Inlay Hints
Inlay hints are special markers that appear in the editor and provide you with additional information about your code, like the names of the parameters. Other types of hints inform you about annotations, code authors, usages, and so on (depending on the language).
Enable or disable inlay hints
To disable a hint that is currently in front of you in the editor:
Right-click the hint and select whether you want to disable the specific type of hints or all hints in this category.
Alternatively, click the hint, press Alt+Enter and select Disable option <inlay_hint_option_name> inlay hint.
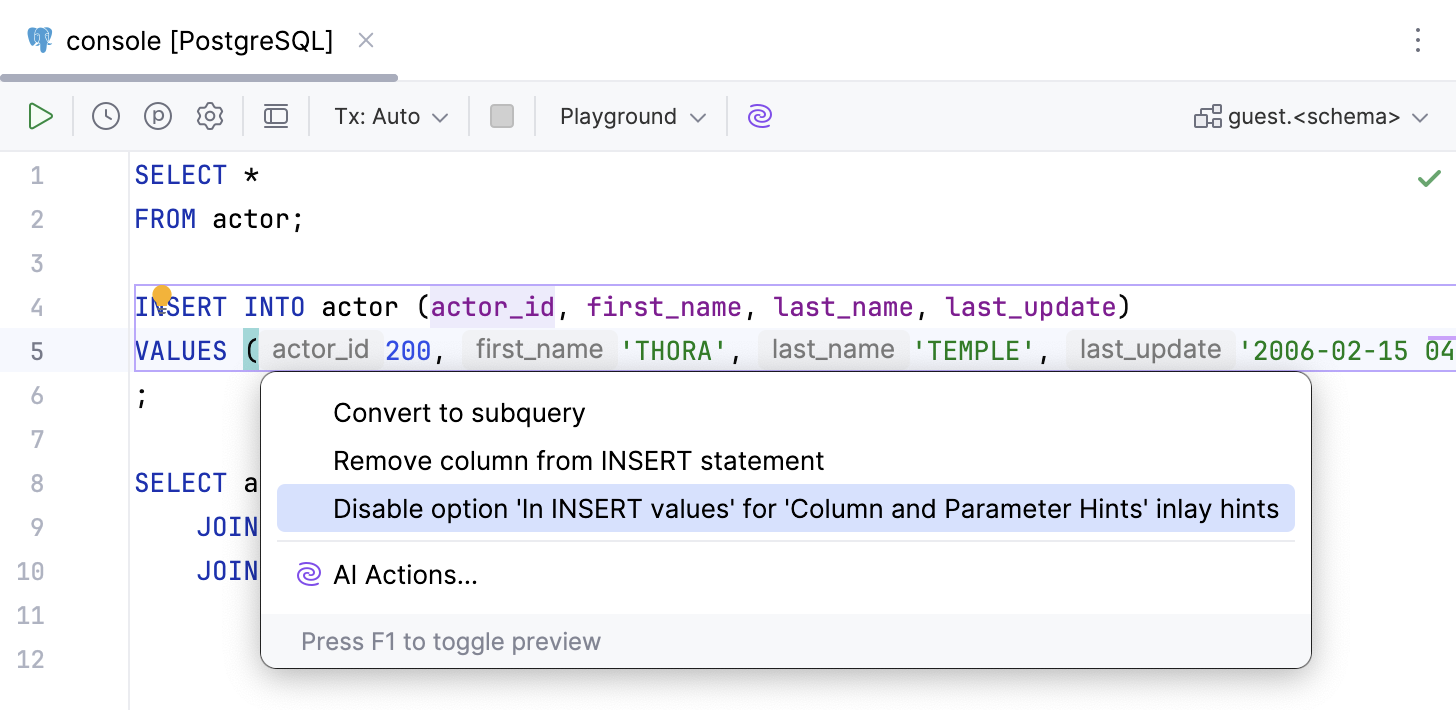
To configure one or more specific groups of inlay hints:
Open the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to , and use the checkboxes next to the hints to hide or show the corresponding category of inlay hints.
In inlay hints settings, you can configure what types of information you want to get in hints.
Change inlay hints appearance
In the Settings dialog (Ctrl+Alt+S) , go to , then select Inline hints.
Select the inlay hint type and state, and configure the font color and effects as required.
SQL
Parameter hints
Display column names in the following blocks:
In INSERT values: show names of columns in
INSERTstatements. Works only in query consoles, not as a language injection.
In SELECT expressions: show names of columns in
SELECTstatements that have context that sets column names. For example,SELECTstatements insideCREATE VIEWandINSERT. Works only in query consoles, not as a language injection.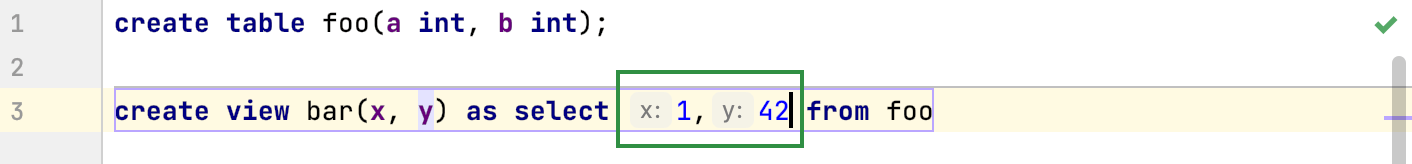
For * references: show names of columns for asterisk (*) references in
SELECTstatements that have context that sets column names. For example,SELECTstatements insideCREATE VIEWandINSERT. Works only in query consoles, not as a language injection.
