Manage AI Enterprise
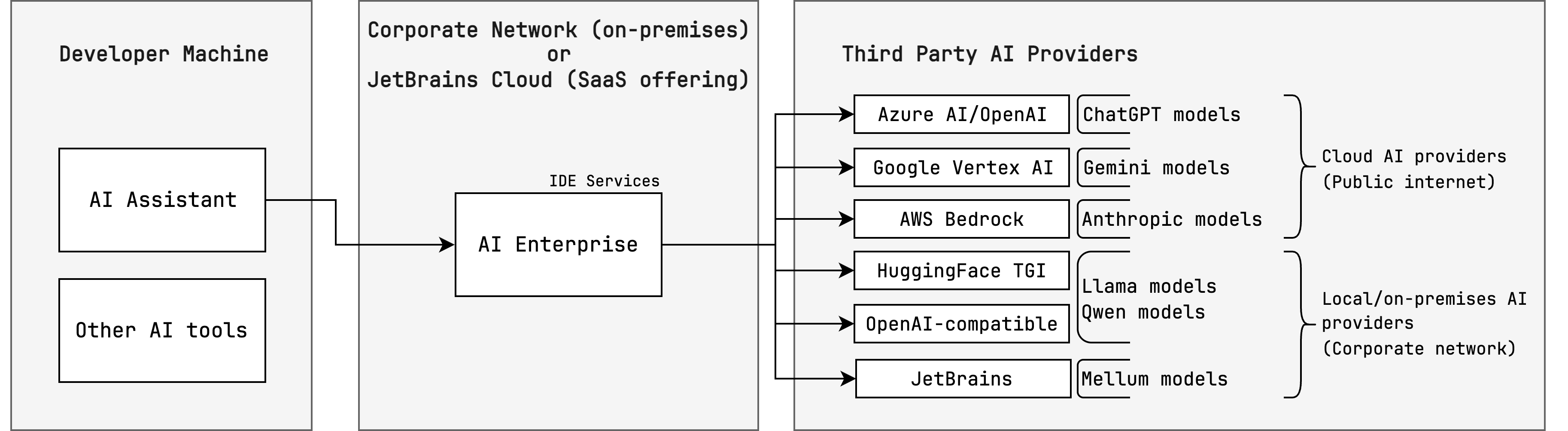
AI Enterprise lets you use different providers of AI services across your organization — JetBrains AI or a custom solution, such as:
You can enable all options and then choose a preferred provider for specific user profiles.
Enable AI Enterprise in your organization
In the Web UI, open the Configuration page and navigate to the License & Activation tab.
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Enable:
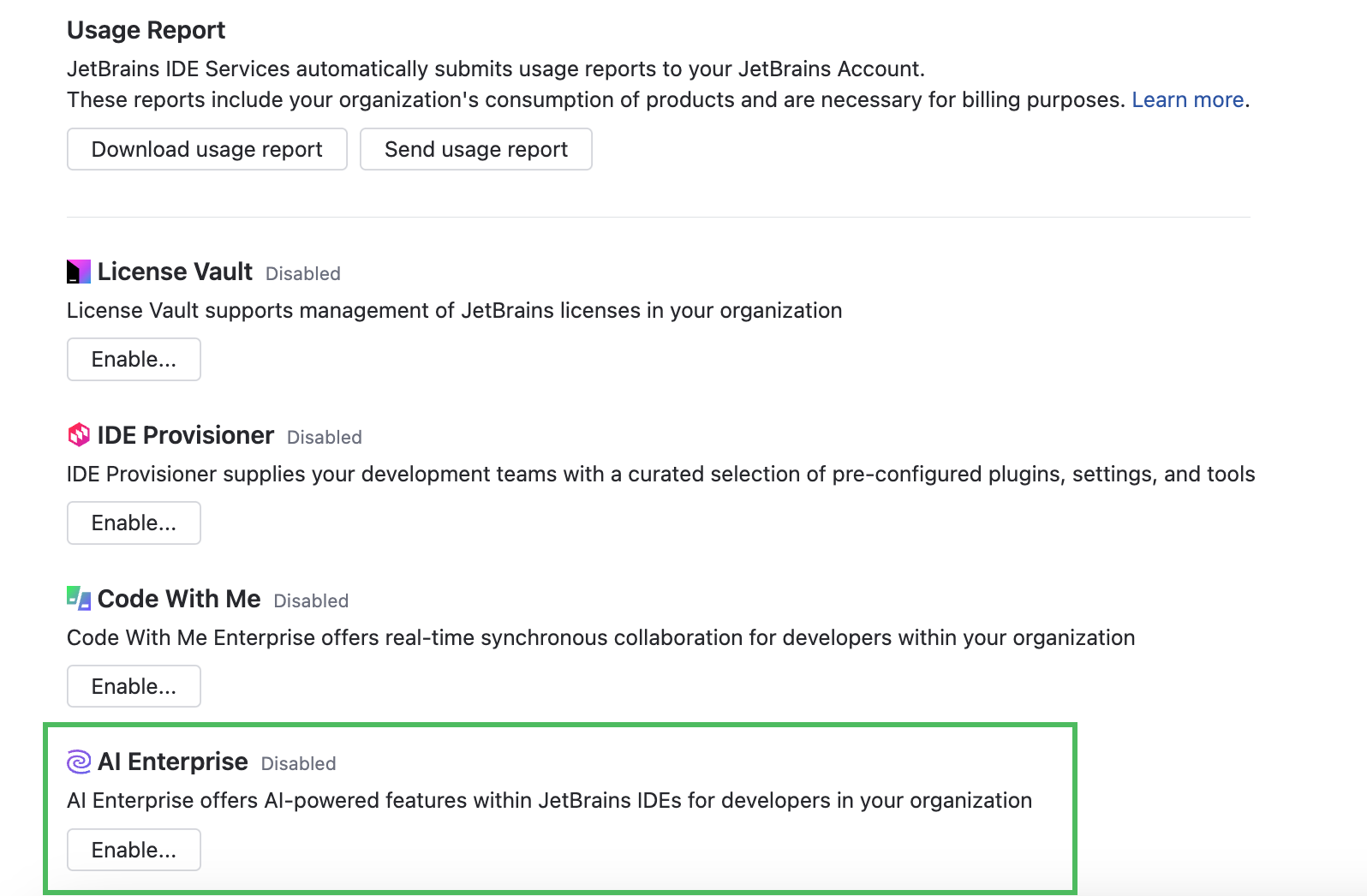
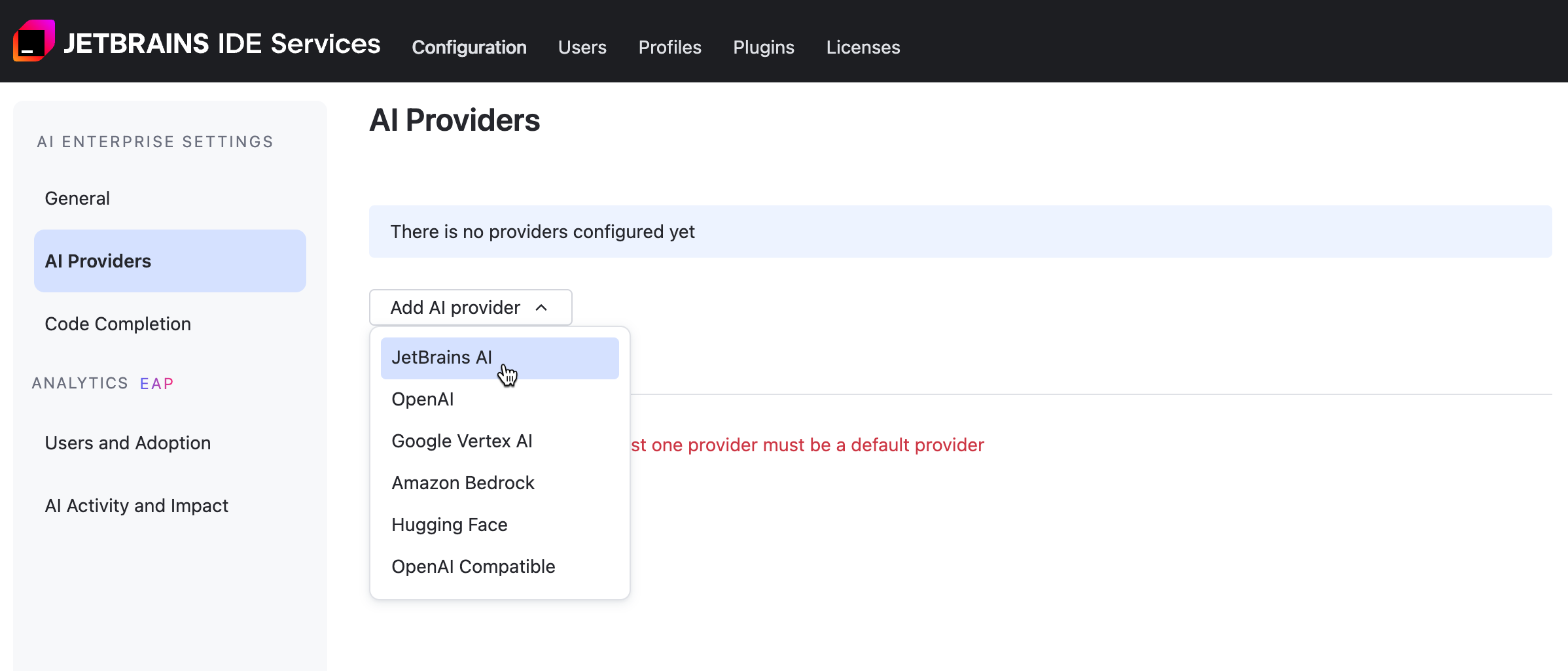
In the Enable AI Enterprise dialog, choose one of the AI providers. For specific configuration instructions, refer to the following procedures:
If you'd like to use different AI providers for specific profiles, you can easily add and enable an additional provider at any time.
Set the usage limit for AI Enterprise.
Click Apply.
After enabling AI Enterprise in your organization, you need to select and enable an AI provider for relevant profiles. Until then, developers won't have access to AI features and the AI Assistant plugin.
Make sure developers are connected to IDE Services Server through the Toolbox App, otherwise they won't be able to use the provisioned AI features.
Use the JetBrains AI service
By default, the AI features in JetBrains products are powered by the JetBrains AI service. This service transparently connects you to different large language models (LLMs) and enables specific AI-powered features within JetBrains products. It's driven by OpenAI and Google as the primary third-party providers, as well as several proprietary JetBrains models. JetBrains AI is deployed as a cloud solution on the JetBrains' side and does not require any additional configuration from your side.
