介绍 JavaScript 现代实践 本文将向您介绍 WebStorm 提供的编码辅助如何帮助您遵循现代 JavaScript 中的重要最佳做法,以编写更简洁、更易维护且性能更高的代码。
在处理旧代码库时,您可能会遇到过时的模式和做法。 WebStorm 通过高亮此类模式并建议快速修复来为您提供帮助。
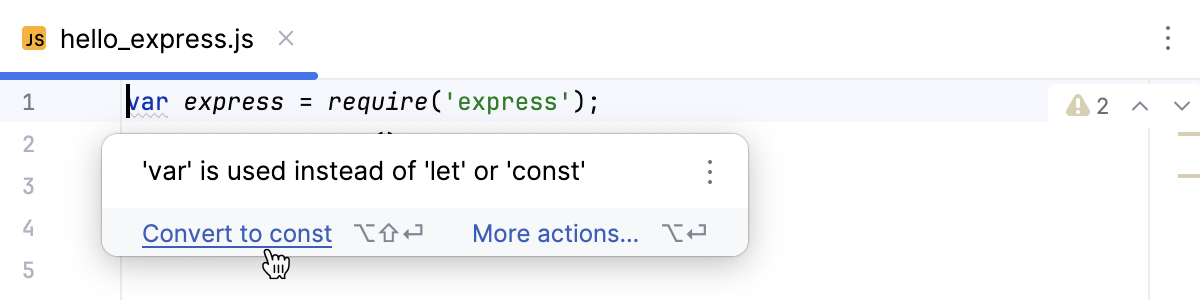
使用 let 和 const 声明变量 let 和 const 提供 块级作用域 ,这种作用域更具可预测性,可减少使用具有函数作用域的 var 声明变量时可能出现的意外错误。
尽管可以有意使用 var 声明,但在旧代码中这可能是旧方法的产物。
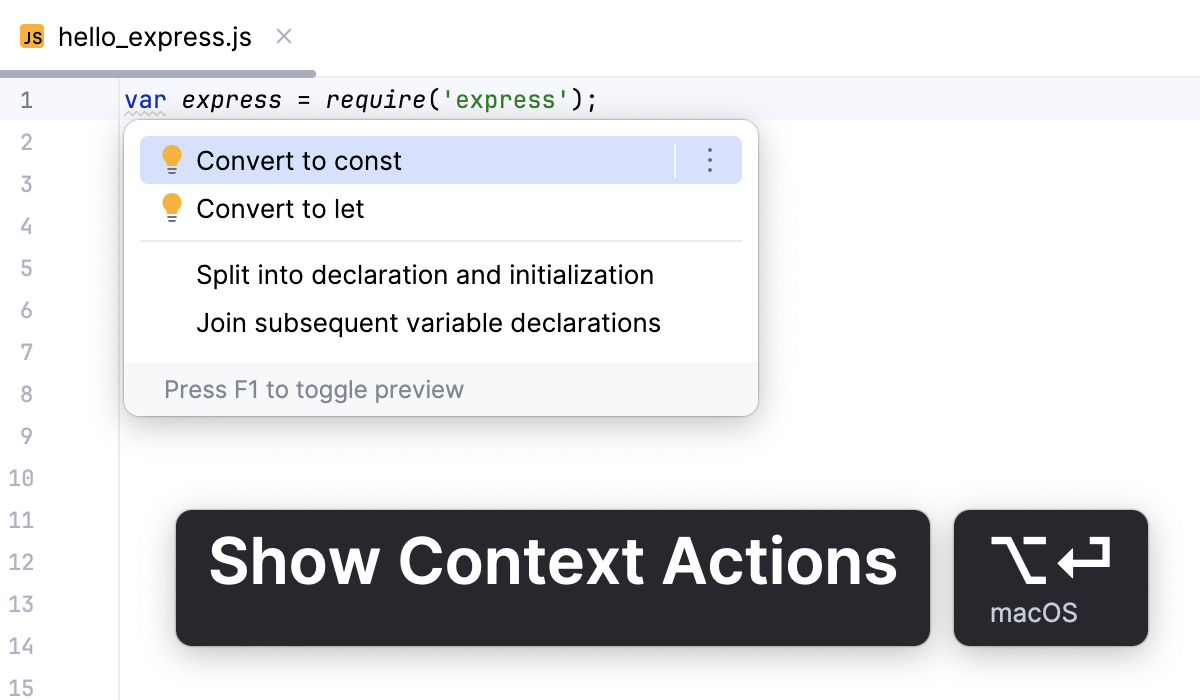
WebStorm 会检测 var 的使用,并建议将其替换为 let 或 const。
示例
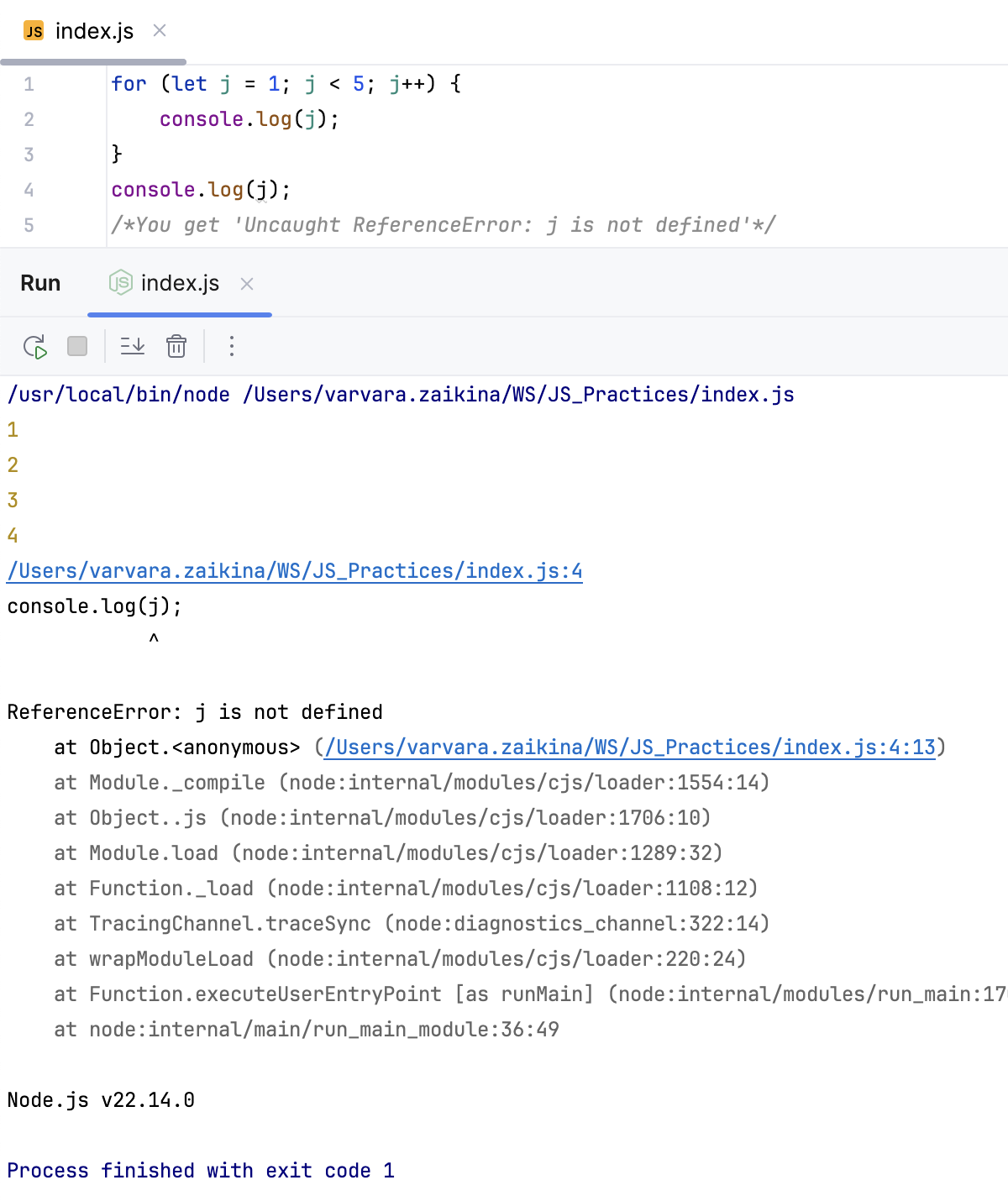
for (let j = 1; j < 5; j++) {
console.log(j);
}
