What’s New in RubyMine 2025.3
RubyMine 2025.3 brings several exciting updates, including:
- Multi-agent AI chat with integrated Junie and Claude Agent.
- Rails-aware MCP server for smarter AI-assisted code exploration.
- Improved completion for qualified constants.
- Faster multi-module project startup with more accurate gem resolution.
Let’s dive into the details!
AI
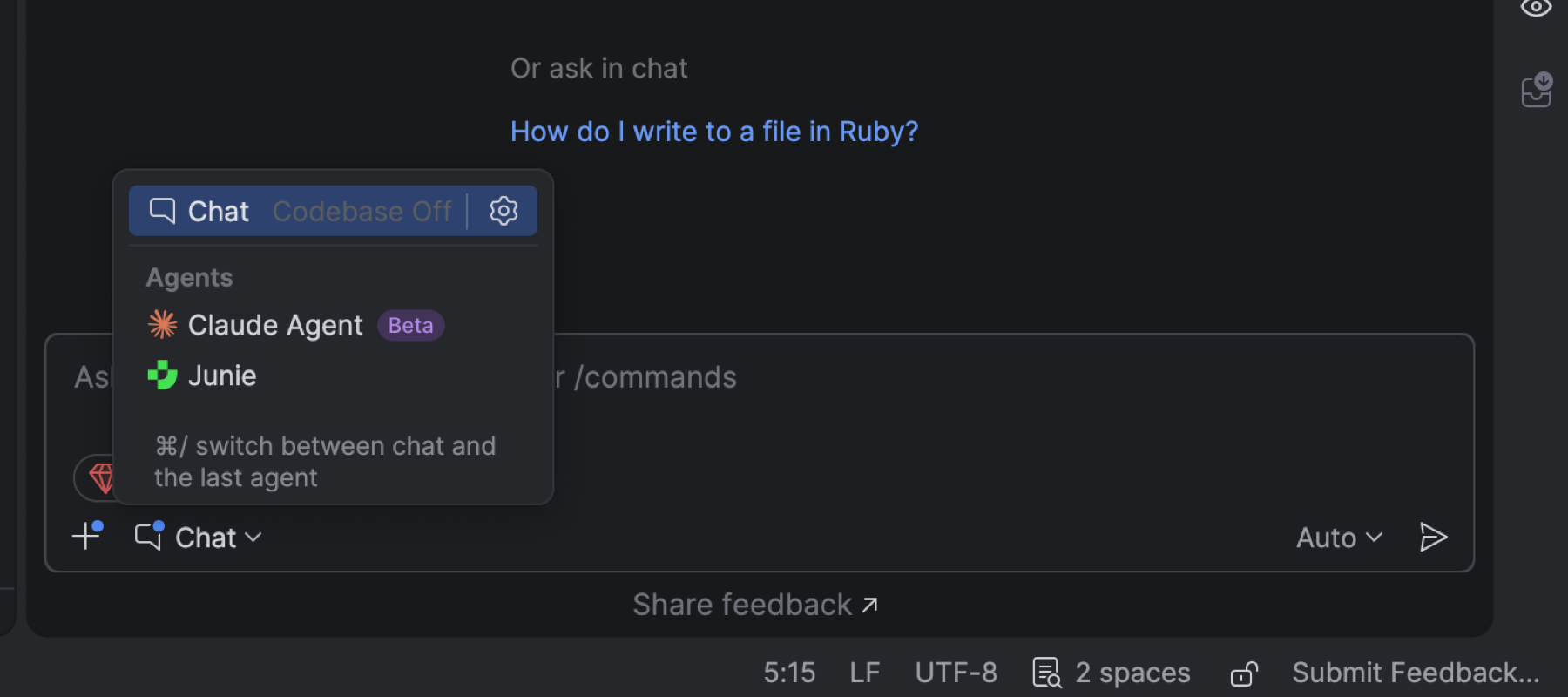
Multi-agent experience: Junie and Claude Agent
Claude Agent has become the first third-party AI agent natively integrated into JetBrains IDEs. With its addition, JetBrains introduces a multi-agent experience that brings even more flexibility and power to your development workflow. Now, with Claude Agent and Junie available in the same chat interface, you can switch between agents seamlessly and get the right kind of assistance for every task.
Note that Junie will still be available in a separate tool window.