Add AI provider: JetBrains AI
Use your own AI provider
AI Enterprise works with Google Vertex AI, Amazon Bedrock, and selected presets powered by OpenAI. You can also connect to the on-premises LLMs using Hugging Face.
OpenAI Platform
Before starting, make sure to set up your OpenAI Platform account and get an API key for authentication. For more information, refer to the OpenAI documentation.
Add AI provider: OpenAI Platform
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
Click Add provider and choose from the menu.
In the OpenAI dialog, specify the following details:
Select OpenAI Platform from the Preset list.
Provide an endpoint for communicating with the OpenAI service. For example,
https://api.openai.com/v1.Provide your API key to authenticate to the OpenAI API. For more details, refer to the OpenAI documentation.
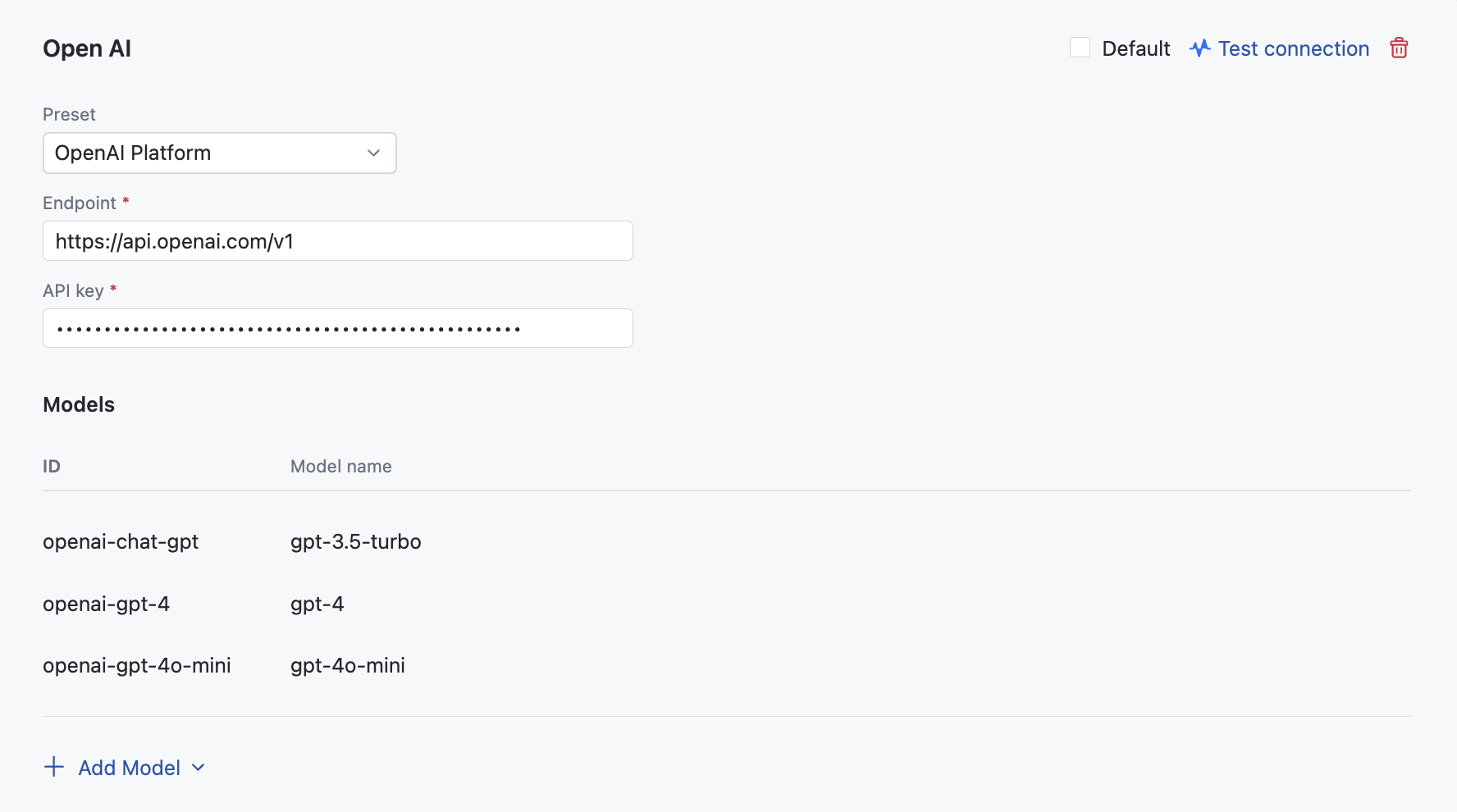
(Optional) AI Enterprise uses the GPT-3.5-Turbo, GPT-4, and GPT-4o mini models for AI-powered features within JetBrains products. However, if you have the GPT-4o model available on your account, we recommend adding it to the list by clicking Add model.
Click .
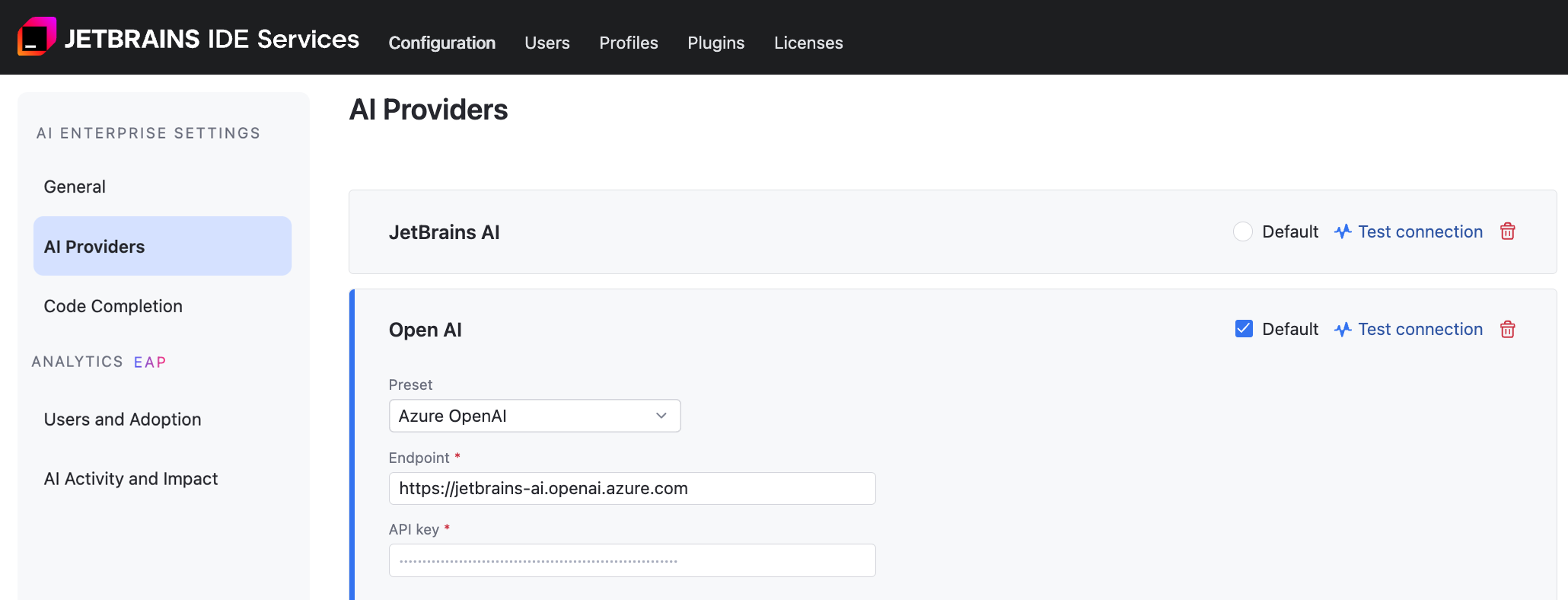
Azure OpenAI
Before enabling Azure OpenAI as your provider, you need to complete the following steps:
Deploy the required models: GPT-3.5-Turbo, GPT-4.
Obtain the endpoint and API key. Navigate to
Obtain the deployment names of your models. You can find them at
Once you have completed the above preparation steps, you can enable Azure OpenAI in your IDE Services.
Add AI provider: Azure OpenAI
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
In the OpenAI dialog, specify the following details:
Select Azure OpenAI from the Preset list.
Provide an endpoint for communicating with the Azure OpenAI service. For example,
https://YOUR_RESOURCE_NAME.openai.azure.com.Provide your API key to authenticate to the Azure OpenAI API.
