Set up environment and load data
This tutorial will guide you through the first steps in data analysis in DataSpell. You will learn how to set up a working environment in DataSpell, load a data set, and create a Jupyter notebook.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that:
You have installed DataSpell. This tutorial was created in DataSpell 2025.2.
You have Python 3.6 or newer on your computer. If you are using macOS or Linux, your computer already has Python installed. You can get Python from python.org.
Run the IDE
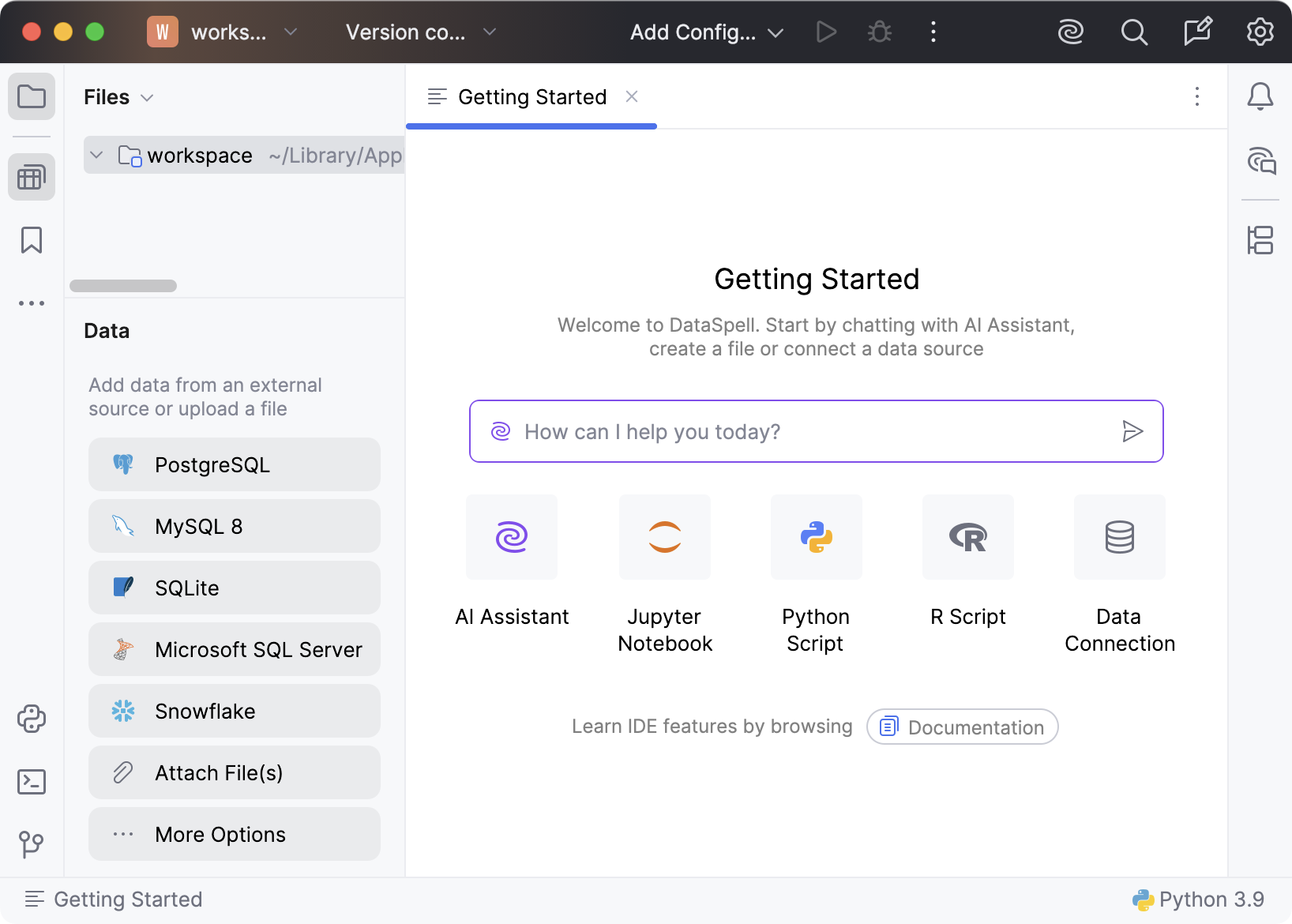
Let's start by running DataSpell. The IDE starts with the default workspace.
Prepare data
Now it is time to get some data for research. In this tutorial, we will use the "Airline Delays from 2003-2016" dataset by Priank Ravichandar licensed under CC0 1.0. This dataset contains the information on flight delays and cancellations in the US airports for the period of 2003-2016.