console.log(j);
/*You get 'Uncaught ReferenceError: j is not defined'*/
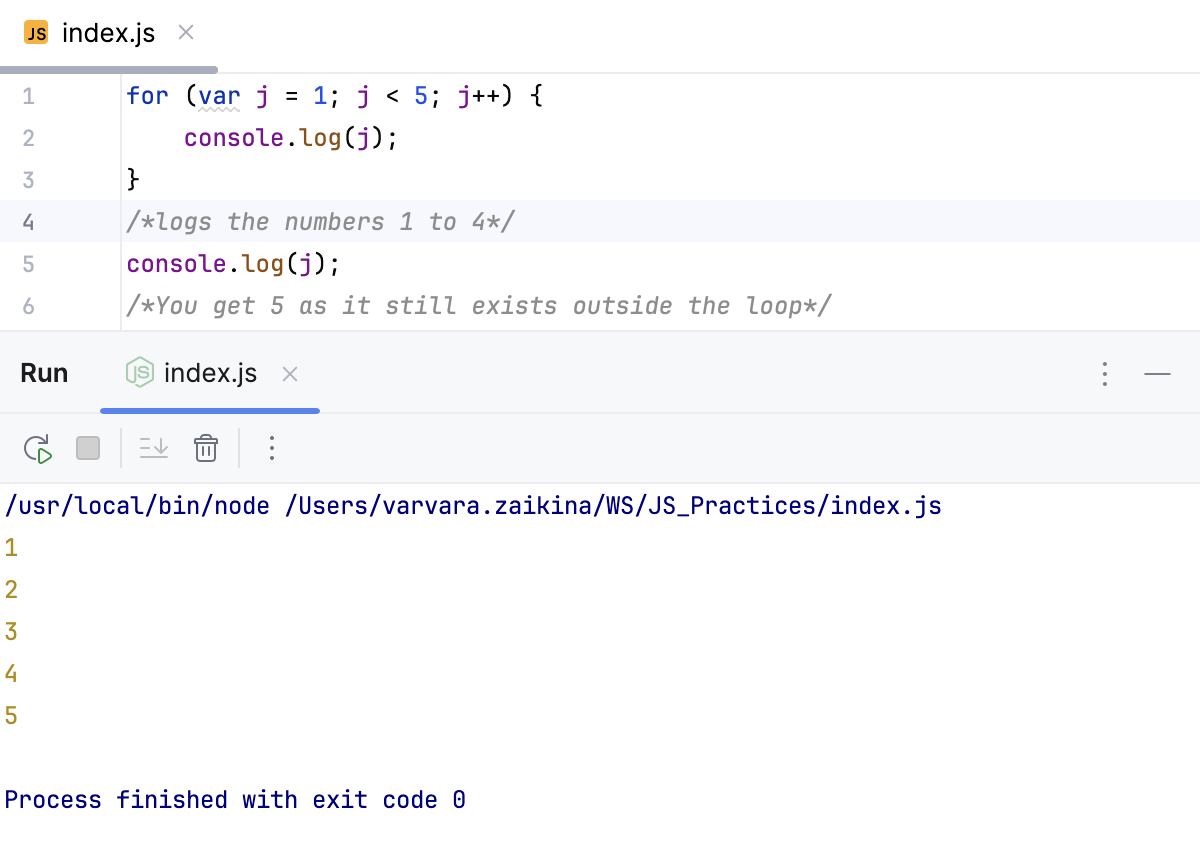
/*If we did this using var:*/
for (var j = 1; j < 5; j++) {
console.log(j);
}
/* logs the numbers 1 to 4*/
console.log(j);
/*You’d get 5 as it still exists outside the loop*/
使用类替代 Function:prototype 尽管在许多旧代码库中,您可能会遇到用于模拟类的 函数 prototype 方法 ,但建议使用 类 ,因为它们具有更简洁的语法。
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.getName = function () {
return this.name;
}
const p = new Person('A');