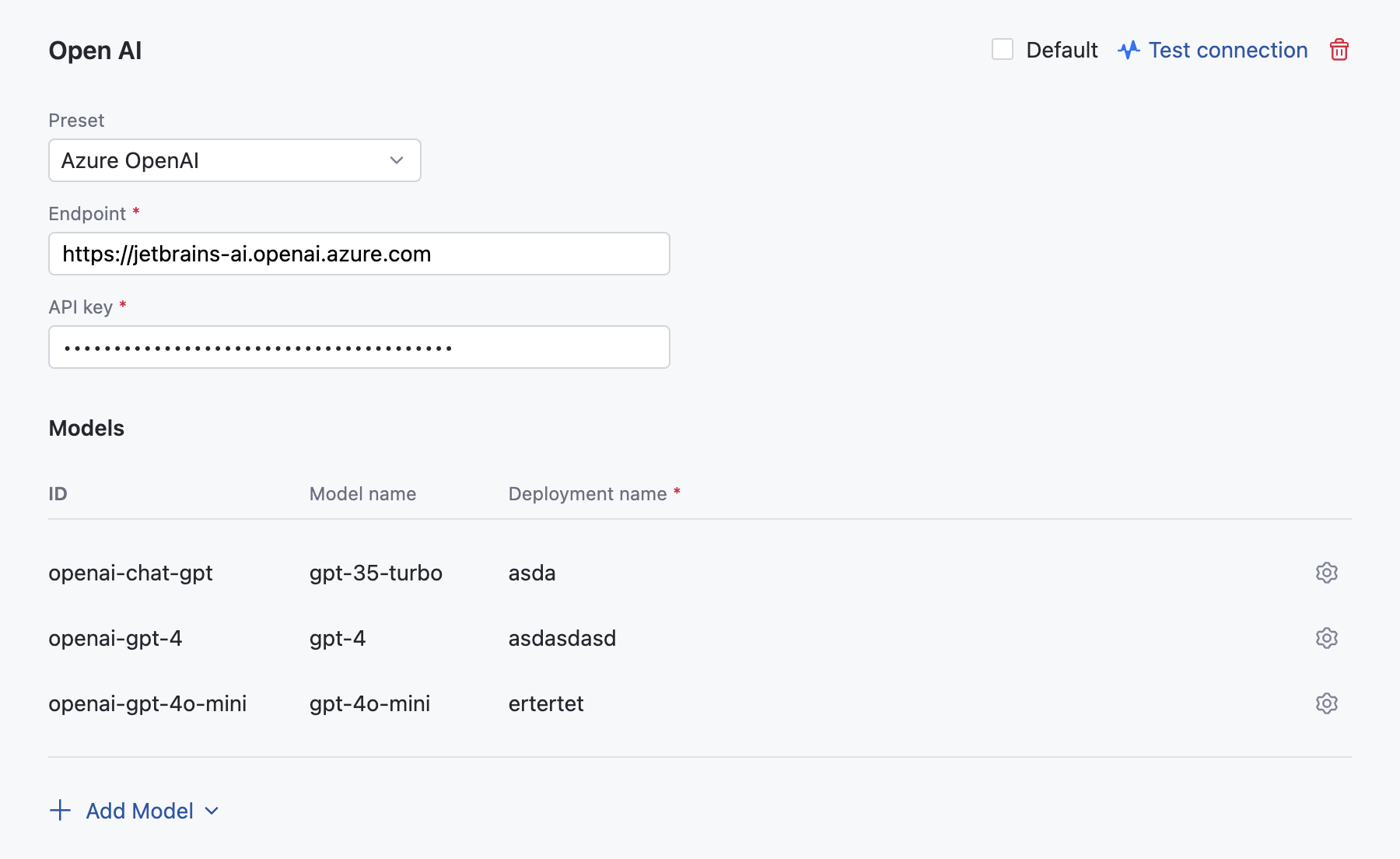
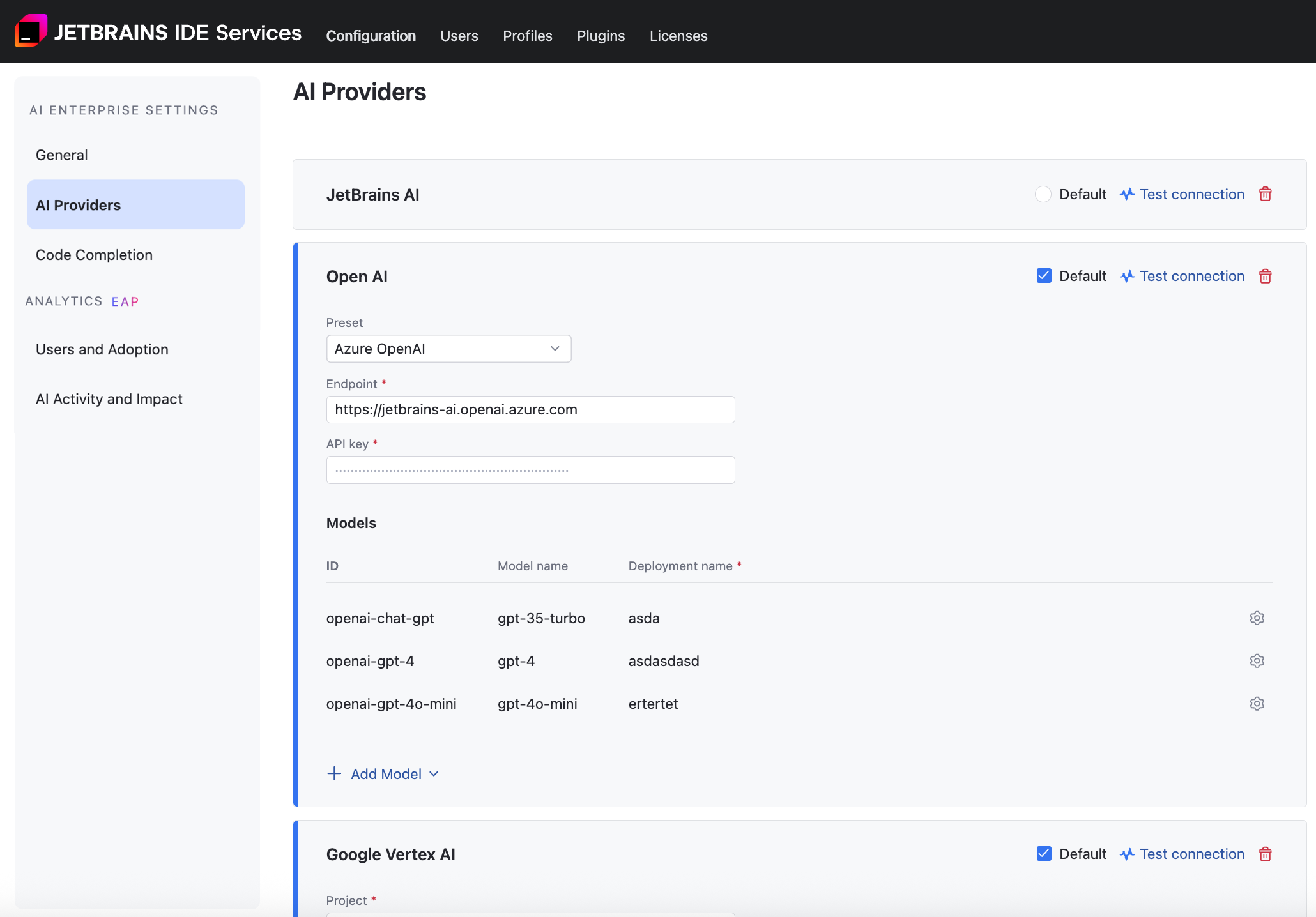
Specify the deployment names of your models. Click the gear icon next to each model to enter its name.
(Optional) AI Enterprise uses the GPT-3.5-Turbo, GPT-4, and GPT-4o mini models for AI-powered features within JetBrains products. However, if you have the GPT-4o model available on your account, we recommend adding it to the list by clicking Add model.
Click .
Google Vertex AI
Before enabling Google Vertex AI as your provider, you need to complete the following steps:
Once you have completed the above preparation steps, you can enable Google Vertex AI in your IDE Services.
Add AI provider: Google Vertex AI
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
In the Google Vertex AI dialog, specify the following details:
In the Project field, specify the name of the Google Cloud project.
In the Region field, specify the Google Vertex AI region.
In the Token field, specify the service account key in the JSON format which you have created earlier.
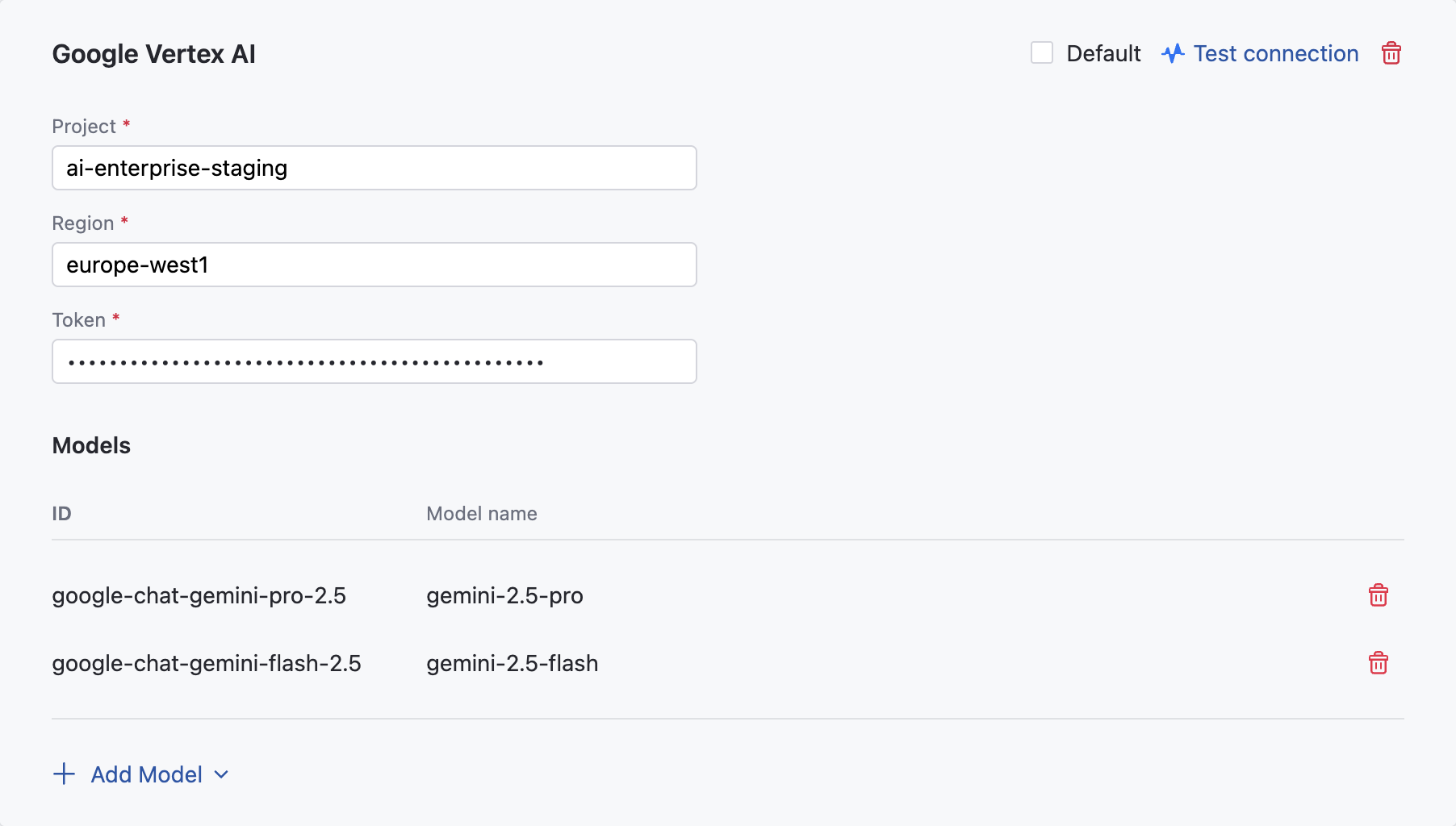
Click .
Amazon Bedrock
AI Enterprise provides an integration with Amazon Bedrock, a fully managed service that provides access to a variety of high-performing foundation models. In the current version, AI Enterprise supports the following LLMs for use in the AI Assistant: Claude 3.0 Haiku, Claude 3.5 Haiku, Claude 3.5 Sonnet V2, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, Claude 4 Sonnet, Claude 4.5 Haiku, and Claude 4.5 Sonnet.
