Helm
Helm is a tool for managing Kubernetes applications. Helm charts are packages of pre-configured resource definitions that you run inside a Kubernetes cluster. A chart contains a description of the package (Chart.yaml) and one or more templates used to generate Kubernetes manifest files.
Enable the Kubernetes plugin
This functionality relies on the Kubernetes plugin, which is bundled and enabled in IntelliJ IDEA by default. If the relevant features are not available, make sure that you did not disable the plugin.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Open the Installed tab, find the Kubernetes plugin, and select the checkbox next to the plugin name.
Install the Go Template plugin
This functionality relies on the Go Template plugin, which you need to install and enable.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open settings and then select .
Open the Marketplace tab, find the Go Template plugin, and click Install (restart the IDE if prompted).
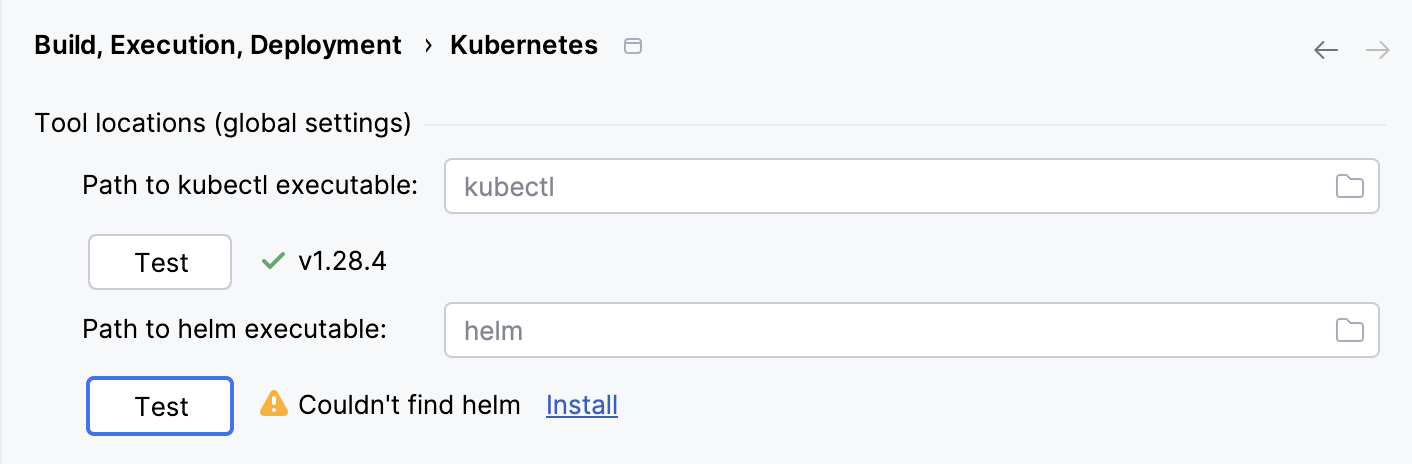
Specify a custom path to Helm
If you install Helm in custom directories, you can manually specify the path to it.
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , select .
In the Path to helm executable field, specify a path to the helm executable file.
Click Test to check the file location. If it's not found, you can either manually check the file location or click Install, and IntelliJ IDEA will download and install missing software.
Coding assistance for Helm charts and templates includes code completion, refactorings, inspections, quick-fixes, and quick documentation. Code completion includes values of dependencies from the specified repository (by default, from Helm Hub).
In Go template directives, IntelliJ IDEA provides completion for Helm built-in objects and for values passed from a values.yaml file or from a custom values file. You can press Ctrl+B to navigate to a source of object values, for example, to a child chart value imported into a parent chart.
In template objects, you can use code folding: press Ctrl+NumPad + and Ctrl+NumPad - to toggle between values and directives. You can also hover over a value to expand and show the directive.
