What’s New in DataSpell 2023.3
DataSpell 2023.3: AI Assistant, dbt Support, SQL Cells, Interactive Tables Productivity Boosters, and More
AI Assistant General Availability
JetBrains AI Assistant is now generally available with a number of new and improved features to increase your productivity in JetBrains IDEs.
Get insights about your DataFrame with JetBrains AI Assistant!
The Explain code feature now offers an effortless way to gain insights into your DataFrame. This tool is conveniently accessible through the context menu in Jupyter Notebook and Python script or by simply clicking on the AI Assistant icon located in the top right corner of your interactive tables. Once activated, AI Assistant will receive essential information about your dataset, such as column names and descriptive statistics. This enables the assistant to provide relevant details about and analysis of your DataFrame. Furthermore, you have the option to explore more in-depth analysis by engaging in a prolonged dialogue with the assistant.
Use AI Assistant in DataSpell as a supplemental feature with a JetBrains AI Service subscription.
dbt
DataSpell now provides support for dbt Core, a modern data transformation framework that is gaining traction within the data community. dbt Core simplifies the data transformation process and encourages best engineering practices in data analysis, such as modularization, testing, and documentation. It is particularly user-friendly for individuals already familiar with SQL.
Here are several benefits of using dbt Core in DataSpell:
- Streamlined project initiation: You can effortlessly initiate your dbt project by utilizing a preconfigured template.
- Simplified run, build, and debug processes: Execute, build, or debug your project with ease using Run Configurations – it only takes a few clicks.
- Intelligent code completion: DataSpell offers intelligent code completion for both SQL and YML files.
SQL and Python
SQL cells
DataSpell has significantly enhanced the connection between SQL and Python by introducing SQL cells, in addition to the existing robust SQL support provided by the bundled Database Tools and SQL plugin. Similar to Python or Markdown cells, SQL cells are now available for use in your Jupyter notebooks. With SQL cells, you can effortlessly retrieve data from your database, and it will automatically be transformed into a pandas DataFrame for immediate use within your notebook. Furthermore, the intelligent code completion feature is fully functional for both SQL code and SQL objects, which include tables and columns, enhancing your SQL coding experience. Creating SQL cells is a straightforward process: simply click on Add SQL Cell.
Full Line code completion
DataSpell's advanced code completion has been further enhanced to provide a more tailored experience. Now, you can take advantage of code completion that is customized for your current file, thanks to a local model integrated directly within the IDE. This model learns from your code, allowing it to suggest entire lines of code and thereby improving the efficiency and effectiveness of your data analysis workflows.
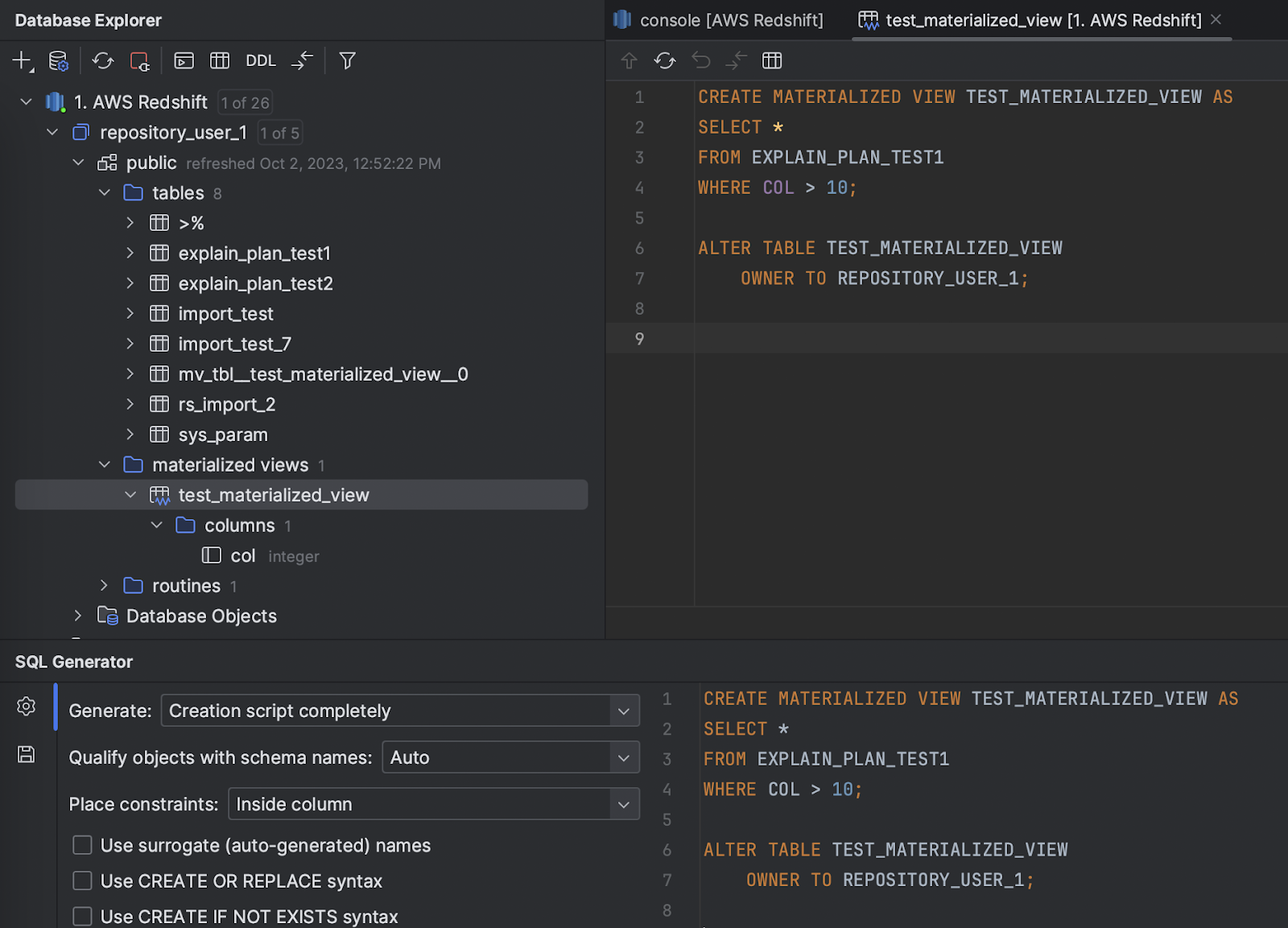