Before adding Amazon Bedrock as an AI provider in IDE Services, you need to set up authentication and access to the supported models.
Step 1. Configure authentication on the AWS side
You can choose one of the following authentication options supported by IDE Services:
Access Keys
Follow the Getting Started instructions to:
Create an AWS account (if you don't already have one).
Create an AWS Identity and Access Management role with the necessary permissions for Amazon Bedrock.
Request access to the foundation models (FM) that you want to use.
Access AWS IAM Identity Center, find your user, and review the Permissions policies section.
In addition to the default permission policy
AmazonBedrockReadOnly, add a new inline policy for the Bedrock service.Configure the new inline policy to have the Read access level for the InvokeModel and InvokeModelWithResponseStream actions.
Generate an access key for your user.
When creating an access key, specify Third-party service as a use case.
You'll need to provide the access key ID and secret when you configure Amazon Bedrock in IDE Services. Make sure to save these values.
IAM Role
Here is how to set up AWS IAM Role for Amazon Bedrock:
Navigate to the IAM service in your AWS Console.
Create Permissions Policy.
Go to . Choose the JSON tab, paste the below permissions policy and click Next. Name it (e.g., "JetBrains-Bedrock-Policy") and create the policy.
Permissions Policy:
{ "Version" : "2012-10-17", "Statement" : [ { "Effect" : "Allow", "Action" : [ "bedrock:InvokeModel", "bedrock:InvokeModelWithResponseStream", "bedrock:ListFoundationModels", "bedrock:GetFoundationModel" ], "Resource" : "*" } ] }Create IAM Role
Navigate to .
Configure Trust Policy
Select Custom trust policy and paste the below trust policy JSON. Click Next
Trust Policy:
{ "Version" : "2012-10-17", "Statement" : [ { "Effect" : "Allow", "Principal" : { "AWS" : "arn:aws:iam::205930650357:role/aws-env-iam-testing-role" }, "Action" : "sts:AssumeRole", "Condition" : { "StringEquals" : { "sts:ExternalId" : "B8983A86714F2468CF7FD95329FF9D61" } } } ] }Attach Permissions
Search for the policy you created in Step 2, select it, and click Next.
Name and Create Role
Give your role a descriptive name (e.g., JetBrains-Bedrock-Access), optionally add tags, and click Create role.
Copy Role ARN
After creation, click on the role name to view details. Copy the Role ARN and paste it in the Role ARN field in the AI provider configuration form in IDE Services.
Default Credentials
Default Credentials is an authentication method that relies on the AWS SDK Default Credential Provider Chain to automatically locate and load AWS credentials from supported sources. This enables applications — including the JetBrains IDE Services integration with Amazon Bedrock — to authenticate to AWS services without manually supplying static credentials.
The provider chain searches for credentials in the following order:
Web identity token (OIDC) — for example, a Kubernetes service‑account token used to assume an IAM role via STS
AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity. More details.Environment variables —
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, and optionallyAWS_SESSION_TOKEN. More details.Container credentials — credentials provided by the container engine (ECS/EKS) for tasks or pods assigned an IAM role. More details.
Instance profile / EC2 metadata service — credentials obtained via the EC2 instance metadata service for an IAM role attached to the instance. More details.
Using this provider chain allows IDE Services to transparently pick up AWS credentials from the running environment, aligning with AWS best practices for credential handling and security.
Set Up Default Credentials Authentication. To enable the Default Credentials authentication method for Amazon Bedrock in IDE Services AI Enterprise, administrators must configure AWS credential sources. Two supported options are described below.
Option 1: IRSA (Recommended for EKS)
When IDE Services runs on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), the recommended approach is to use Kubernetes ServiceAccounts combined with IAM Roles for Service Accounts (IRSA) for secure credential handling. AWS documentation
Create an OIDC provider for your EKS cluster (one‑time setup):
eksctl utils associate-iam-oidc-provider --cluster <cluster‑name> --approveThis step associates the cluster’s OIDC provider. AWS Guide: Create an IAM OIDC provider
Create an IAM role with a trust policy allowing
sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentityfor the ServiceAccount.Annotate the Kubernetes ServiceAccount with the IAM role ARN:
metadata: name: <service-account-name> namespace: <namespace> annotations: eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:role/<ROLE_NAME>Configure IDE Services in your Helm values:
useS3AutoConfiguration: true featureFlags: bedrock-iam-role-auth: on bedrock-default-credentials: on
Option 2: Environment Variables (Non‑production / Testing)
If IRSA is not available in your environment, you may supply credentials via environment variables. This method is less secure and recommended only for development or testing.
Create AWS access keys in IAM with permissions to access Amazon Bedrock and S3.
Generate
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY, and optionallyAWS_SESSION_TOKEN.Create a Kubernetes secret to hold the keys:
kubectl create secret generic aws-credentials \ --from-literal=AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<your_access_key_id> \ --from-literal=AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<your_secret_access_key>Inject environment variables into the IDE Services deployment (via Helm or manifests) to expose the keys to the container environment.
Configure IDE Services:
useS3AutoConfiguration: true featureFlags: bedrock-default-credentials: on
Important: While this method works for testing, it does not provide credential rotation, least‑privilege enforcement, or audit benefits that IRSA offers. Use it with caution.
Step 2. Configure access to models on AWS side
Follow the AWS instructions to request access to the following supported models:
Claude 3.0 Haiku
Claude 3.5 Haiku
Claude 3.5 Sonnet V2
Claude 3.7 Sonnet
Claude 4 Sonnet
Claude 4.5 Haiku
Claude 4.5 Sonnet
Step 3. Add AI provider: Amazon Bedrock
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
Click Add AI Provider and choose Amazon Bedrock.
The Amazon Bedrock configuration dialog will appear.
In the Region field, specify the AWS region that supports Amazon Bedrock.
Use cross-Region inference. This option automatically chooses the most suitable AWS Region within your geographic area to handle user requests. This enhances the experience by optimizing resource utilization and ensuring high model availability. (Required for Claude 3.7 Sonnet model)
Choose the authentication option you have set up on the AWS side:
Default Credential - no additional input required if configured on the AWS side.
IAM Role - enter the role ARN you have created on the AWS side.
Access key - specify the access key ID and the access key secret.
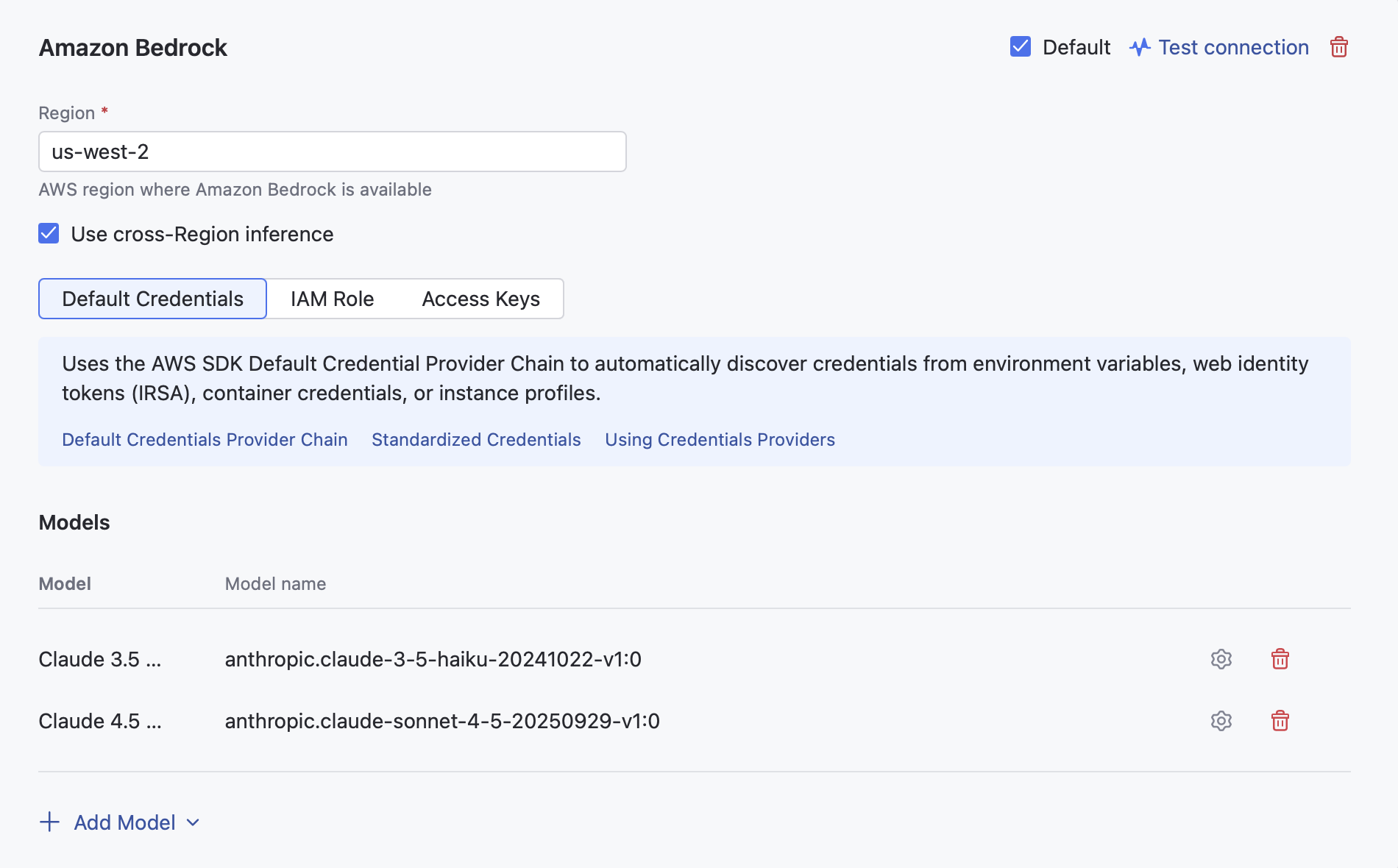
Click Add Model and choose the model you want to use from the list.
In the configuration dialog, specify the model name and click .
Save your settings.