Transparent AI quota tracking
You can now view your remaining AI Credits, renewal date, and any top-up credits directly inside RubyMine. If your AI quota runs out, you can initiate a top-up directly from the IDE.
This update makes it easier to monitor and manage your AI resources – bringing more clarity and convenience to managing AI usage.
Ruby
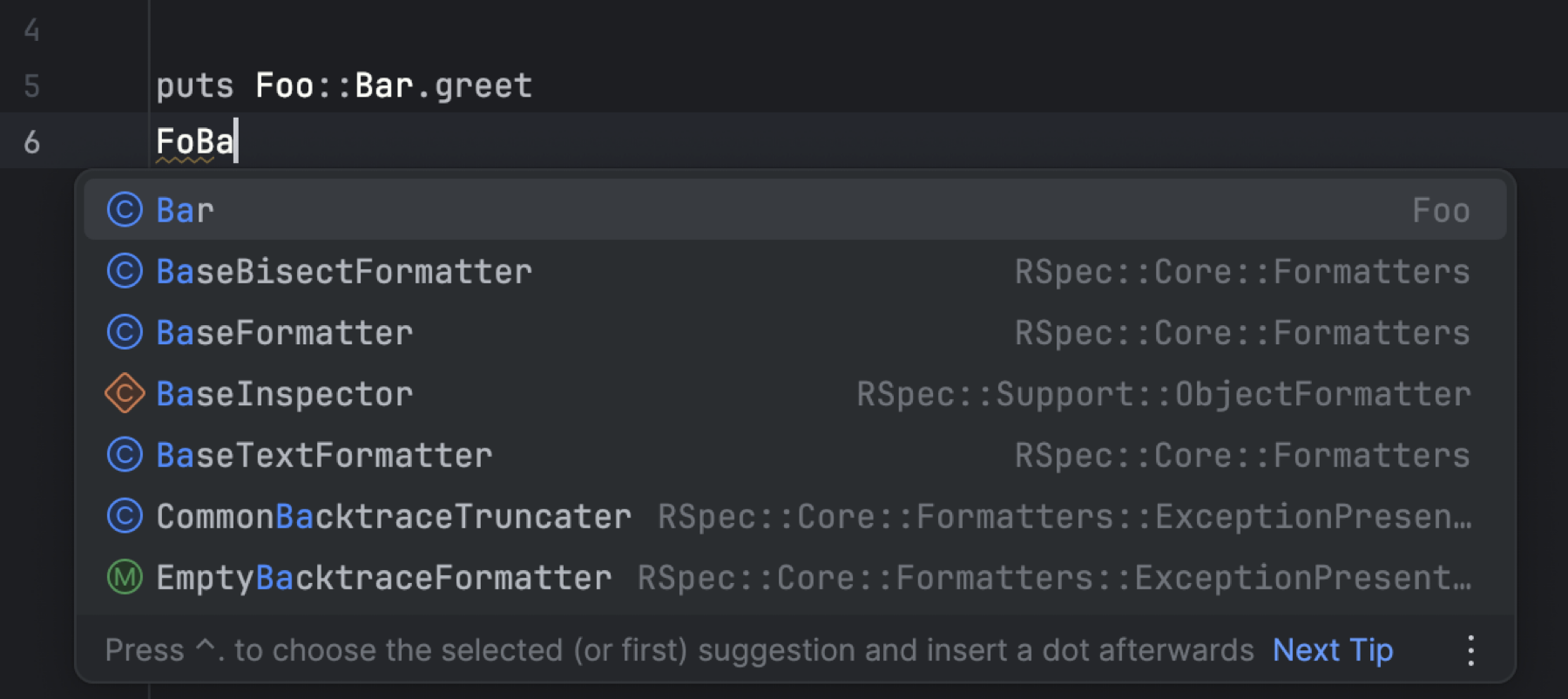
Improved completion for qualified constants
Completion now supports fuzzy searching across namespaces. This means you can type parts
of a class or module name, even nested ones, and RubyMine will suggest the correct
constants. For example, typing FoBa will bring up Foo::Bar.
To disable fuzzy completion for more precise suggestions, go to Settings | Editor | General | Code Completion and deselect the Match suggestions across namespaces checkbox.

Global variable type declaration fixes
Go to Type Declaration now works correctly for global variables of all types, making it easier to understand code and navigate through it.

Unicode regex support improvement
The IDE no longer throws an Illegal unicode escape sequence error for valid regex patterns. Regexes now work as expected, enabling full use of Ruby's extended Unicode syntax for emojis and other characters, without causing the IDE to throw false errors.