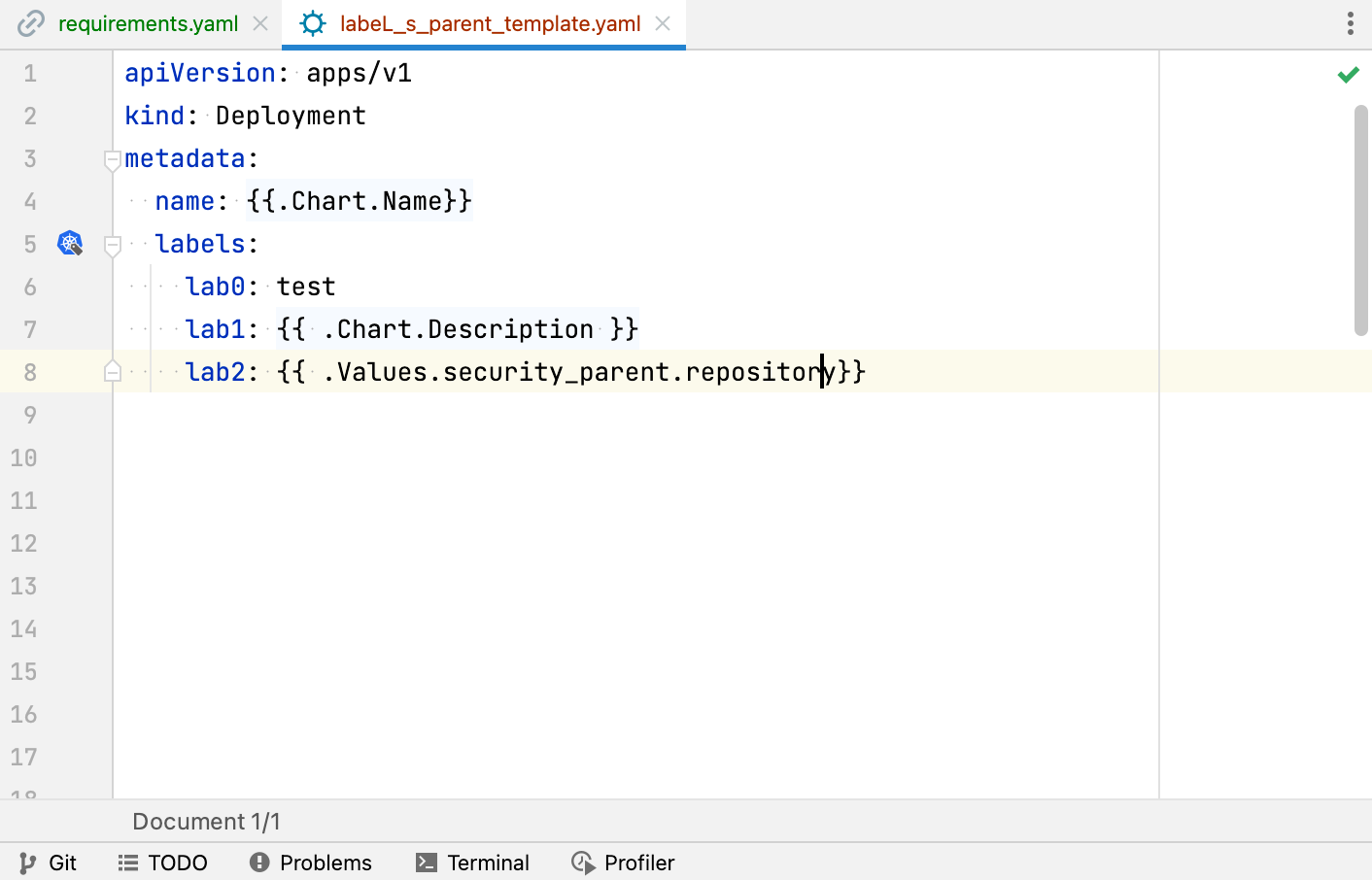
You can also use gutter icons to navigate between label definitions and label selectors, and between overridden and overriding values.
Create a new Helm chart
In the Project tool window, right-click a folder and select .
In the Create New Helm Chart window that opens, enter a name for the chart.
This runs the helm create command, which adds all the basic files required to get started:
.helmignore: Patterns to ignore when building packages
Chart.yaml: A basic chart description with metadata
values.yaml: Default values for chart templates
charts/: Directory for sub-charts
templates/: Directory for chart definitions
_helpers.tpl: Partials and functions for your templates
NOTES.txt: Information that is printed out after a chart is deployed
deployment.yaml: Example Kubernetes deployment definition
ingress.yaml: Example Kubernetes ingress definition
service.yaml: Example Kubernetes service definition
Preview the result of Helm template rendering
You can render chart templates locally using the helm template command. Specify one or more YAML files containing values from any folder on your file system. This supports such use cases as using separate value files for different environments.
If a template file is opened in the editor, click
on the right side of the editor.
Alternatively, right-click the chart and select from the context menu.
In the Render Helm Template dialog, add one or multiple files containing values for rendering. These could be any YAML files from your file system.
Optionally, you can provide individual comma-separated values in the Additional values section.