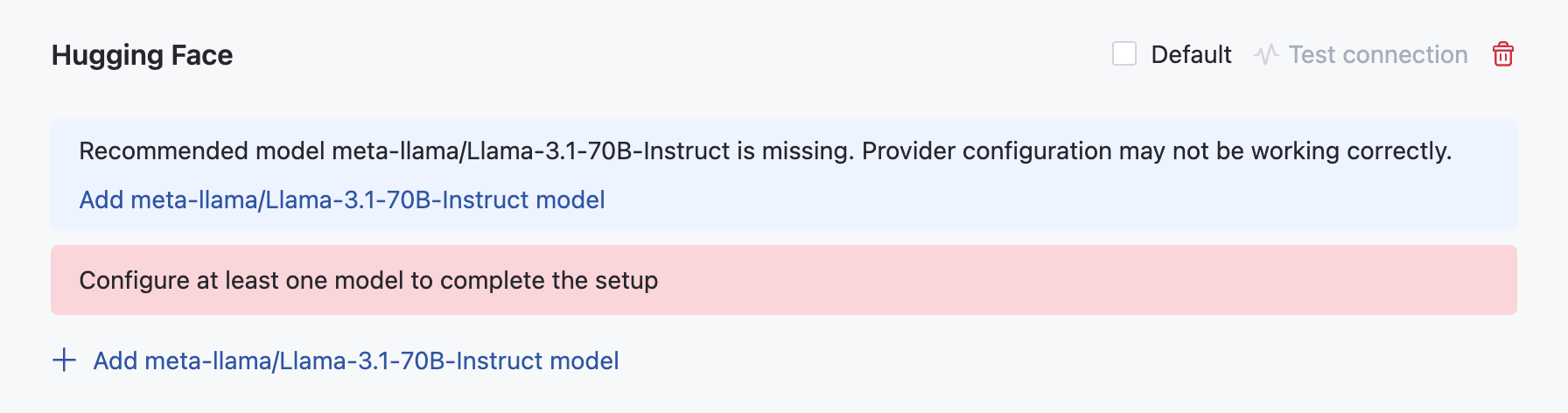
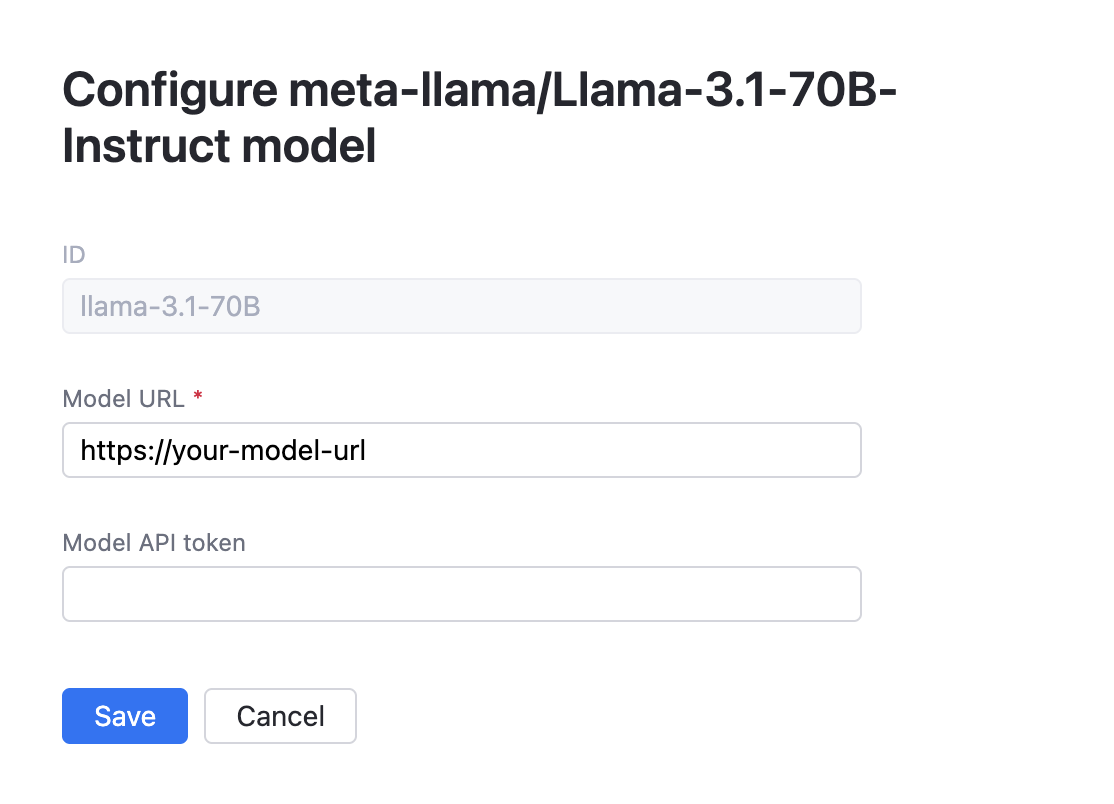
Hugging Face
AI Enterprise allows you to use on-premises models, such as Llama 3.1 Instruct 70B powered by Hugging Face, for air-gapped operations.
For deploying and serving Llama 3.1 Instruct 70B, use the instructions provided in the official Hugging Face documentation. Refer to this section to learn about model-specific requirements.
Add AI provider: Hugging Face
OpenAI Compatible
AI Enterprise supports integration with AI routers such as OpenRouter and LM Studio, allowing you to access a wide range of models from various pre-approved providers.
This setup enables you to use well-known, high-performing models like Claude and GPT, as well as custom models that may not be available otherwise. For example, you can select custom models such as Grok and DeepSeek for use in AI Assistant Chat.
You can operate AI Enterprise in an isolated environment by connecting to an OpenAI compatible server deployed on-premises, such as llama.cpp, vLLM, LMStudio.
Add AI provider: OpenAI Compatible
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
In the OpenAI Compatible dialog, specify the following details:
Specify an endpoint for communicating with your AI router service. For example
https://openrouter.ai/api/v1Provide your Bearer token to authenticate with your AI router service. If your service requires a custom header for authentication, obtain and provide header Name and Value in the corresponding fields.
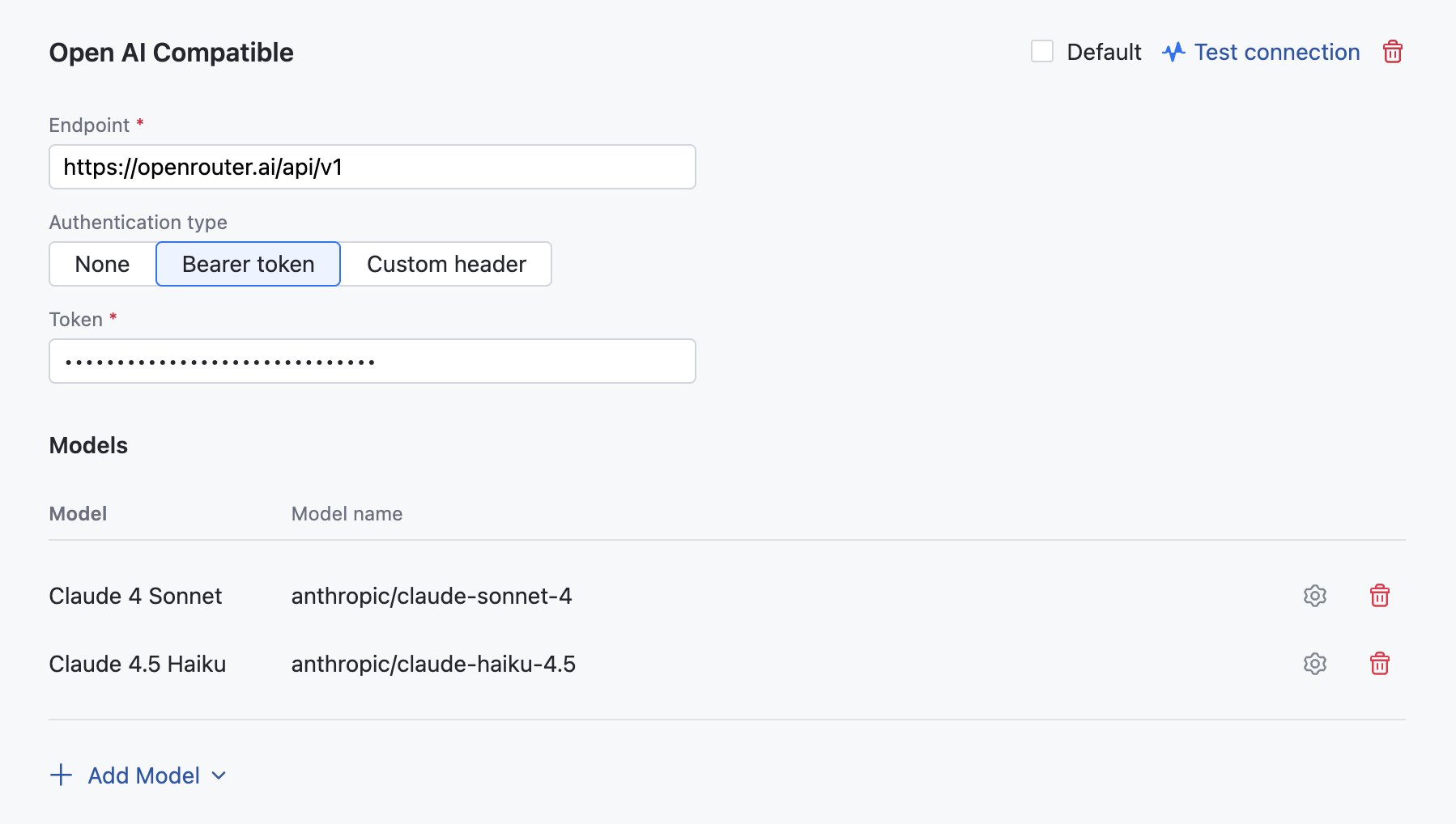
Click Add Model and choose the model you want to use from the list.
If the model you are adding doesn't support Tools calling, Functions calling or Multimedia messages, uncheck these options.
If adding a custom model:
In the Configure ... model dialog, choose the model name that matches your initial selection.
Set Max input/output tokens. Custom models require specifying input and output context lengths — the maximum tokens a model can handle per request. Tools like AI Assistant and Junie use these values to decide how much data to include as context. Set them according to the limits defined by the provider or model documentation. The input limit is especially important, since it determines how tools select and trim files or history for processing.
Please note that performance of custom models cannot be guaranteed.
Click Save.
Repeat these steps for additional models.
Click .
Junie coding agent
JetBrains Junie is an AI-powered coding agent designed to work directly within supported JetBrains IntelliJ IDEA-based IDEs and is available as a plugin.
Unlike traditional code assistants, Junie can autonomously perform tasks such as generating code, running tests, fixing errors, and adapting to project-specific guidelines—all while keeping the developer in control. It understands project context, supports collaborative workflows, and aims to enhance both productivity and code quality.
