Install on a Kubernetes cluster using Helm charts
This page guides you through installing and configuring Datalore On-Premises on a Kubernetes cluster.
Kubernetes deployment of Datalore On-Premises contains the following components:
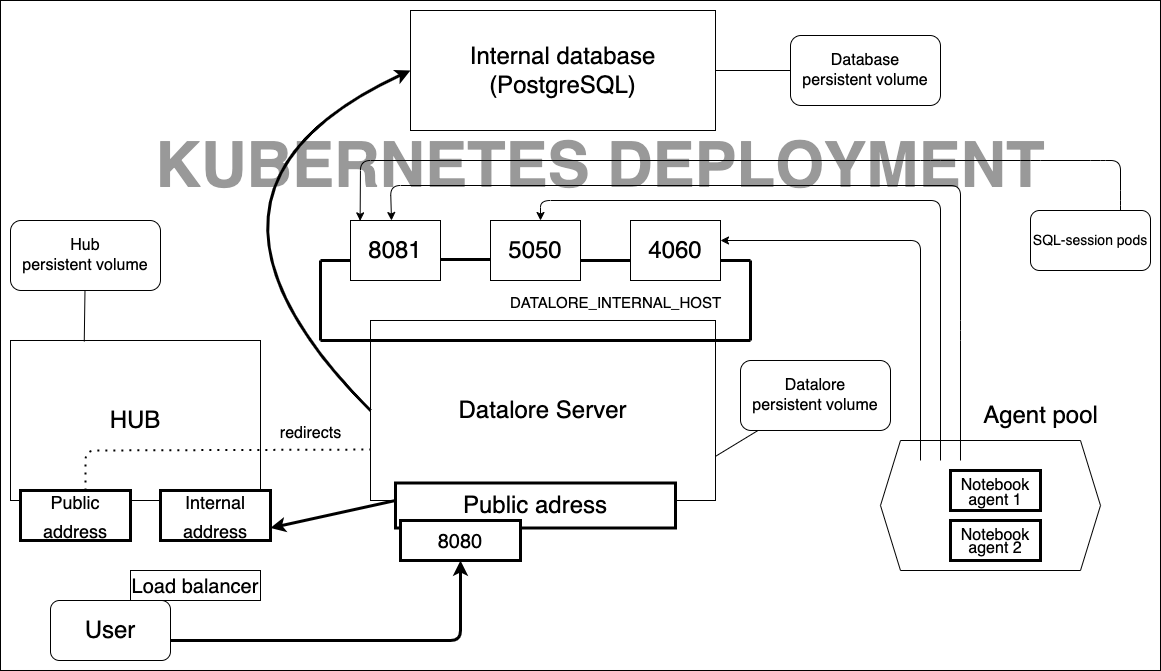
The installation process consists of two parts:
Basic installation to get Datalore On-Premises up and running.
Configuration steps to customize the installation.
- Prerequisites
Before you start, be sure to:
Set up a Kubernetes cluster.
Install
kubectllocally and configure it to work with this cluster.Install Helm.
Install an Ingress controller to be able to expose Datalore.
- Hardware requirements
Datalore On-Premises requires resources for running both the server, database, and computations. When selecting the amount of resources, consider your expected computational workload and the number of agents working concurrently.
CPU: Minimum 1 core (2 or more cores recommended)
RAM: Minimum 4 GB (8 GB recommended). At least 4 GB is recommended for each notebook running concurrently.
Available memory: Minimum 4 GB (6 GB or more recommended)
- AWS EKS deployment considerations
Datalore’s Reactive mode may not operate properly on an Amazon EKS cluster with the Amazon Linux compute nodes (default option). We recommend that you use Ubuntu 22.04 with the corresponding AMIs specifically designed for EKS.
To find an AMI for manual setup, select a suitable option from the worker node image list based on the cluster version and region.
To configure the cluster deployment using Terraform, you can use the sample Terraform config file.
- AWS Fargate restrictions
AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers.
Datalore On-Premises can run in Fargate, but you need to be aware of the following restrictions:
Attached files and Reactive mode do not work because of Fargate’s security policies.
Spawning agents in privileged mode, which is the default setup, is not supported by Fargate.
Fargate does not support EBS volumes, which are our default volume option.
As a workaround, we suggest that you set up an AWS EFS, create the
PersistentVolumeandPersistentVolumeContainerobjects, and edit the datalore.values.yaml config file as shown in the example:volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: postgresql-data spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: efs-sc resources: requests: storage: 2Gi - metadata: name: storage spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany storageClassName: efs-sc resources: requests: storage: 10Gi
Basic Datalore installation
Step 1. Add the Datalore Helm repository
To add the repository, run the following command:
Step 2. Start configuring deployment
Create a datalore.values.yaml file.