Rails
Sunset of the Rails Project view
Starting with RubyMine 2025.3, the Rails Project view has been removed.
This change was made because:
- The growing complexity of modern Rails applications made it difficult to maintain a dedicated Project view that works reliably across all types of projects.
- The feature's usage was extremely low, so we decided to focus our development efforts on more impactful improvements.
- The best parts of the Rails Project view – such as enhanced navigation and visibility of model attributes – are planned to be reimplemented in a way that benefits all RubyMine users.
Bundler
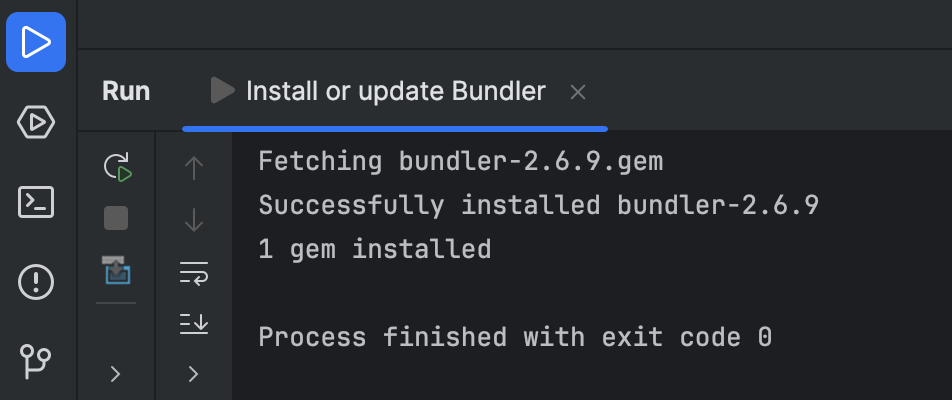
Bundler installation moved to the console
Bundler is now installed directly via the Run tool window instead of through a modal dialog.
RubyMine automatically installs the required Bundler version based on your project's dependencies, making the process smoother and preventing permission errors.
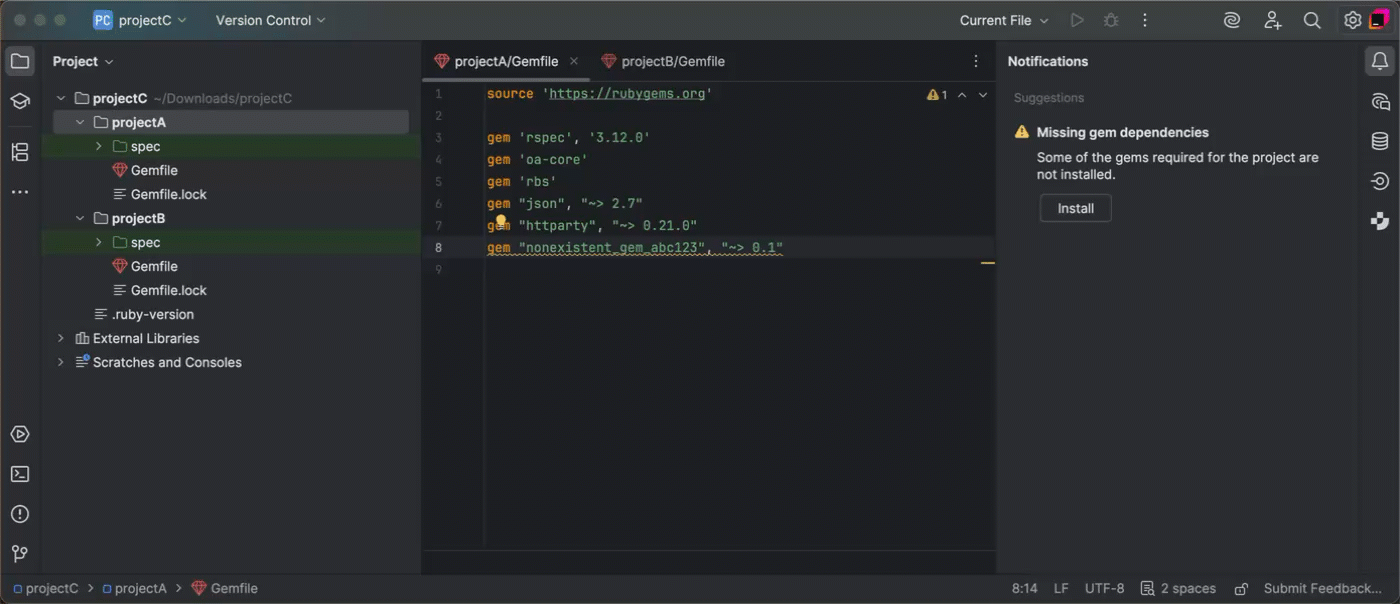
Uninterrupted gem installation in multi-module projects
Even if gem installation fails for one module, RubyMine now continues installing gems for the remaining modules. Each failed module maintains its own error log in a separate tab, allowing you to inspect the problem without interrupting the parent installation process.