Junie can be powered by large language models (LLMs) provided by the JetBrains AI service, or, as an alternative, it can use a specific set of models available through OpenAI and Amazon Bedrock.
Enable Junie
If you have JetBrains AI service enabled, no further configuration of AI Enterprise settings are required. To make Junie available to developers, proceed to enable it in selected profiles.
If JetBrains AI service is not enabled, you should select Azure OpenAI, Open AI Platform, or Amazon Bedrock as your provider and configure as follows:
On your dashboard (home page), locate the AI Enterprise widget and click Settings.
Enable and configure either of the following AI providers:
Add the following models to the configuration:
GPT-4o
GPT-4o-Mini or GPT-4.1-Mini
GPT-4.1
GPT-5 or GPT-5.2
Add the following models to the configuration:
GPT-4o
GPT-4o-Mini or GPT-4.1-Mini
GPT-4.1
GPT-5 or GPT-5.2
Add the following models to the configuration:
Claude 4.5 Sonnet
Claude 4.5 Haiku or Claude 3.5 Haiku or Claude 3.0 Haiku
Select Use cross-Region inference.
To make Junie available to developers, proceed to enable it in selected profiles.
AI Enterprise Settings
Enable additional AI providers
When enabling AI Enterprise for your organization, you get to choose only one AI provider. To enable an additional provider:
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
Click Add provider and choose one from the menu.

If you're adding a Google Vertex, OpenAI, or AWS Bedrock provider, refer to the specific configuration instructions for further steps.
Click Save.
Test connection to AI provider
If AI models stop responding, test the connection. The problem could be related to authentication, such as an expired token, or configuration changes on the AI provider's end. A failed connection test returns an error with a description to help you identify and fix the issue.
You can also check the connection when adding an AI provider to make sure your configuration is correct and that the API key or token you entered is valid.
To test the connection:
Set default AI providers
If you have more than one AI provider enabled for your organization, the providers you set as default will be preselected when you enable AI Enterprise in profiles. Additionally, it allows you to centrally switch providers for all profiles that have the Default provider option currently selected.
You can set multiple default providers, except when JetBrains AI is selected — in that case, it must be the only default provider.
To choose default providers:
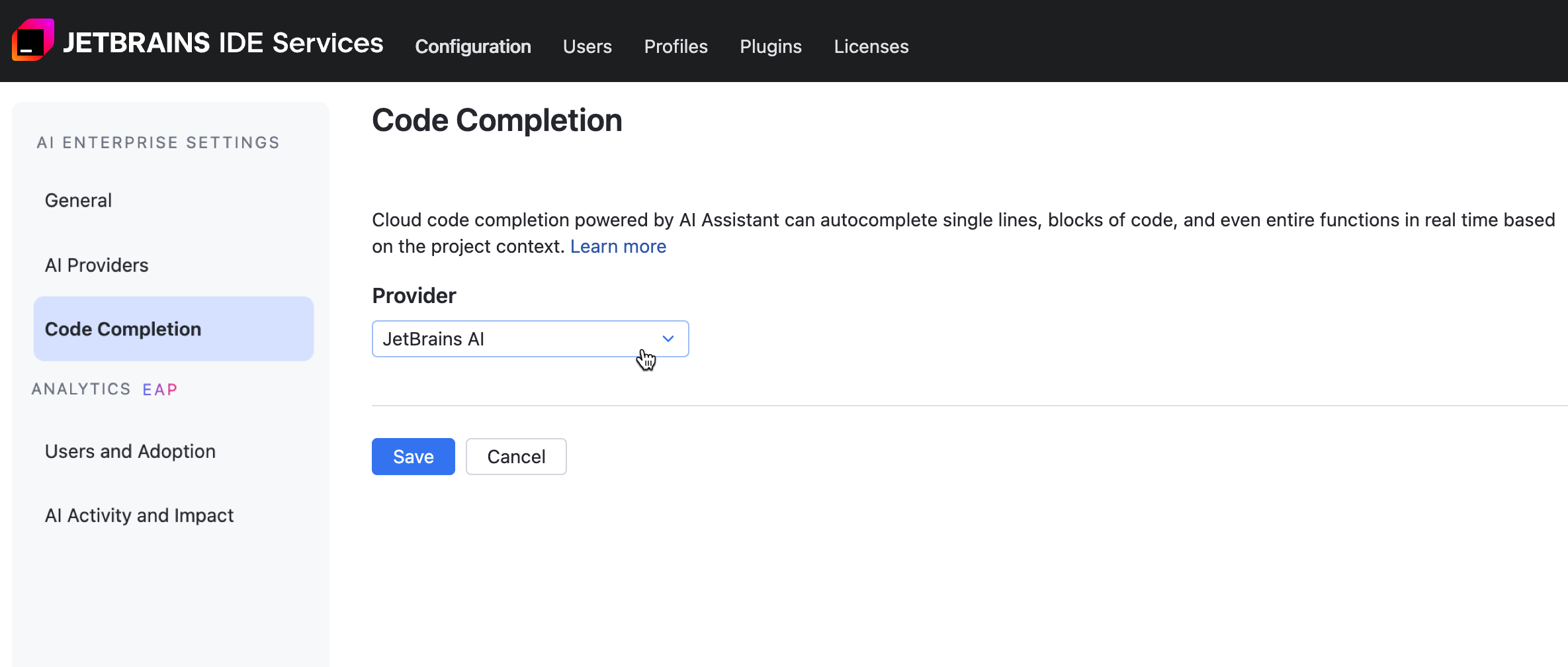
Set the Code Completion provider
The Mellum engine powers code completion in AI Enterprise. You can configure whether to use a self-hosted Mellum instance, the JetBrains-hosted Mellum service (JetBrains AI), or let the system automatically select the most suitable provider from available options.
To set the Code Completion provider:
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
From the menu, select one of the following options:
: Automatically selects the most suitable provider from those which are available for the particular user. If JetBrains AI is available, it will be used.
: uses Mellum hosted by JetBrains.
: uses a Mellum engine installed on-premises.
Click Save.
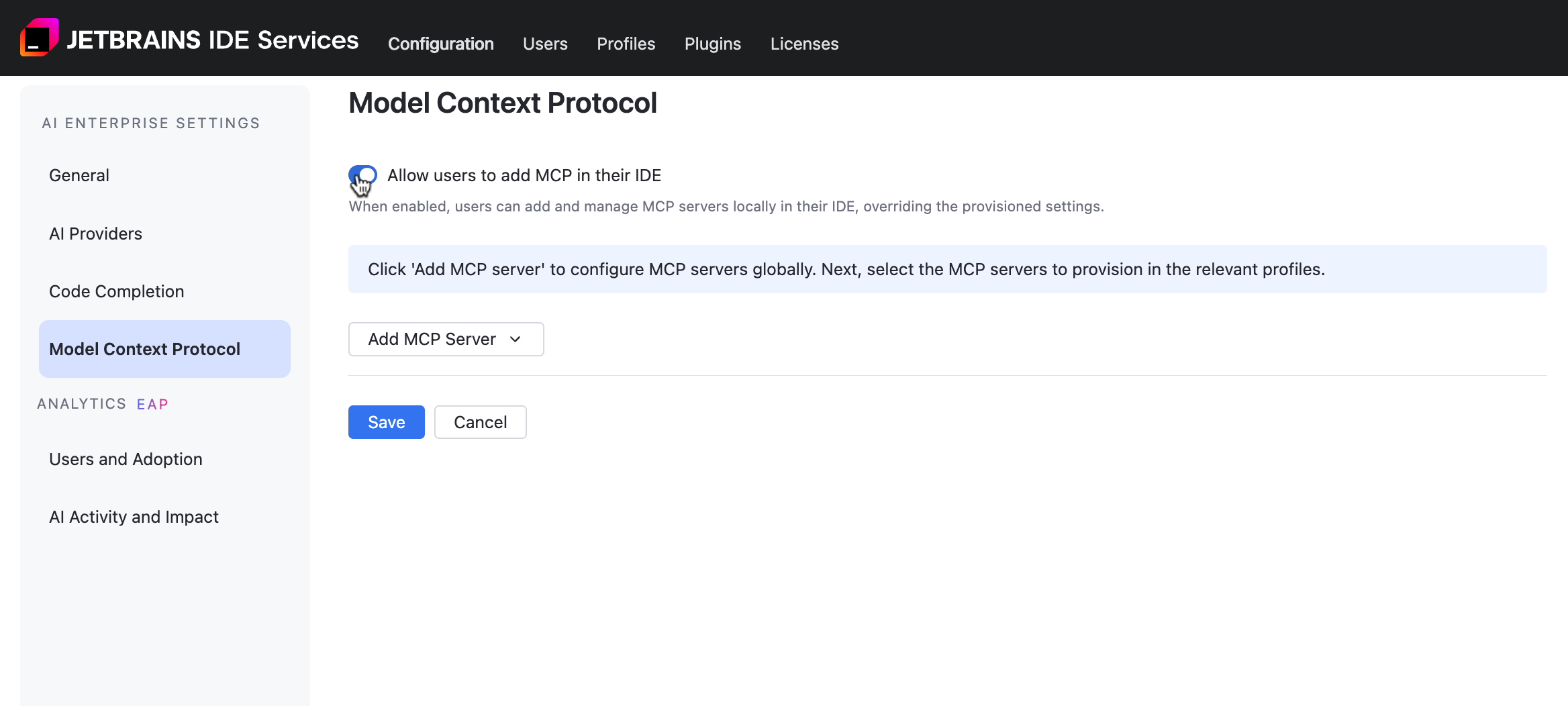
Model Context Protocol Settings
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a method that allows LLMs to interact with resources, systems, or data. You can configure command and remote MCP servers and define whether developers can add other ones.
Disable adding MCP servers in IDE by users
Add a Command MCP Server
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
Click and select from the menu.