We will load the data, analyze it, and find out which airport had the highest ratios of delayed and canceled flights.
Attach the data to the workspace
Download the dataset from kaggle.com by using the Download link in the upper-right corner.
Extract airlines.csv from the archive.
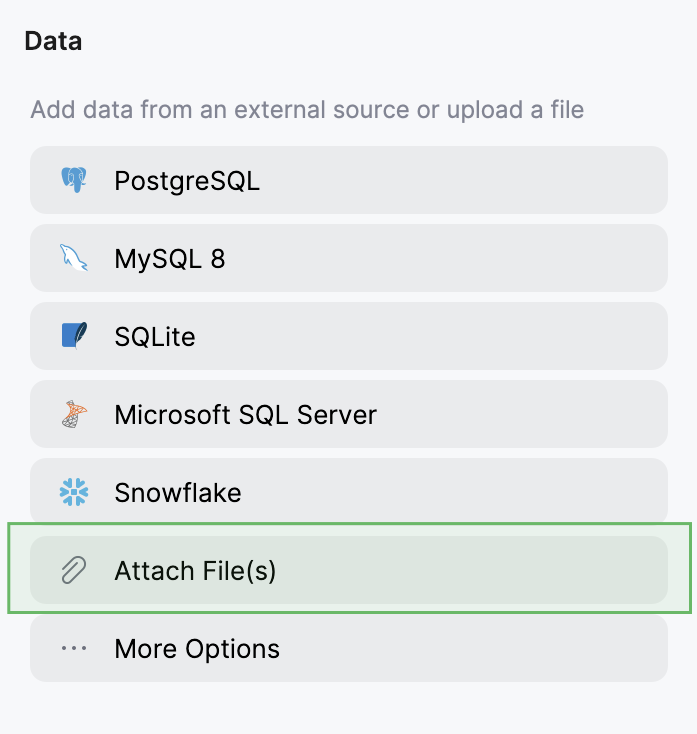
In the Data tool window, click Attach File(s) and select airlines.csv file.
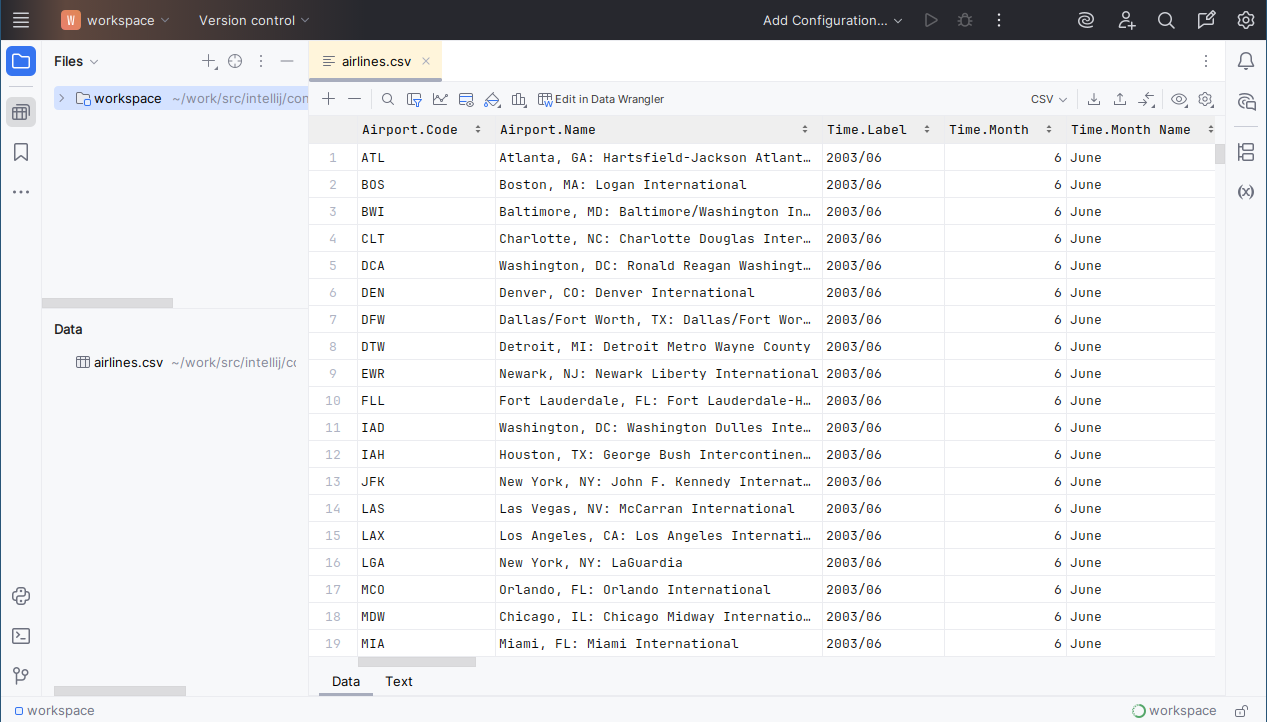
Now airlines.csv is shown in the Data tool window. Double-click the file to open it in the editor:
Next, we will create a Jupyter notebook.