Other databases and SQL plugin improvements
- Materialized views in Redshift are now introspected and displayed in a dedicated node in the Database Explorer.
- Introducing DynamoDB support
Interactive tables
In-table statistics
Simplified access to descriptive statistics for a dataframe can help data professionals significantly boost their efficiency. In DataSpell, we've made this process more user-friendly. You can now easily access essential data insights, such as missing values, mean, standard deviation, and more, directly in the table header. This functionality is available in both Jupyter notebooks and Python scripts, supporting both pandas and Polars. Additionally, you can effortlessly identify the data type of each column by glancing at the icons in the table's header.
Categorical data distribution statistics
When dealing with categorical data, you can have easy access to viewing distribution in interactive tables. This feature allows you to quickly observe a list of the most frequently occurring values, along with their respective percentages. In cases with numerous unique values, you can easily access the total count of these distinct entries within the column.
Data distribution histograms in tables
A data distribution histogram is an essential tool in data analysis, providing a visual snapshot of data distribution, as well as aiding in pattern recognition, outlier detection, and data quality assessment. In DataSpell, you can now easily access these histograms directly in table headers. These histograms are accessible in the default compact mode and also in the detailed view.
Simplifying data visualization in tables
To streamline your data analysis workflow, we are introducing a significant enhancement – our easy graph builder. This new feature streamlines the creation of graphs from your table data, enabling quick and effortless data visualization. Simply click on the chart view in the top left corner, then select the gear icon, choose your desired graph type, and begin visualizing your data with ease and efficiency.
AI Assistant in tables
Access valuable DataFrame insights by clicking the AI Assistant icon in the top right corner of your interactive tables. The assistant provides instant information, and you can engage in further analysis by continuing the conversation.
UI and navigation
Hide main toolbar
We’ve implemented an option to hide the main toolbar when using the IDE’s default viewing mode, just like in the old UI. To declutter your workspace and remove the toolbar, select Appearance and uncheck the Toolbar option.
Improved navigation
To enhance your navigation experience when working with a variety of file types in the editor at the same time, we’ve introduced default color-coded highlighting for editor tabs, mirroring their appearance in the Project tool window.
Speed Search
The Speed Search functionality, which allows you to quickly navigate within tool windows and dialogs, is now available via a shortcut. Once the focus is placed on a tree or list, you can easily invoke the search from the tool window’s Options menu, by pressing ⌘ F on macOS or Ctrl+F on Windows or Linux, or simply by starting to type your query.