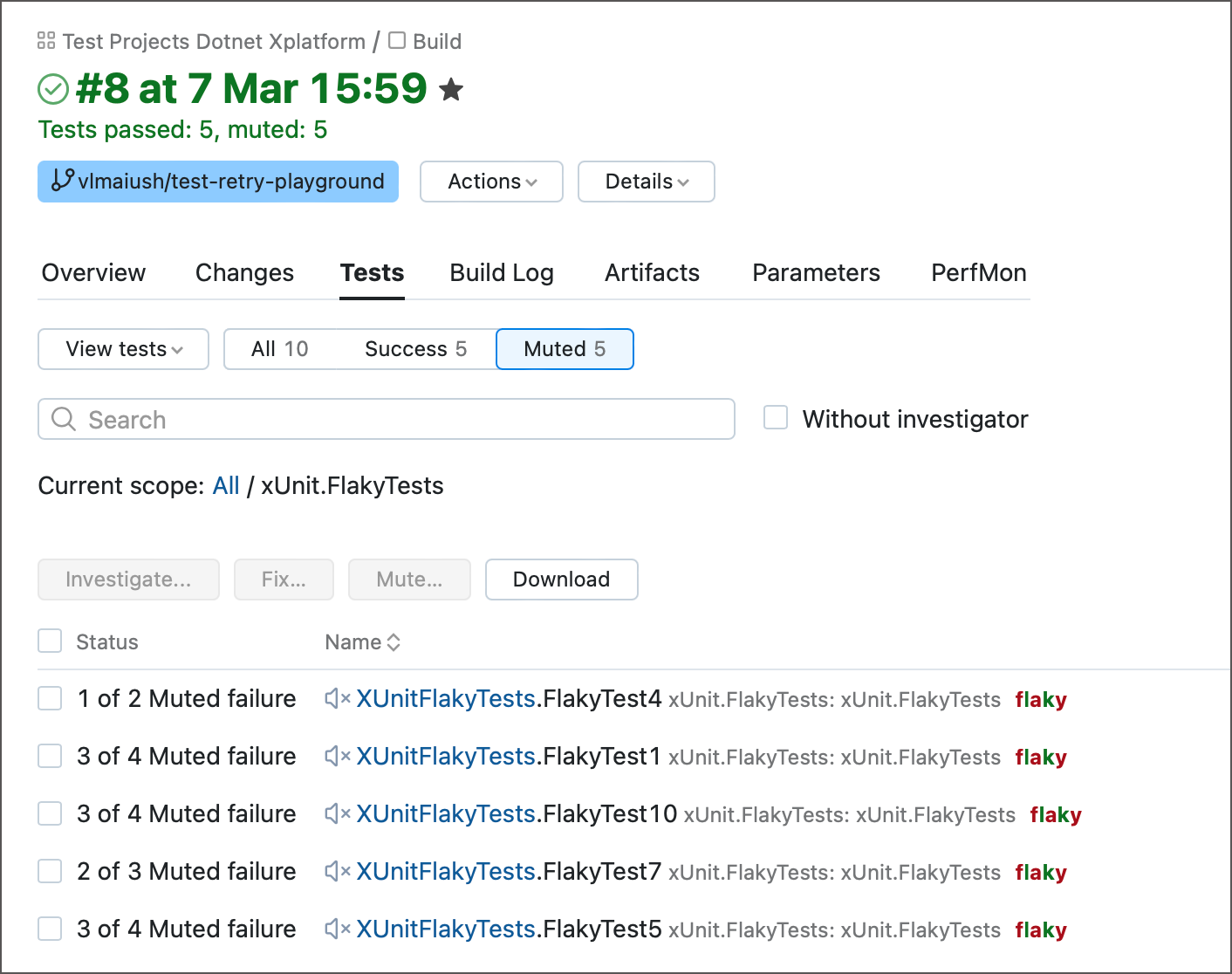
- Settings file
The path to the
.runsettingsfile.
'devenv' Command Options
The .NET runner supports the Visual Studio command-line mode with the devenv command.
Devenv allows configuring custom options for the IDE, build, debug, and deploy projects from the command line using different switches.
devenv shares some of the common options with the basic CLI commands of the .NET runner (see the corresponding section for more details).