Code insight
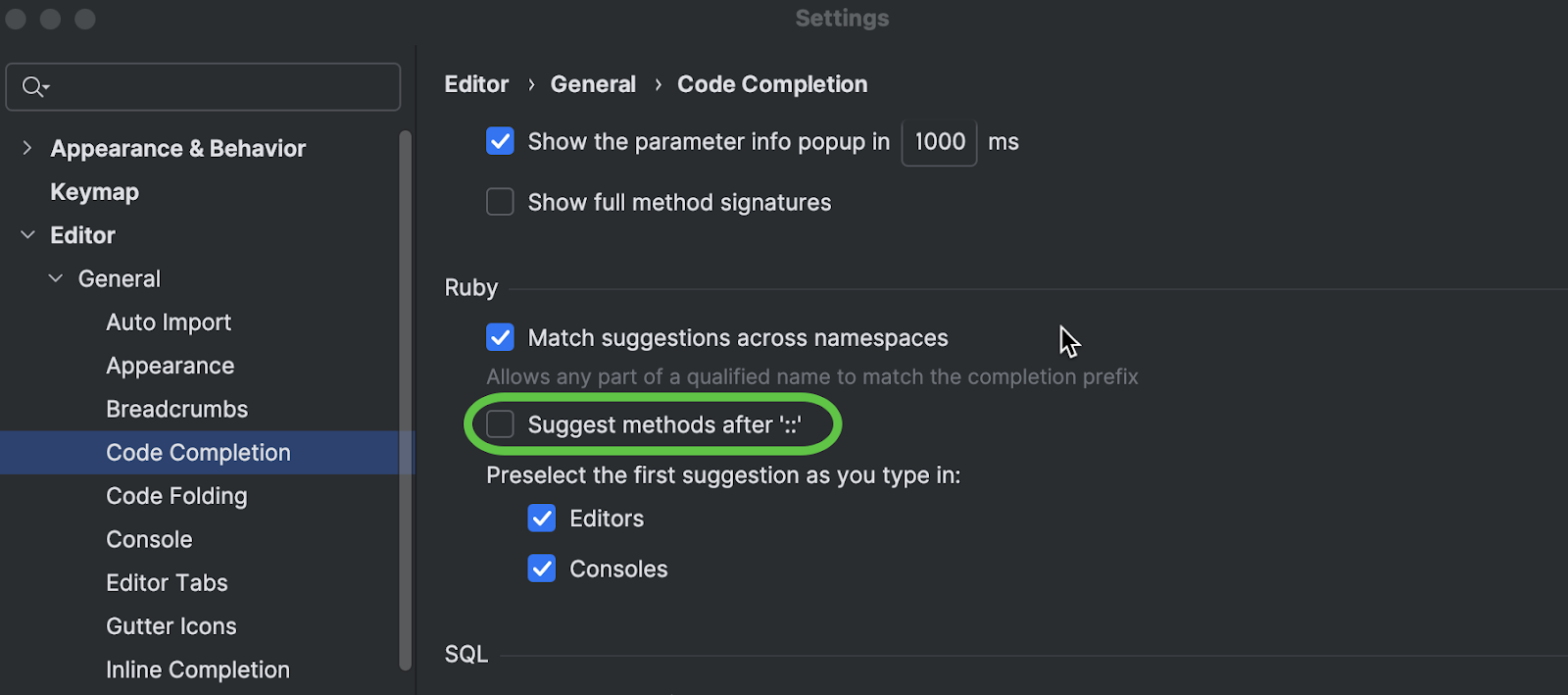
Cleaner autocomplete after ::
In RubyMine 2025.3, autocompletion of singleton method names after :: is
disabled by default. Typing String:: now shows only classes, modules, and
constants, reducing clutter while preserving accurate navigation and method resolution.