Create a Jupyter notebook
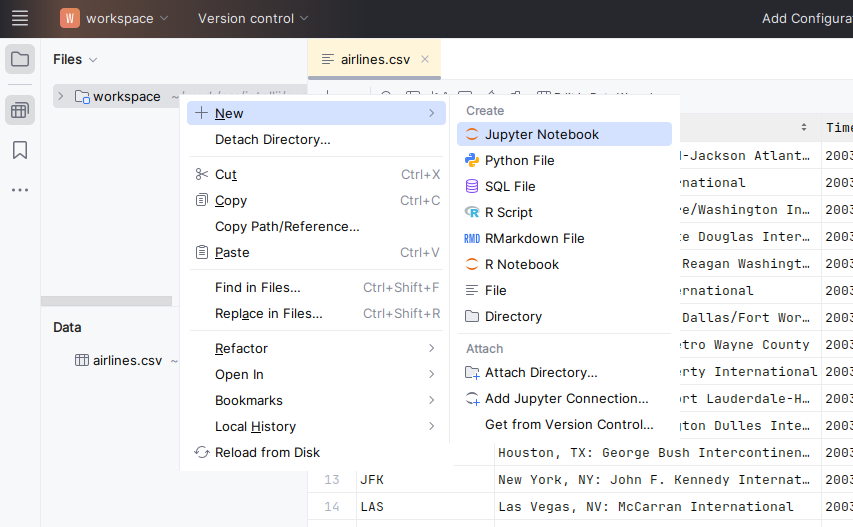
In the Files tool window, select the directory you want to create the notebook in. In our case, it is
workspace. Then do one of the following:Right-click the directory and select New from the context menu.
Press Alt+Insert.
Select Jupyter Notebook from the Create list.
In the dialog that opens, type a file name. For example, my_notebook.
DataSpell creates a notebook document with the *.ipynb extension. The document is displayed with a corresponding icon.
The newly created notebook contains one empty cell:
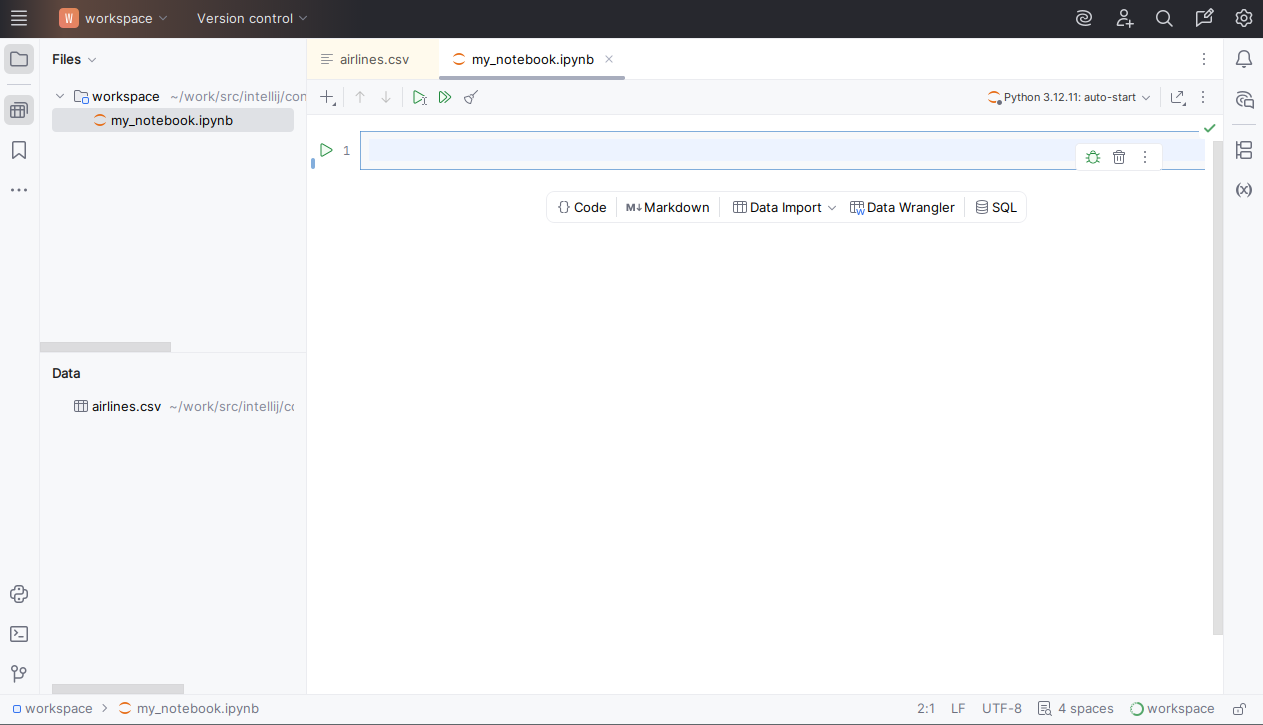
Import data into the notebook
Now we can import the airlines.csv to our notebook.