- Build action
One of the supported values:
cleanrebuildbuilddeploy
- Visual Studio version
The version of the installed Visual Studio. Leave
<Any>to use the latest installed version.See the Agent Requirements section for more details.
Container Settings
This build step can run inside a container deployed by Docker or Podman.
Classic build configuration steps display a set of properties that allow you to specify the image name, platform, and additional run arguments. The Pull image explicitly ensures TeamCity pulls an image from the target container every time this step runs.
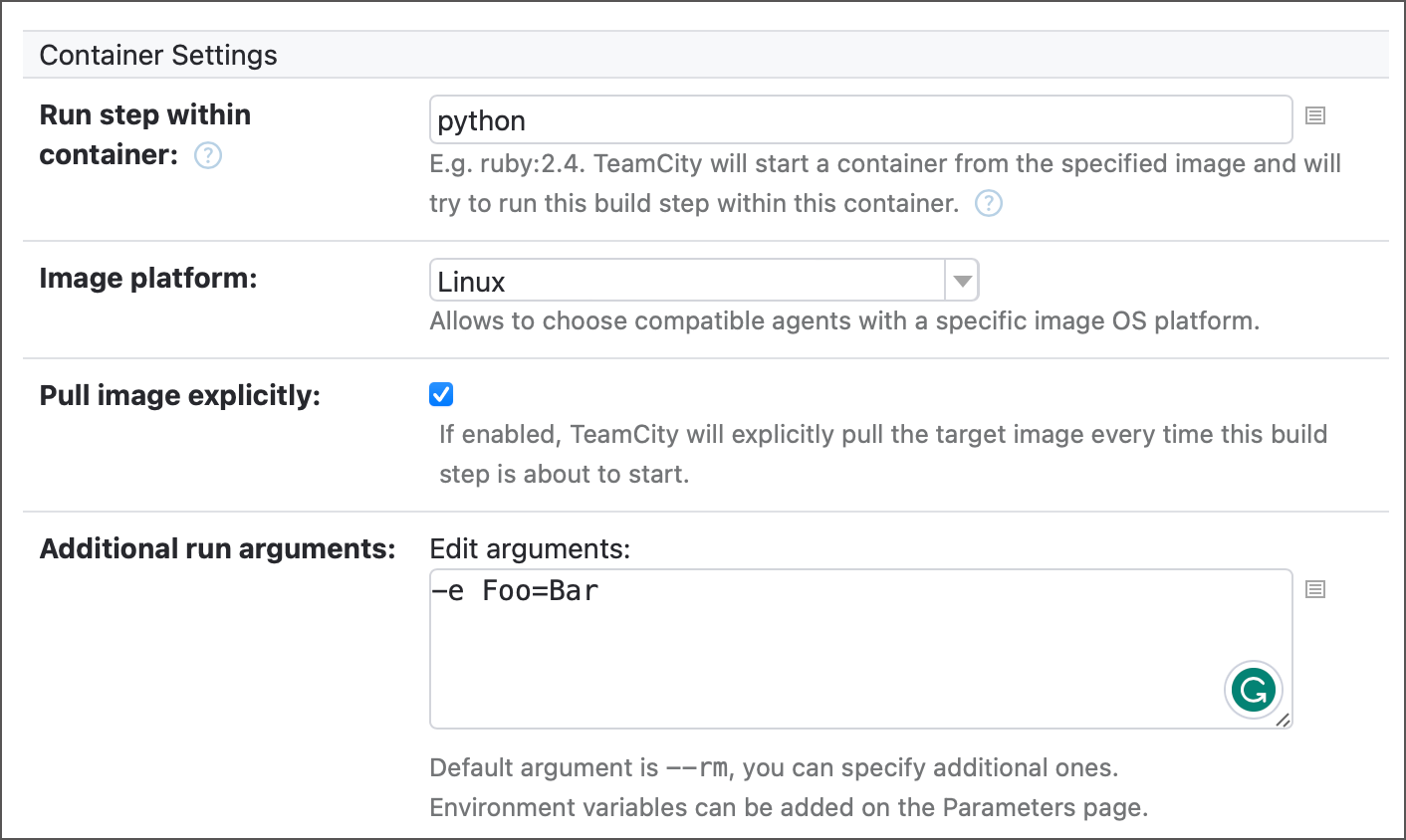
To point TeamCity to a registry where it should look for the specified image, add Docker/Podman connection to your project. By default, this connection allows TeamCity to pull images from Docker Hub in anonymous mode, but you can set it up for any container registry.