To re-enable this option, go to Settings | Editor | General | Code Completion and select the Suggest methods after '::' checkbox.
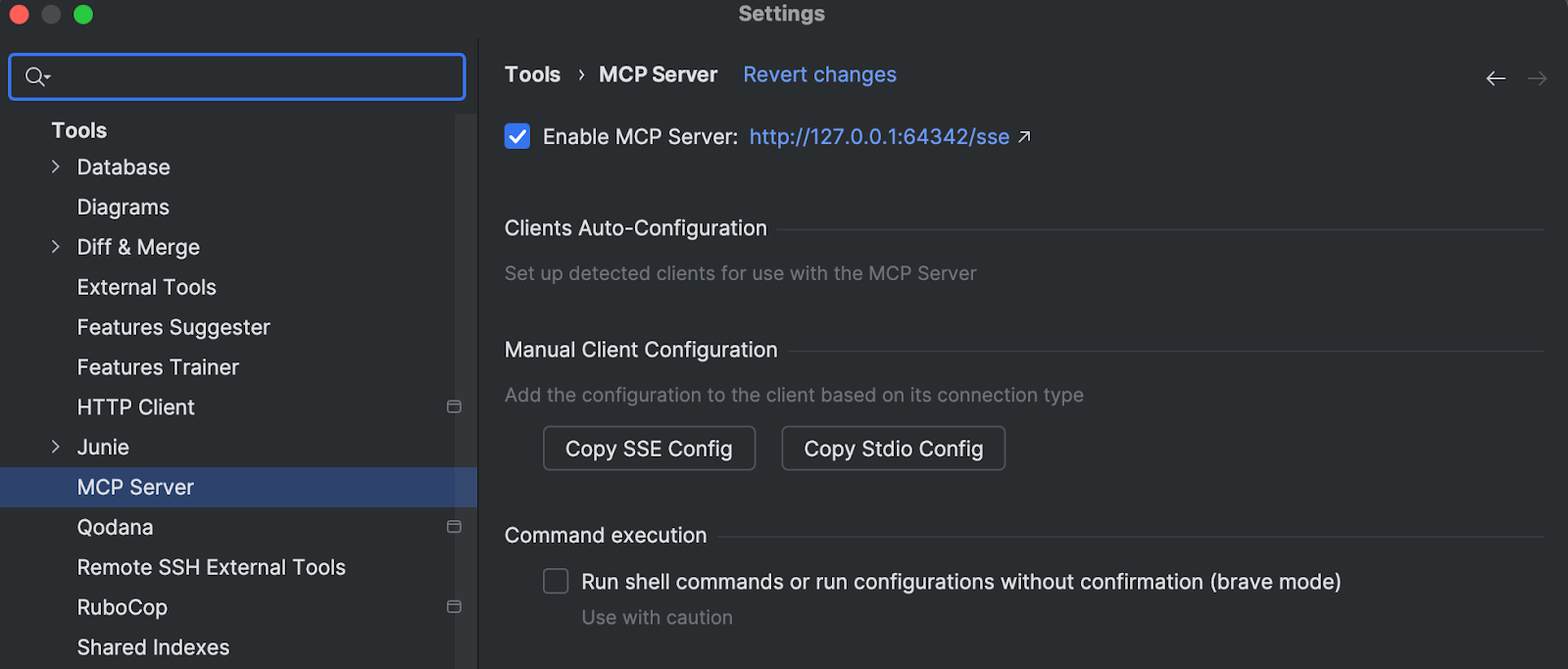
Rails-aware MCP server
The MCP server in RubyMine now includes Rails-specific tools. It automatically recognizes Rails code and project structure, making AI-assisted code exploration in such projects faster and more reliable.
While the server comes preconfigured for AI Assistant, you can also set it up for external clients.
User experience and performance
Accurate gem resolution for Ruby projects
RubyMine now ensures that code navigation, completion, and symbol resolution are restricted to the current module and its dependencies, excluding gems or interpreters used in other modules of the same project. This eliminates noise from unrelated modules, making code insight more precise and easier to work with in larger projects.
Improved startup for multi-module projects
Startup for multi-module projects has been refined to provide a better user experience. Each module is processed only once, progress bars are consolidated, and redundant background tasks are removed. This reduces clutter and eliminates distracting notifications when opening large projects.