console.log(p.getName()); // 'A'
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
getName() {
return this.name;
}
}
const p = new Person('A');
console.log(p.getName()); // 'A'
WebStorm 提供一个重构建议,您可通过 转换为 class 上下文操作调用。
将文本光标放在要转换的函数名称上,然后按下 Alt+Enter 。
从列表中选择 转换为 class 。
在 重构预览 中,查看建议的更新内容,准备就绪后点击 重构 。
使用箭头函数表达式 箭头函数 提供更简洁的语法,并自动绑定 this 上下文,这在类方法中尤其有用,在这些方法中 this 容易丢失。
const numbers = [1, 2];
numbers.map(function (num) {
return num * 2;
});
const numbers = [1, 2];
numbers.map(num => num * 2);
借助 WebStorm,您可以使用专用上下文操作引入箭头函数。
将光标放在匿名函数内部并按下 Alt+Enter 。
从弹出列表中选择 转换为箭头函数 。
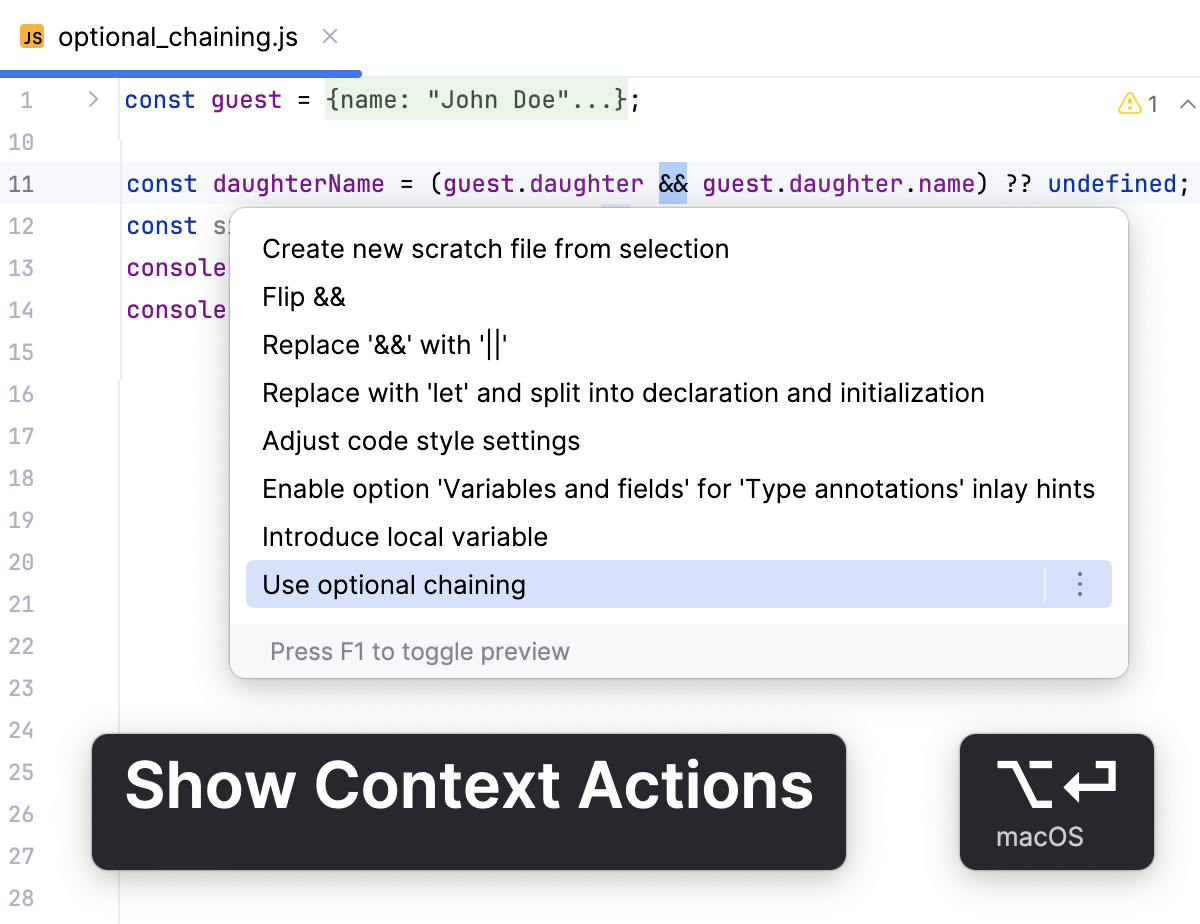
使用可选链 可选链 运算符 (?.) 会自动检查属性、数组元素或方法是否存在,然后再尝试访问它。 如果链中的任何部分为 null 或 undefined ,则返回 undefined ,而不是抛出错误。 如果不使用可选链,则此检查需要冗长且重复的代码。
const guest = {
name: "John Doe",
son: {
name: "Ben"
},
daughter: {
name: "Catherine"
}
};
const daughterName = (guest.daughter && guest.daughter.name) ?? undefined;
const sisterName = (guest.sister && guest.sister.name) ?? undefined;