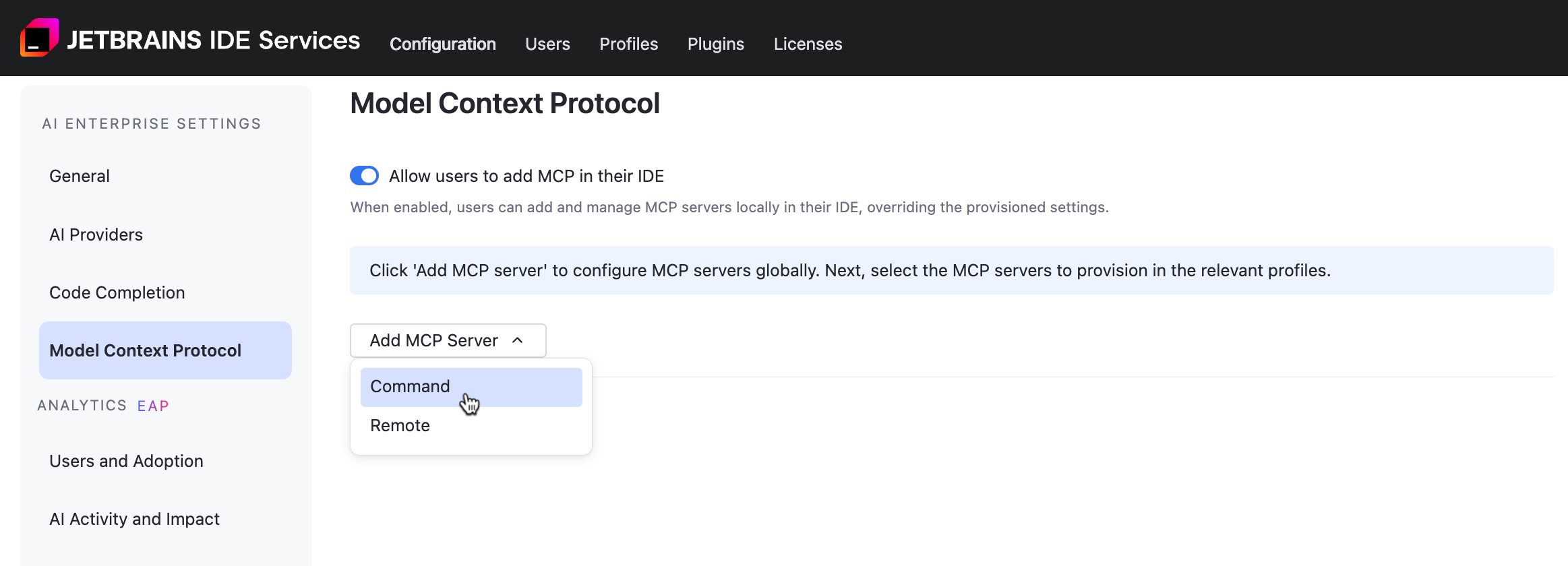
Enter the following details:
- specify a name for the MCP server.
- specify the command used to launch the MCP server.
(Optional) - specify additional parameters passed to the command at server startup.
(Optional) - specify variables the server may need (API keys or configuration settings).
Click Save.
Add a Remote MCP Server
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Open the tab.
Click and select from the menu.
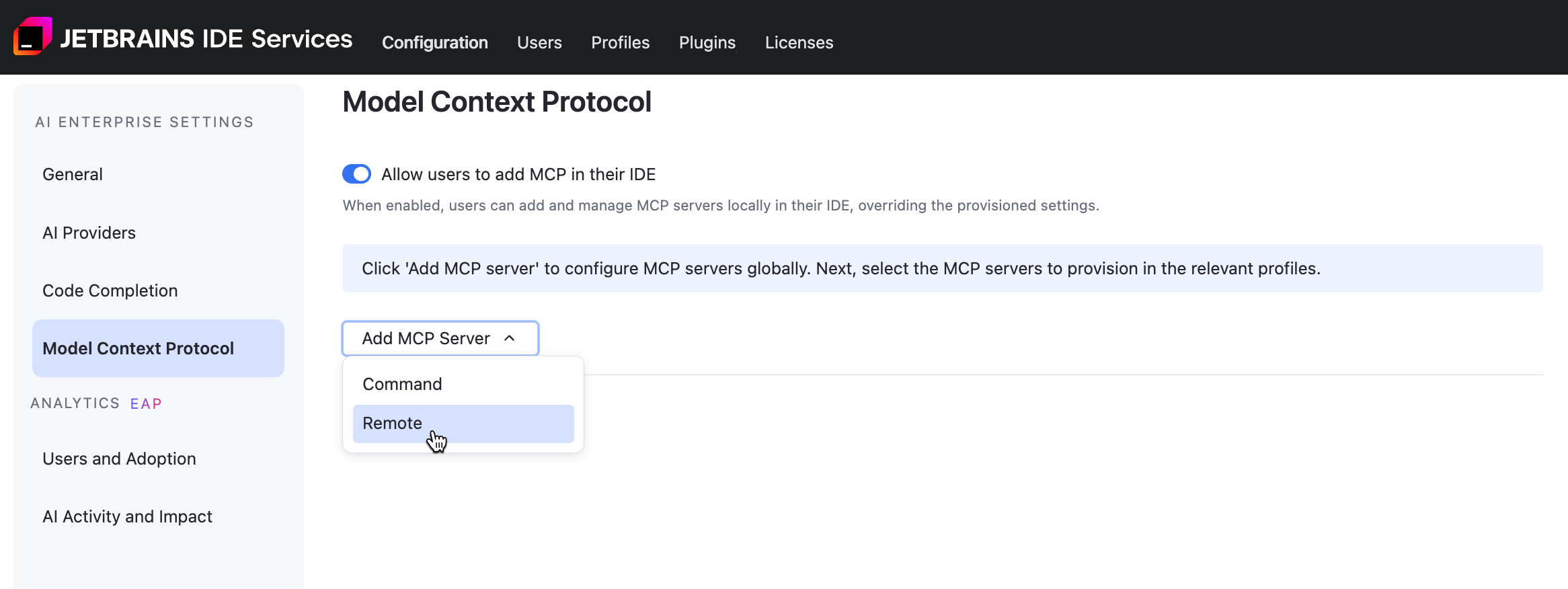
Enter the following details:
- specify a name for the MCP server.
- specify a URL for the MCP server.
(Optional) - specify authentication information (API keys or access tokens) that the server uses to validate and authorize the request.
Click Save.
Update the AI Enterprise usage limit
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
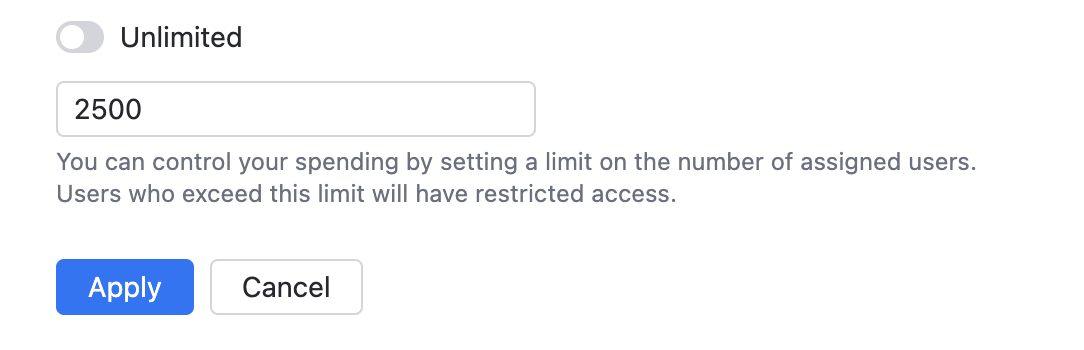
On the AI Enterprise Settings page, configure the usage limit for AI Enterprise:
Enable the Unlimited number of users option to let all users with AI Enterprise enabled on the profile level gain access to the AI features.
Disable the Unlimited number of users option and specify the limit on the number of AI Enterprise users. Users above this limit will have restricted access to the product features.
Click Save.
Allow detailed data collection
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
In the General tab, use the Allow detailed data collection option to enable or disable detailed data collection in your organization. When you enable this option, users will be asked to grant permission for data sharing. Collecting AI interaction data helps improve LLM performance.
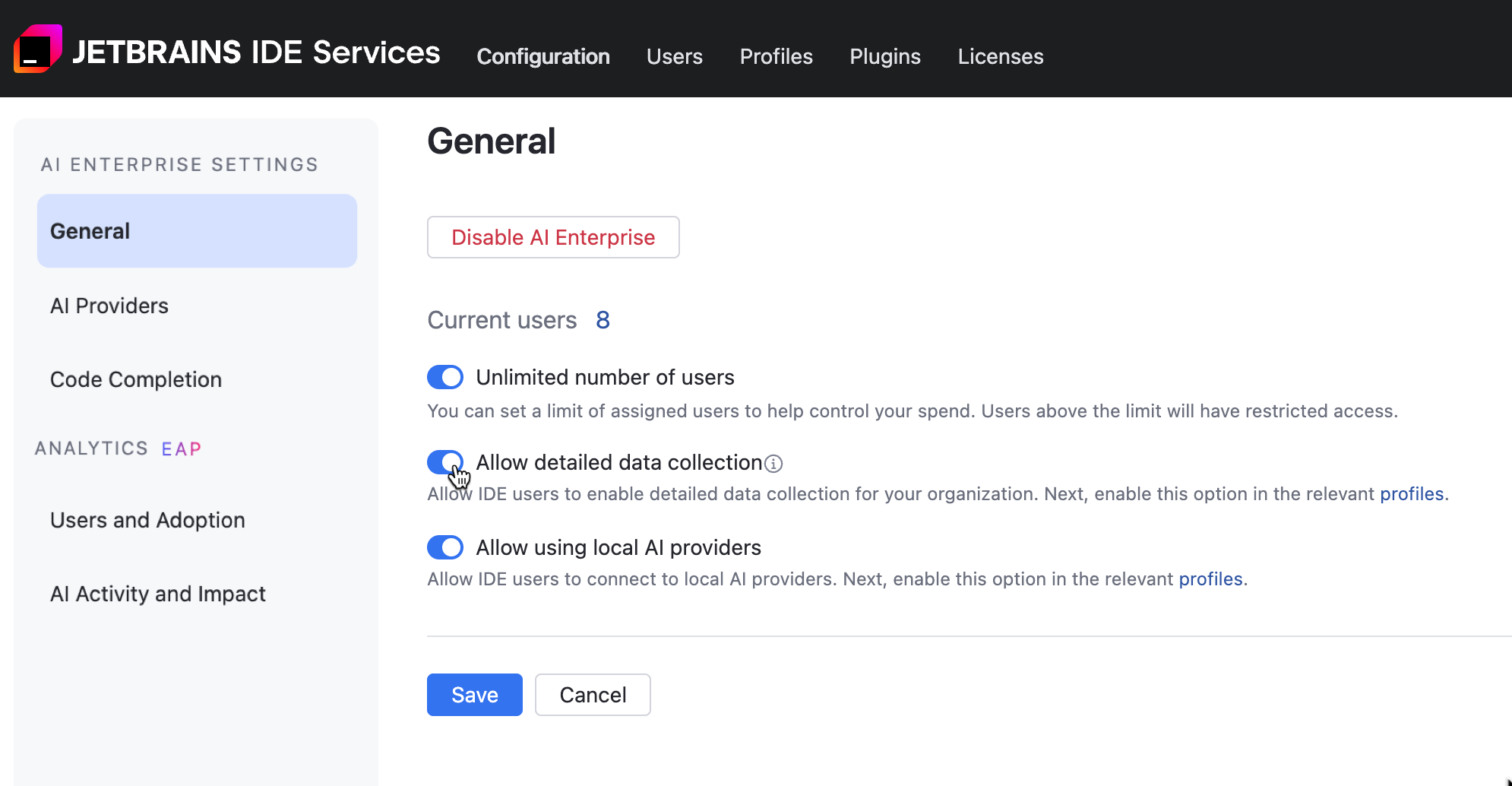
Click Save.
