Introduce Variable refactoring
This refactoring allows you to create a new local variable or constant based on a selected expression, initialize it with the expression, and finally replace all occurrences of the expression in the method with references to the newly introduced variable.
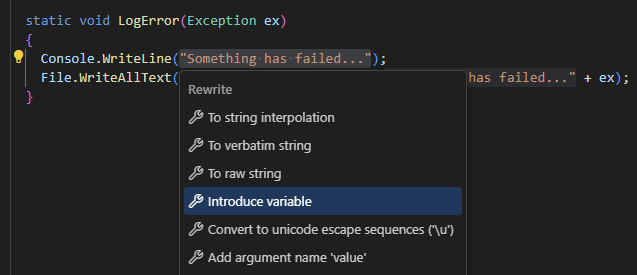
In the example below, we use this refactoring to replace two occurrences of the same string "Something has failed..." with a variable:
static void LogError(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Something has failed...");
File.WriteAllText(@"c:\Error.txt", "Something has failed..." + ex);
}
static void LogError(Exception ex)
{
var message = "Something has failed...";
Console.WriteLine(message);
File.WriteAllText(@"c:\Error.txt", message + ex);
}
Replace one or more occurrences of an expression with a variable
Select an expression in the editor.
Right-click and choose Refactor | Introduce Variable from the context menu.
If more than one occurrence of the selected expression is found, ReSharper lets you choose whether to apply the refactoring to all occurrences or only to the current one.
ReSharper adds the new local variable and initializes it with the expression.
18 February 2026