console.log(daughterName);
console.log(sisterName);
const guest = {
name: "John Doe",
son: {
name: "Ben"
},
daughter: {
name: "Catherine"
}
};
const daughterName = (guest.daughter?.name) ?? undefined;
const sisterName = (guest.sister?.name) ?? undefined;
console.log(daughterName);
console.log(sisterName);
WebStorm 提供上下文操作以引入 ?. 运算符。
将文本光标放在要转换的表达式上,然后按下 Alt+Enter 。
从弹出列表中选择 使用可选链 。
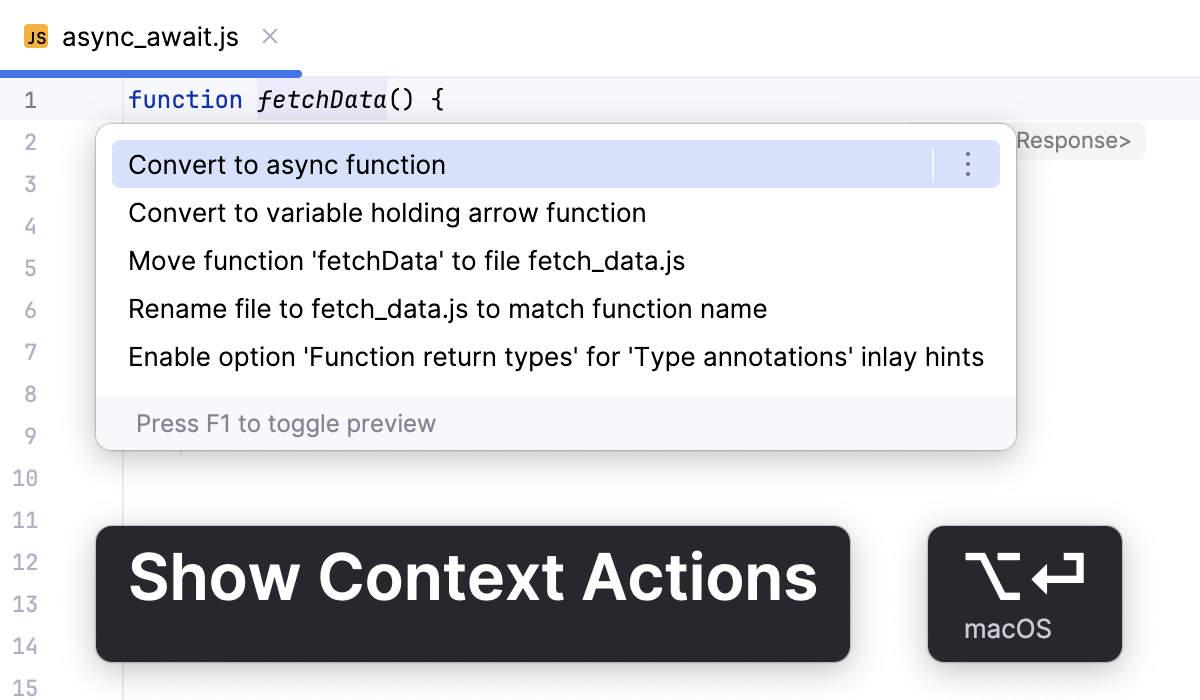
使用 async/await 语法 async/await 语法 通过消除对 .then() 和 .catch() 链式调用的需求,简化了异步操作的处理。 这使您的代码更易读、更易维护,也更容易理解,尤其是在处理多个异步调用时。