For set operations (UNION, INTERSECT, EXCEPT): show names of columns in
SELECTstatements when they are used in set operations likeUNION,INTERSECT, andEXCEPT. Works only in query consoles, not as a language injection.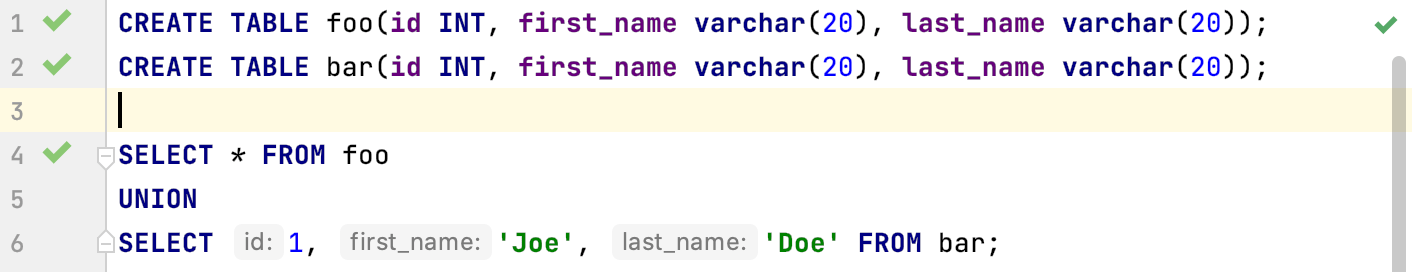
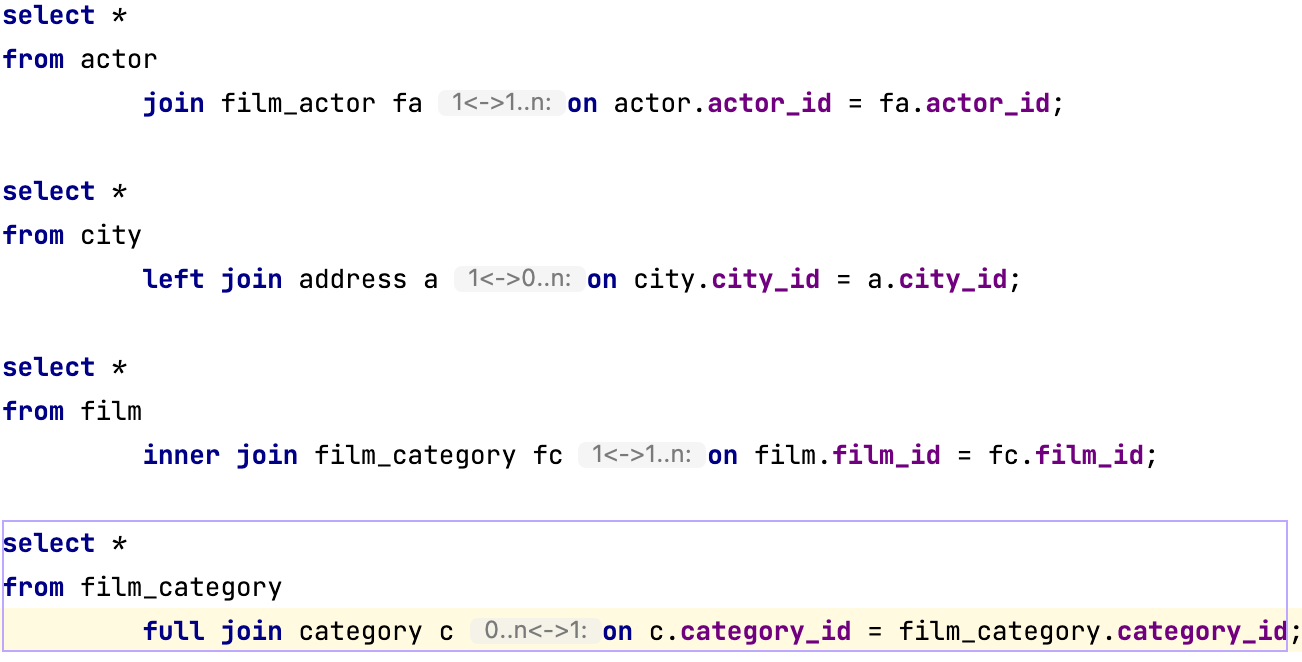
JOIN cardinality
Display the numerical relationship between rows of one table and rows in the other. Common cardinalities include one-to-one (1<->1), one-to-many (1<->1..n), many-to-many(1..n<->1..n), and optional (0..n). The optional cardinality appears when the referring field is nullable.
You can configure inlay hints for the following types of JOIN:
INNER JOINLEFT JOINRIGHT JOINFULL JOIN