See the following article for more information: Container Wrapper.
Toggle Run in Docker on to run a step inside a container. When enabled, this element displays two options.
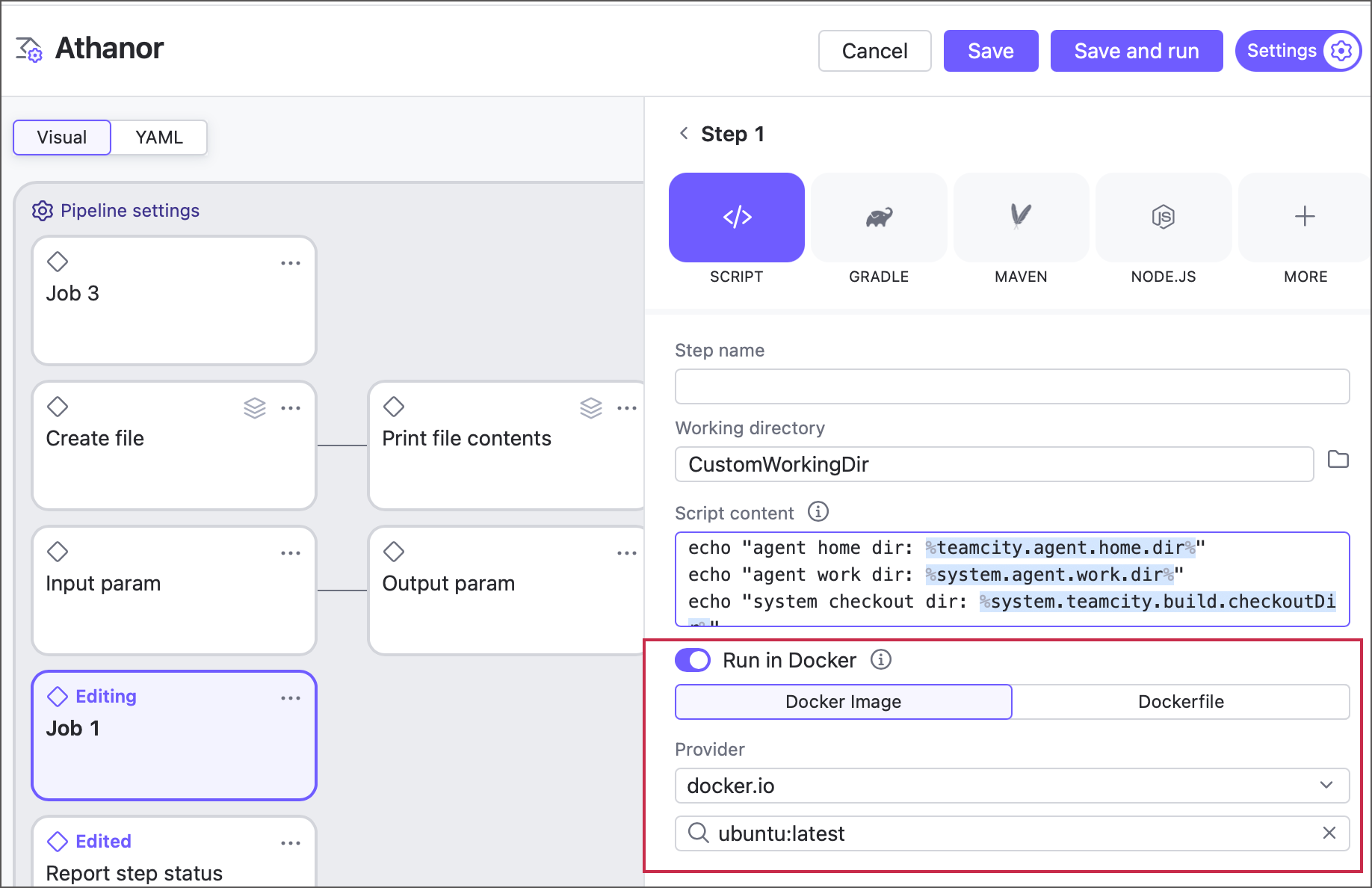
Docker image — allows you to pull an image from a Docker or Podman registry. By default, TeamCity can pull Docker Hub images in anonymous mode. For other cases (private images, custom image registries, non-anonymous mode that ensures you do not violate Docker Hub rate limits), configure a Docker integration on a pipeline or job level.