To import the data, do one of the following:
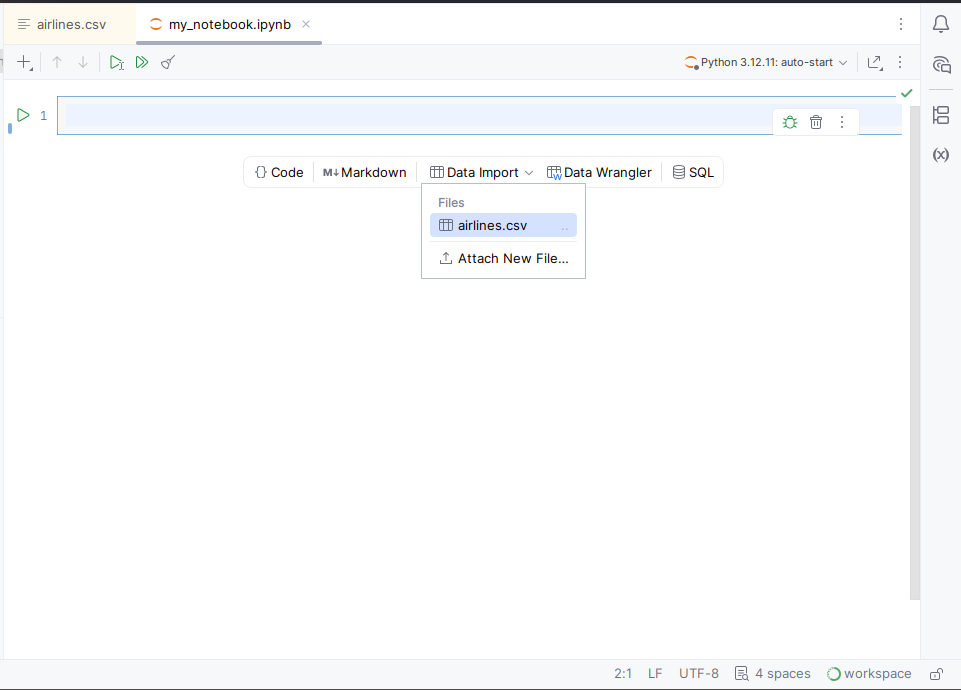
Create the new data import cell from the toolbar by clicking Data Import and selecting airlines.csv from the Files list.
Drag the airlines.csv file to the notebook.
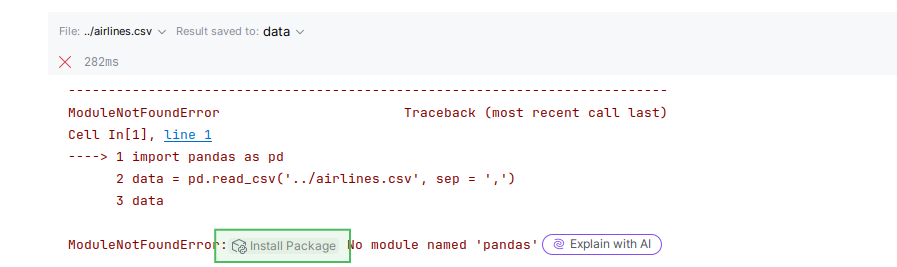
If there is an error about missing pandas library, click Install package button and run the cell again:
If you see the No Python interpreter configured for the project warning, click one of the links to configure the interpreter:
Click Install Miniconda link to install miniconda.