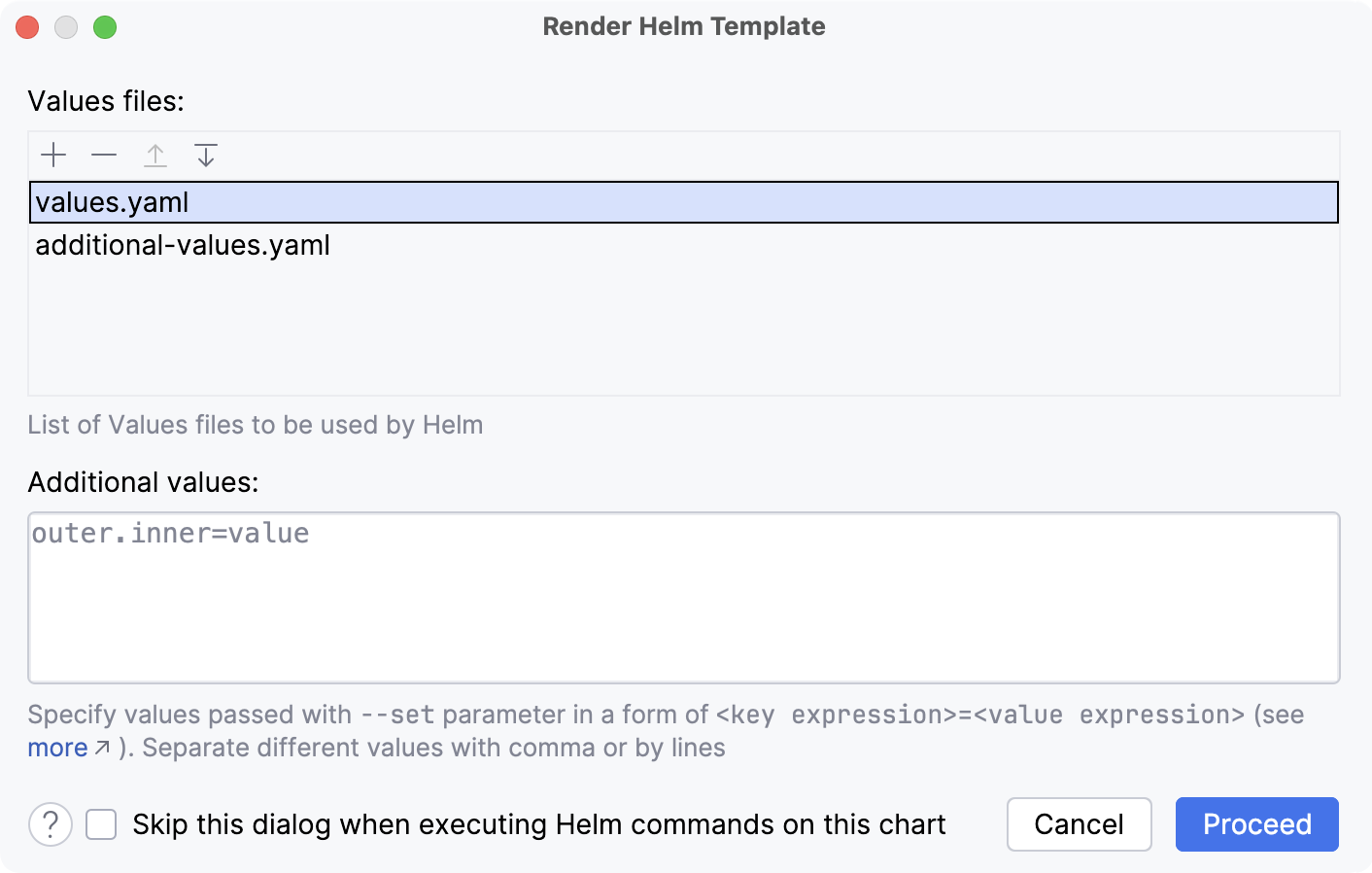
Click Proceed. This runs the helm template command and renders the Helm chart with the specified values.
IntelliJ IDEA opens the rendered preview inside the diff viewer, comparing it with the original template file.
Update external dependencies
Right-click the chart and select from the context menu.
This runs the helm dependency update command.
In Helm 2, dependencies should be specified in the requirements.yaml file. This action also generates or updates requirements.lock.
In Helm 3, dependencies should be specified in the Chart.yaml file. If you specify the dependencies in the wrong file, IntelliJ IDEA provides an inspection with a quick-fix to move them.
There is also a gutter icon for updating dependencies in both the requirements.yaml and Chart.yaml files respectively.
Examine a chart for possible issues
Right-click the chart, point to Helm, and click Helm Lint.
This runs the helm lint command that executes a series of tests to discover possible problems without actually installing the chart.