Add the Datalore domain by adding the following parameter to datalore.values.yaml:
dataloreEnv: ... # Make sure the URL doesn't have a trailing slash DATALORE_PUBLIC_URL: "<url>"Replace
<url>with the desired URL.Datalore requires at least two volumes to store the files attached to notebooks and outputs that notebooks produce.
To configure volumes, add the following parameters to datalore.values.yaml:
volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: storage spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 120Gi - metadata: name: postgresql-data spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi
Step 3. Create a Kubernetes secret for the database password
To create a Kubernetes secret for storing the database password in a secure way:
Generate the password and store it in the Kubernetes secret, as described below. The
pwgentool is used here as an example. You can use any other tool or method to generate a password.PASSWORD=$(pwgen -N1 -y 32) kubectl create secret generic datalore-db-password --from-literal=DATALORE_DB_PASSWORD="$PASSWORD"Modify (or add, if not present yet) the
databaseSecretblock in yourdatalore.values.yamlas follows:databaseSecret: create: false name: datalore-db-password key: DATALORE_DB_PASSWORDThe value of the name value is referring to a secret name defined at the previous step, while the key value is referring to the key within the secret that contains the password.
(Optional) If you are moving from plain text password storage to the secret reference: remove the
passwordkey with its value from thedatabaseSecretblock.
Step 4. (Optional) Use an external Postgres database
Datalore requires a PostgreSQL database (version 15 or higher). The default Helm chart that deploys Datalore also provisions a single-instance PostgreSQL database.
If you want to use an external database, take the following steps:
Deploy a Postgres database (version 15 or higher), create a database user, and get the connection string.
Add the
internalDatabaseparameter to datalore.values.yaml:internalDatabase: falseAdd the database user and connection string in the
dataloreEnvblock as follows:dataloreEnv: ... DB_USER: <database_user> DB_URL: "jdbc:postgresql://<database_host>:<database_port>/<database_name>"
Step 5. (Optional) Enable an email allowlist
You can enable an allowlist for new user registration so that only users with email addresses included in the allowlist can register.
To do this, add the following parameter to datalore.values.yaml:
The tab will be available in the Admin panel. For more details, see Restrict registration with Email allowlist.
Step 6. (Optional) Enable user filtration based on Hub group membership
By default, all Hub users can get registered unless you disable registration in the Admin panel.
If you want to grant Datalore access only to members of a specific Hub group, add the following parameter to datalore.values.yaml:
Step 7. Deploy Datalore
To deploy the Datalore server into the default namespace, run the following command and wait for Datalore to start up:
helm install -f datalore.values.yaml datalore datalore/datalore --version 0.2.38Forward traffic from localhost:8080 to the Datalore server:
kubectl port-forward svc/datalore 8080
To deploy the Datalore server into a non-default namespace, run the following command:
helm install -n <namespace> -f datalore.values.yaml datalore datalore/datalore --version 0.2.38To specify the non-default namespace for your agents configs, define the namespace variable in the datalore.values.yaml file as shown in the code block:
agentsConfig: k8s: namespace: <namespace> instances: ...For more details, see Configure agents.
Under
dataloreEnvin datalore.values.yaml, define the following variables:DATABASES_K8S_NAMESPACEString
Kubernetes namespace where all database connector pods will be spawned.
Default:
defaultGIT_TASK_K8S_NAMESPACEString
Kubernetes namespace where all Git-related task pods will be spawned.
Default:
default
You can find the full list of customizable server configuration options in Configure Datalore server.
Forward traffic from localhost:8080 to the Datalore server:
kubectl -n <namespace> port-forward svc/datalore 8080
Step 8. Expose Datalore
To route traffic to Datalore, configure Ingress.
(Optional, recommended) If you use a reverse proxy, enable Gzip compression by following these instructions.
Step 9. Add your Datalore license
Open the URL you earlier specified in
DATALORE_PUBLIC_URLand register as a new user. This first user automatically receives the Super Admin role.Add your license. To do this, click your avatar at the top right, select , and provide your license key.
For more information about Datalore licensing, see Manage licenses.
Next steps
Required configuration steps
Configure agents: Customize how your agents work to manage your computational resources.
Enable GPU machines: Enable GPU machines in your installation.
Manage users: Create and manage users and viewers.
Configure plans: Customize resource usage among your Datalore users.
Optional configuration steps
Set up JetBrains Hub: Integrate an authentication service.
Use a sidecar container: Use a two-container configuration to run the notebook agent without elevated privileges.
Customize or update environment: Build custom images tailored for your needs.
Enable gift codes: Activate the service for generating and processing gift codes.
Enable the email service: Activate email notifications.
Enable audit logging: Turn on extended activity logging for Datalore users.
Keywords
Datalore installation, Datalore deployment, install Datalore, installation procedures, installation requirements, Kubernetes deployment