Dockerfile — allows you to build a custom image from a Dockerfile.
Code Coverage
JetBrains dotCover is supported as a coverage tool for msbuild, test, vstest, and a number of custom commands. To merge snapshots produced by multiple individual .NET runners into one consolidated report, add the dotCover to your configuration.
Custom Commands
The .NET step allows launching any custom .NET command or executable file as is. To do this, select <custom> in the Command setting of a build step.
This command supports the following unique settings:
- Executables
A list of newline-separated files to run. Supported file extensions are
.com,.exe,.cmd,.bat,.sh, and.dll, as well as files without extension.- Command line parameters
A list of custom commands or arguments to complement the specified executable.
Depending on the entered settings, the .NET runner will transparently treat each custom command. Refer to the following list for common use case examples:
Use case | Executables | Command line parameters | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
Install the specified .NET Core tool on your machine | tool install \<toolname\> | Runs | |
Run a .NET application with arguments | MyApp.dll | -- arg1 arg2 arg3 | Runs |
whoami.exe | Runs the Windows | ||
Run XUnit tests via console | C:\XUnit\xunit.console.exe | C:\TestAssemblies\MyTests.dll -xml C:\TestResults\MyTests.xml | Runs XUnit tests on Windows via |
Run all CMD files in the | scripts/*.cmd | arg1 arg2 | Uses the default Windows command-line interpreter |
Run SH files with the same arguments | build_src.sh | -c release | Uses |
Authentication in Private NuGet Feeds
TeamCity allows you to authenticate using private NuGet feeds. Read more in NuGet.
Parameters Reported by Agent
When starting, the build agent reports the following parameters:
- DotNetCLI
The .NET CLI version.
- DotNetCLI_Path
The path to .NET CLI executable.
- DotNetFramework<version>[_x86|_x64]
Defined only if the corresponding version(s) of .NET Framework runtime is installed.
- DotNetFramework<version>[_x86|_x64]_Path
This parameter's value is set to the corresponding framework runtime version(s) path(s).
Note that this parameter is defined only for the latest installed version per major release. For example, if you installed versions 3.5, 4.5, and 4.8, this parameter will only be defined for 3.5 and 4.8. Version/Parameter 4.5 will be omitted since a newer version of .NET Framework 4 is present. To explicitly define such a version, consider using theDotNetFrameworkTargetingPack<version>_Pathparameter instead.- DotNetFrameworkSDK<version>[_x86|_x64]
Defined if the corresponding version(s) of .NET Framework SDK is installed.
- DotNetFrameworkSDK<version>[_x86|_x64]_Path
The path to the corresponding framework SDK version.
- DotNetFrameworkTargetingPack<version>_Path
The path to the corresponding Reference assemblies (AKA Targeting Pack) location.
- DotNetCoreSDKx.x_Path
The .NET SDK version.
- DotNetWorkloads_<version>
Lists all .NET workloads installed on the agent machine.
The<version>suffix is the version of an installed .NET SDK. For instance, if version 7.0.300 is installed, the agent will report the `DotNetWorkloads_7.0.300` parameter.
In addition to these full SDK versions, agents report workload parameters with shortenedmajor.minorsuffixes. For example, if an agent machine has 7.0.100, 7.0.200, and 7.0.300 .NET SDKs installed, theDotNetWorkloads_7.0parameter that refers to the highest 7.0.300 version will be reported.
The parameter value is a string of comma-separated workload names, according to folders in the <dotnet_dir>/metadata/workloads/<sdk_version>/InstalledWorkloads directory. For instance, "android,maui-ios,wasm-tools".- WindowsSDK<version>
Defined only if the corresponding version of Windows SDK is installed.
- WindowsSDK<version>_Path
The path of the corresponding version of Windows SDK.
- VS<Version>
Defined if the corresponding version(s) of Visual Studio is installed
- VS<Version>_Path
The path to the Visual Studio installation folder (the directory that contains devenv.exe).
- teamcity.dotnet.nunitlauncher<version>
The path to the directory that contains the standalone NUnit test launcher,
NUnitLauncher.exe. The version number refers to the version of .NET Framework under which the test will run. The version equals the version of .NET Framework.- teamcity.dotnet.nunitlauncher.msbuild.task
The path to the directory that contains the MSBuild task
dllproviding the NUnit task for MSBuild, Visual Studio (sln).- teamcity.dotnet.msbuild.extensions2.0
The path to the directory that contains MSBuild 2.0 listener and tasks assemblies.