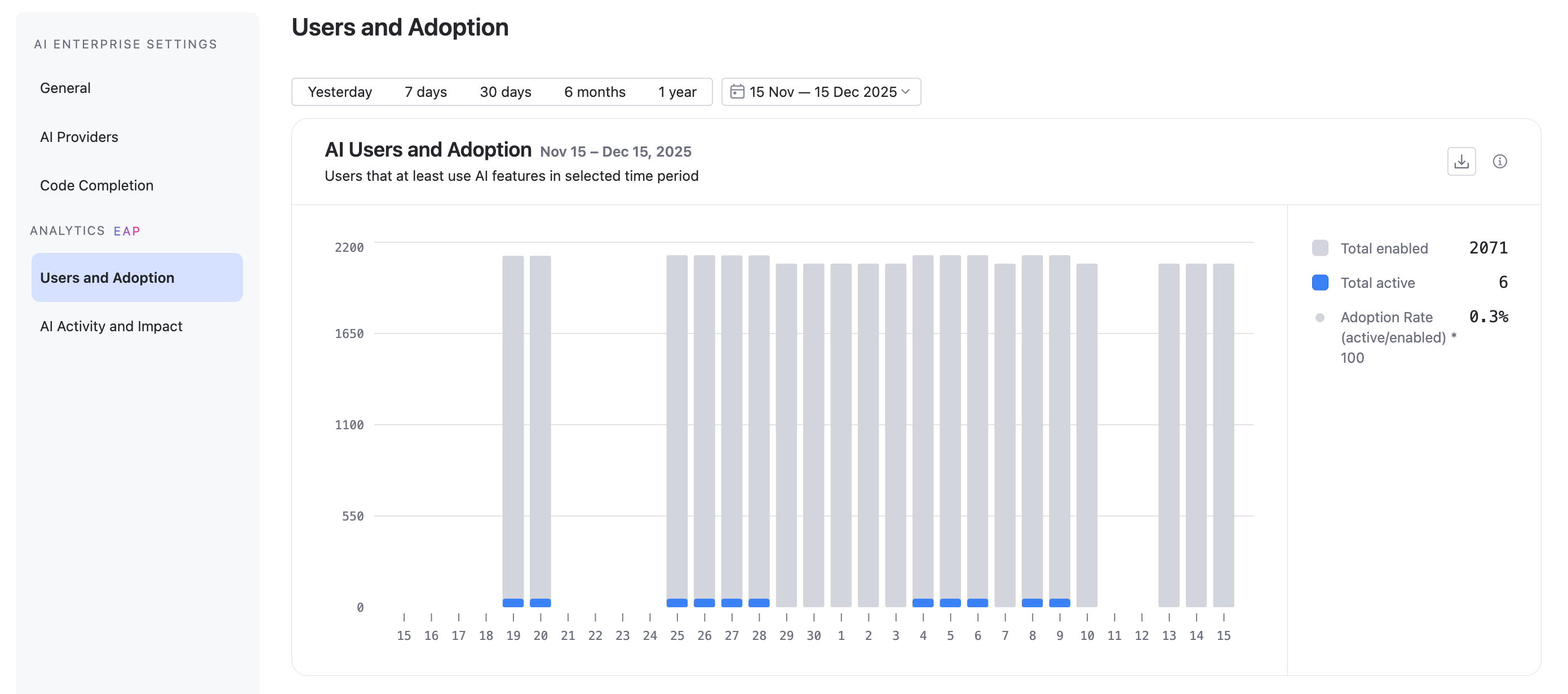
Get Analytics for your organization
Navigate to .
Scroll down to the AI Enterprise section and click Settings.
Navigate to the or tab.
For more information, refer to Users and Adoption and AI Activity and Impact topics.
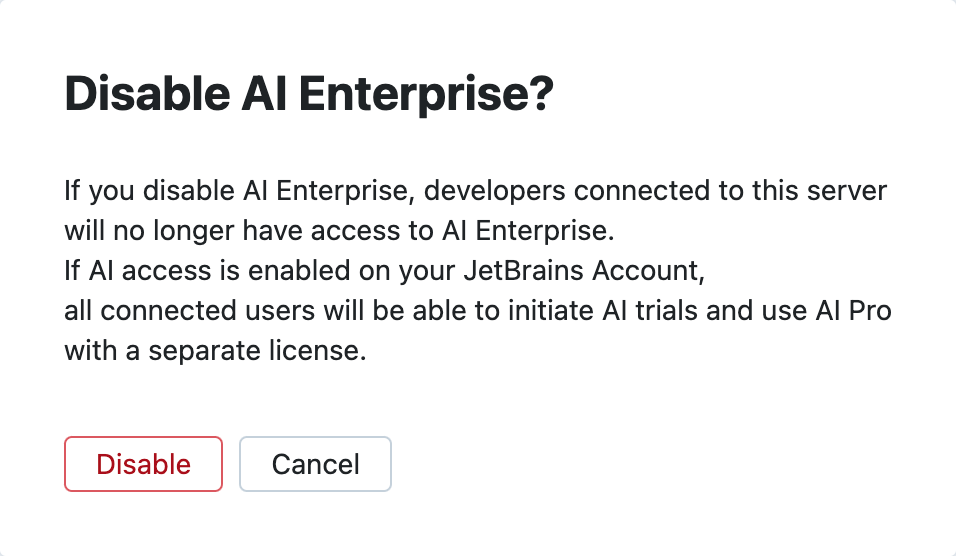
Disable AI Enterprise for your organization
Add more AI Enterprise users to your IDE Services
With the prepaid billing model, you can purchase more resources for your IDE Services license from your organization's JetBrains Account.
Log in to your JetBrains Account with the organization or team administrator permissions.
In the menu on the left, click your organization's name.
At the top of the page, click .
On the license overview page, select the Team Tools & Services tab.
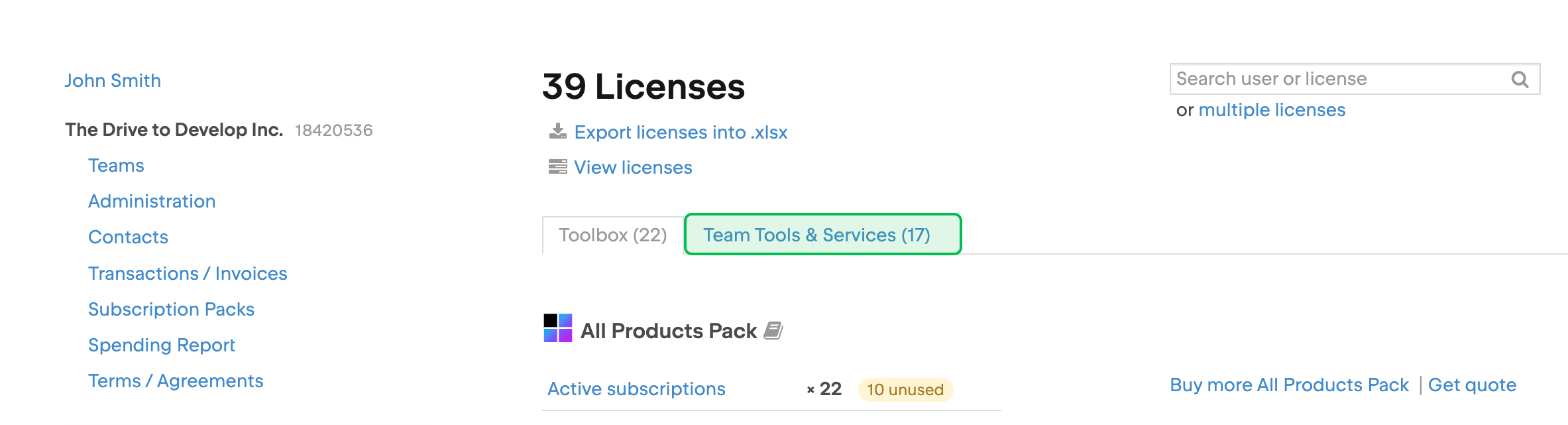
Locate the IDE Services license and click Add more resources. You may need to scroll down to find the license.
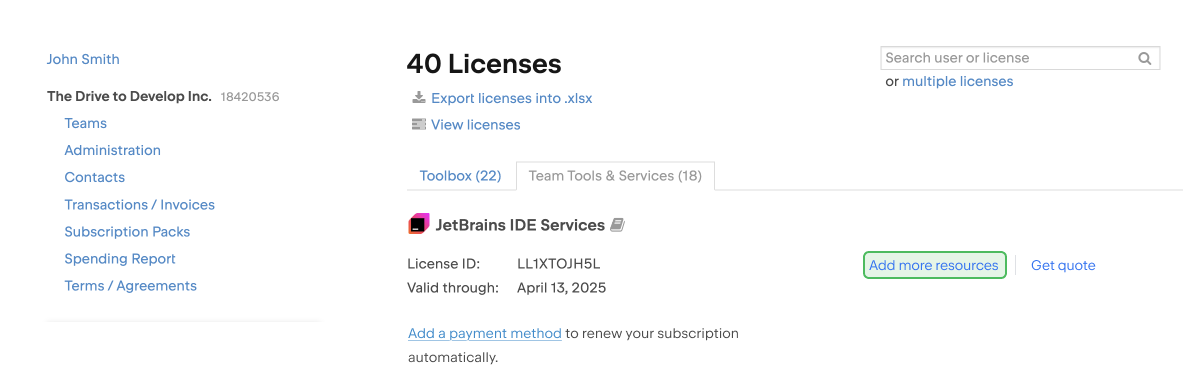
The checkout page will open. There you can select the resources you want to add and pay for them.