Click Configure Python interpreter to configure a Python interpreter for your workspace. For more information about the interpreter, refer to Creating a new virtual environment

Run the notebook
Next, let's run the notebook. There are several ways to do that:
To execute all code cells in your notebook, click
on the notebook toolbar.
To run just the current cell, press Ctrl+Enter.
When executing one cell at a time, mind code dependencies. If a cell relies on some code in another cell, that cell should be executed first.
The output is displayed under the import cell:
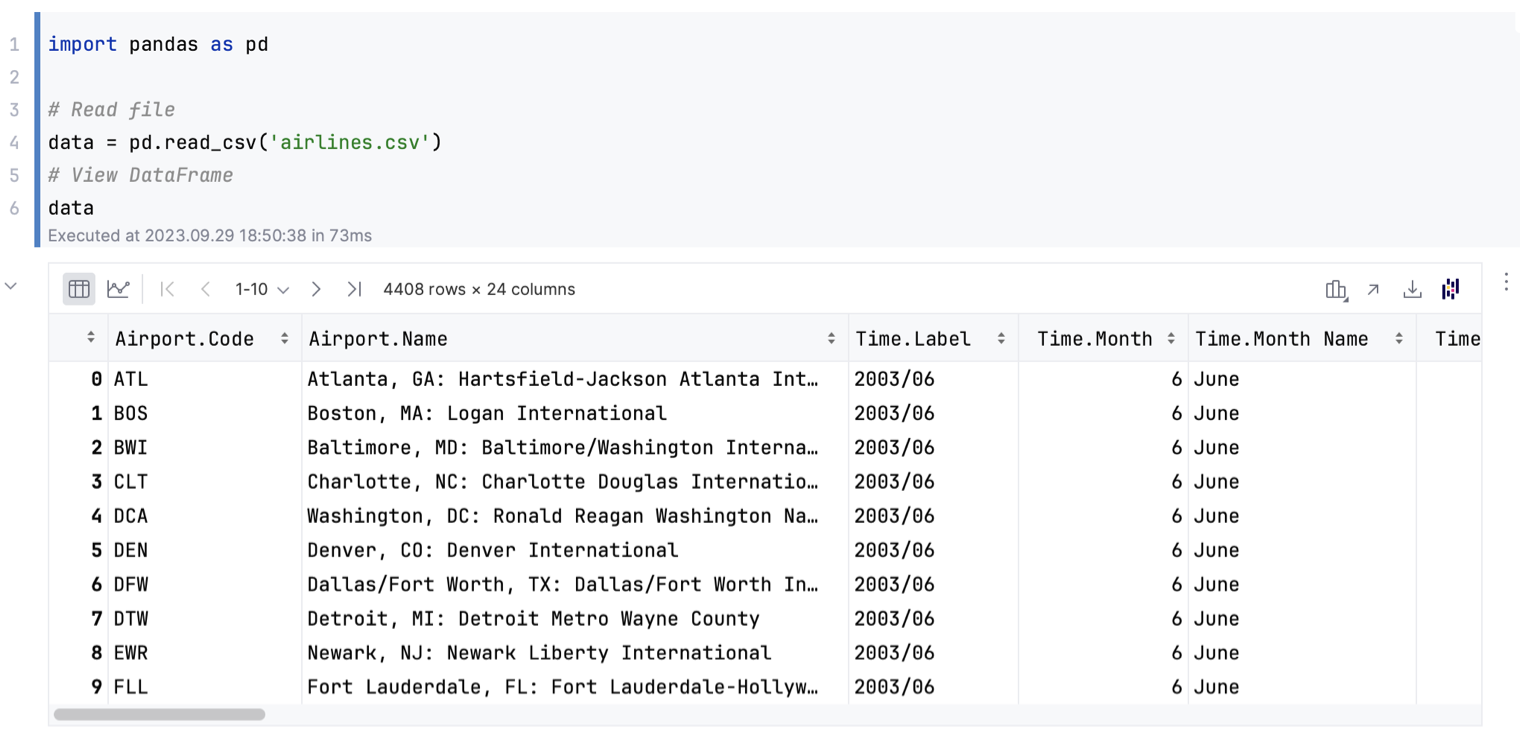
You can scroll the output cell. DataSpell will load and display the data dynamically.
Summary
Congratulations on completing this basic data analysis tutorial! Here is what you have done:
Downloaded a dataset and prepared it for research
Created a notebook and ran it for the first time
As a next step, learn to visualize data with matplotlib.