- teamcity.dotnet.msbuild.extensions4.0
The path to the directory that contains MSBuild 4.0 listener and tasks assemblies.
Migrating from Deprecated Runners to .NET Runner
Migrating from MSBuild Runner
Since TeamCity 2019.2.3, the .NET runner is the recommended method for building projects with the MSBuild engine. We have included the msbuild command to our refactored .NET runner to ensure long-term support of the .NET platform development strategy.
You can safely switch MSBuild steps in your existing build configurations to the .NET runner. Make sure to copy all additional command-line parameters and other important settings to the new runner. See the msbuild section for more details on the settings available in the .NET runner.
Additional features you will get in the .NET runner are:
Support of cross-platform MSBuild for .NET projects.
Ability to build a project for a different platform specified in the Runtime field.
Ability to run the project in a Docker container with our Container Wrapper extension.
Consider the following notes before migrating:
The .NET runner uses x86 run platform by default. If the x86 version is not available, it will use x64.
The .NET runner provides code coverage only for dotCover.
Mono is not supported with this runner.
If you are actively using either Mono or NCover/PartCover in your MSBuild steps, please let us know about it via any of the feedback channels.
Migrating from Visual Studio (sln) Runner
The Visual Studio (sln) build runner is using the MSBuild engine under its hood and provides a few tweaks for the VS users to ease their experience with building projects in TeamCity. Since TeamCity 2019.2.3, the .NET runner is the recommended method for building projects with the MSBuild engine which makes it a migration option for the users of the Visual Studio (sln) step as well.
In general, to softly switch each existing Visual Studio (sln) build step to the .NET runner you need to:
Remember/copy the values of your Visual Studio (sln) runner's settings and command-line parameters.
Switch the Visual Studio (sln) build step to the .NET runner and select the
msbuildcommand.Fill in the fields according to the
msbuildsection.
Note that certain fields have different analogs in the .NET runner:The MSBuild version should be specified instead of the version and platform of Visual Studio. See the reference on versions.
Paths to solutions should be specified in the Projects field.
Refer to the respective section for more information on migration to msbuild.
Migrating from Visual Studio Tests Runner
Since TeamCity 2019.2.3, the .NET runner is the recommended method for testing projects with VSTest instead of the Visual Studio Tests runner. We have included the vstest command to our refactored .NET runner to ensure a long-term support of the .NET platform development strategy.
You can safely migrate existing Visual Studio Tests build steps to the .NET runner with the selected vstest command. Make sure to copy all additional command-line parameters and other important settings to the new runner. See the vstest section for more details on the settings available in the .NET runner.
Additional features you will get in the .NET runner are:
Support of cross-platform VSTest for .NET projects.
Real-time test reporting by default.
Support of ARM platform, along with x86 and x64.
Ability to run and test the project inside a Docker container with our Container Wrapper extension.
Consider the following notes before migrating:
The .NET runner supports the new
.runsettingsformat of the VSTest settings file. However, it does not support the obsolete run configuration file format used in the Visual Studio Tests runner.Instead of the framework version, the .NET runner requests to specify the VSTest version.
The .NET runner provides code coverage only for dotCover. If you are actively using NCover or PartCover in your MSBuild steps, please let us know about it via any of the feedback channels.
The .NET runner does not support the MSTest tool since all features of its framework are covered by VSTest. If you were using MSTest as the engine of the Visual Studio Tests runner, we suggest that you switch to VSTest when migrating to the .NET runner.
Parallel Testing
If the .NET runner executes test or vstest commands, TeamCity can split the workload into several batches. In this case testing is carried out in separate automatically generated builds (on separate build agents). To enable this behavior, add the Parallel Tests build feature to the TeamCity build configuration.
.NET runner F.A.Q.
How to pass parameters containing spaces
The best way to pass a parameter value containing space characters is to use system properties. For example, you can add the system.Platform parameter with the Any CPU value in Build Configuration Settings | Parameters and then refer to this value as %system.Platform% inside the .NET step.
An alternative approach is to wrap the command-line parameter as follows: "/p:Platform=Any CPU".