function fetchData() {
return fetch('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log(data);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
}
async function fetchData() {
try {
let response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/data');
let data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
借助 WebStorm,您可以通过 转换为异步函数 上下文操作将 async/await 语法引入代码中。
将光标放在要引入 async/await 语法的函数处并按下 Alt+Enter 。
从弹出列表中选择 转换为同步函数 。
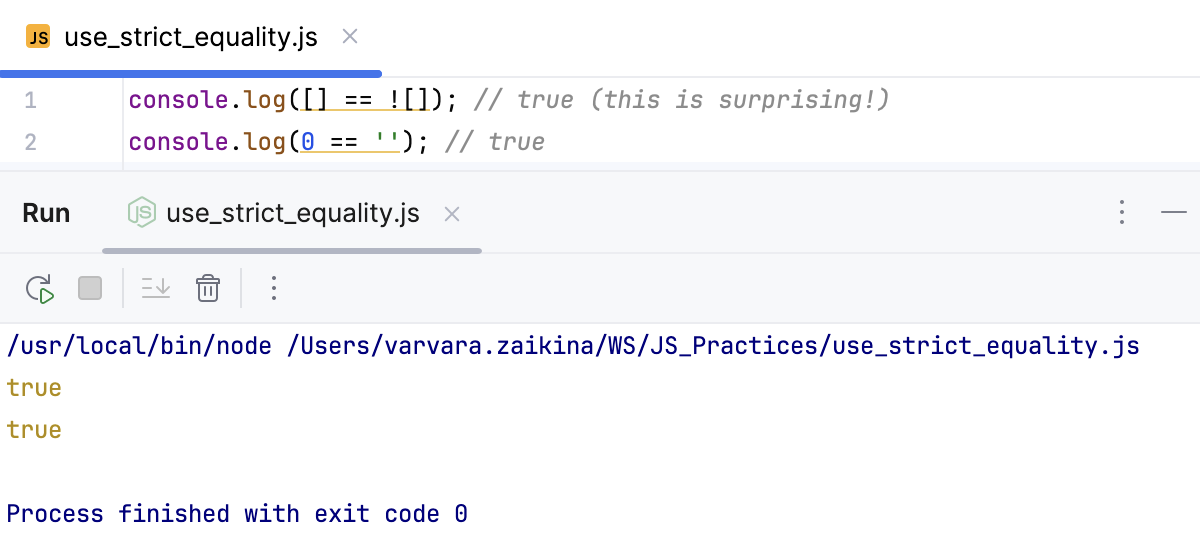
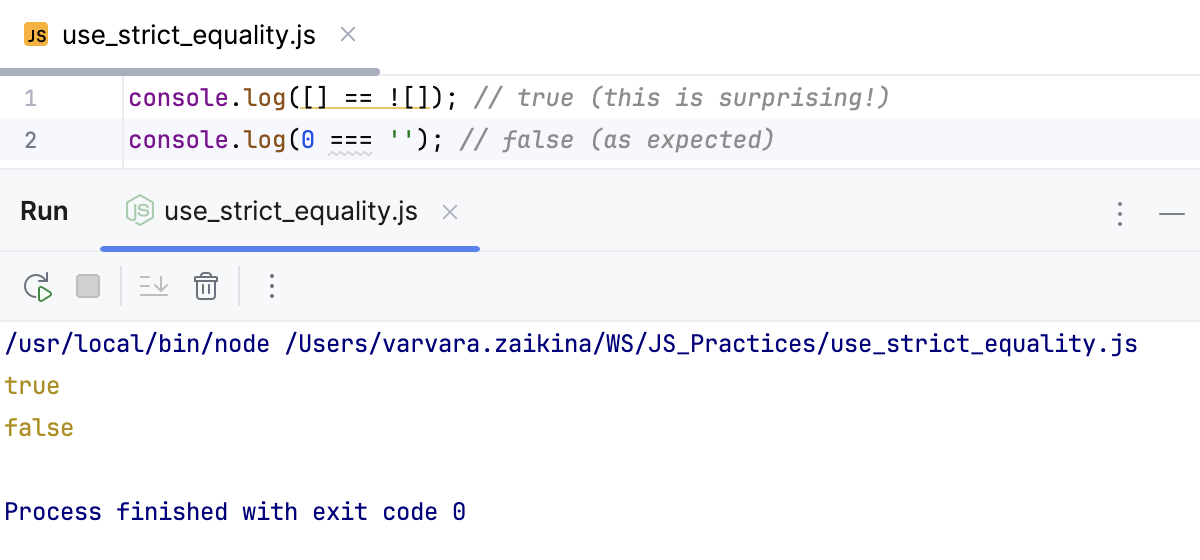
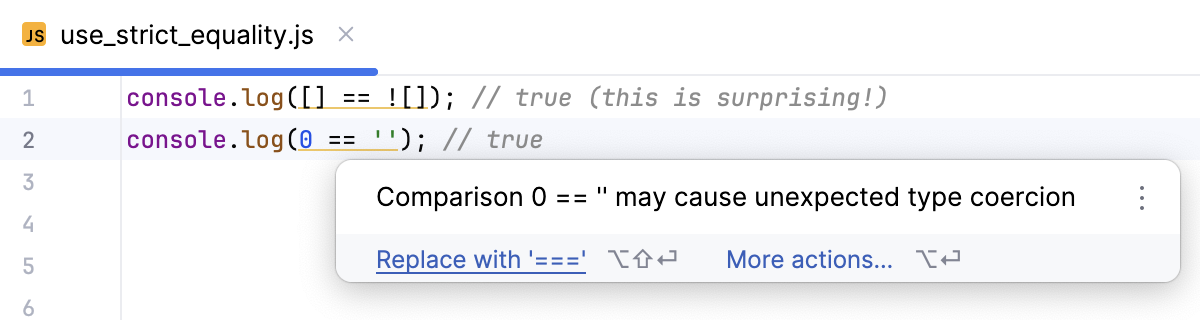
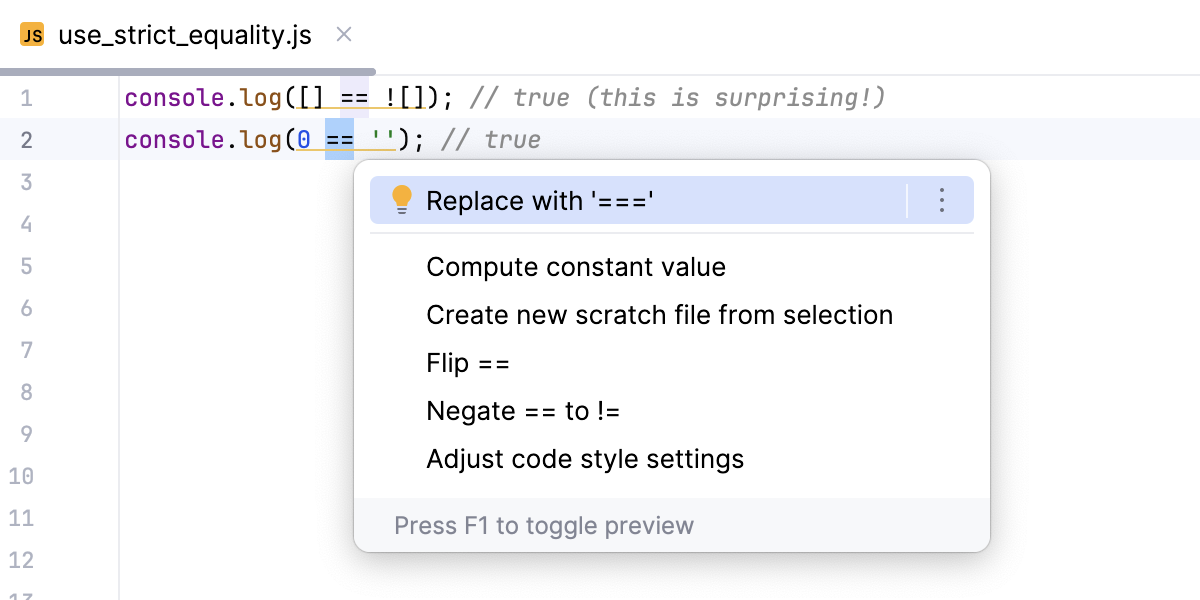
使用严格相等 (===) 使用 严格相等 (===) 代替宽松相等 (==) 可实现更可预测且更可靠的行为,因为严格相等不会执行类型转换,而是直接比较值和类型。
console.log([] == ![]); // true (this is surprising!)
console.log(0 == ''); // true
console.log([] == ![]); // true (this is surprising!)
console.log(0 === ''); // false (as expected)
WebStorm 会检测使用宽松相等可能引发的问题,高亮显示不可靠的代码段,并建议快速修复。
最后修改日期: 2025年 12月 8日